
The 25-NB (25x-NBx) series, sometimes alternatively referred to as the NBOMe compounds, is a family of serotonergic psychedelics. [1] They are substituted phenethylamines and were derived from the 2C family. [1] They act as selective agonists of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor. [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] The 25-NB family is unique relative to other classes of psychedelics in that they are, generally speaking, extremely potent and relatively selective for the 5-HT2A receptor. [1] Use of NBOMe series drugs has caused many deaths and hospitalisations since the drugs popularisation in the 2010s. This is primarily due to their high potency, unpredictable pharmacokinetics, and sellers passing off the compounds in the series as LSD. [9]
Toxicity and harm potential
NBOMe compounds are often associated with life-threatening toxicity and death. [10] [11] Studies on NBOMe family of compounds demonstrated that the substance exhibit neurotoxic and cardiotoxic activity. [12] Reports of autonomic dysfunction remains prevalent with NBOMe compounds, with most individuals experiencing sympathomimetic toxicity such as vasoconstriction, hypertension and tachycardia in addition to hallucinations. [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] Other symptoms of toxidrome of include agitation or aggression, seizure, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, hypertonia, rhabdomyolysis, and death. [13] [17] [11] Researchers report that NBOMe intoxication frequently display signs of serotonin syndrome. [18] The likelihood of seizure is higher in NBOMes compared to other psychedelics. [12]
NBOMe and NBOHs are regularly sold as LSD in blotter papers, [11] [19] which have a bitter taste and different safety profiles. [13] [10] Despite high potency, recreational doses of LSD have only produced low incidents of acute toxicity. [10] Fatalities involved in NBOMe intoxication suggest that a significant number of individuals ingested the substance which they believed was LSD, [15] and researchers report that "users familiar with LSD may have a false sense of security when ingesting NBOMe inadvertently". [13] While most fatalities are due to the physical effects of the drug, there have also been reports of death due to self-harm and suicide under the influence of the substance. [20] [21] [13]
Given limited documentation of NBOMe consumption, the long-term effects of the substance remain unknown. [13] NBOMe compounds are not active orally, [a] and are usually taken sublingually. [1]: 3 When NBOMes are administered sublingually, numbness of the tongue and mouth followed by a metallic chemical taste was observed, and researchers describe this physical side effect as one of the main discriminants between NBOMe compounds and LSD. [23] [24] [25]
Neurotoxic and cardiotoxic actions
Many of the NBOMe compounds have high potency agonist activity at additional 5-HT receptors and prolonged activation of 5-HT2B can cause cardiac valvulopathy in high doses and chronic use. [11] [16] 5-HT2B receptors have been strongly implicated in causing drug-induced valvular heart disease. [26] [27] [28] The high affinity of NBOMe compounds for adrenergic α1 receptor has been reported to contribute to the stimulant-type cardiovascular effects. [16]
In vitro studies, 25C-NBOMe has been shown to exhibit cytotoxicity on neuronal cell lines SH-SY5Y, PC12, and SN471, and the compound was more potent than methamphetamine at reducing the visibility of the respective cells; the neurotoxicity of the compound involves activation of MAPK/ERK cascade and inhibition of Akt/PKB signaling pathway. [12] 25C-NBOMe, including the other derivative 25D-NBOMe, reduced the visibility of cardiomyocytes H9c2 cells, and both substances downregulated expression level of p21 (CDC24/RAC)-activated kinase 1 (PAK1), an enzyme with documented cardiac protective effects. [12]
Preliminary studies on 25C-NBOMe have shown that the substance is toxic to development, heart health, and brain health in zebrafish, rats, and Artemia salina, a common organism for studying potential drug effects on humans, but more research is needed on the topic, the dosages, and if the toxicology results apply to humans. Researchers of the study also recommended further investigation of the drug's potential in damaging pregnant women and their fetus due to the substance's damaging effects to development. [29] [30]
Emergency treatment
At present, there are no specific antidotes for NBOMes, and all acute intoxication is managed by symptomatic treatments, such as administration of benzodiazepines, antipsychotic drugs, and antiarrhythmic agents, such as beta blockers; some emergency interventions are intended to specifically treat rhabdomyolysis, which may lead to critical complications such as metabolic acidosis and acute kidney injury. [12]
Chemical structure
The 25-NB compounds are mostly N-benzylphenethylamines, [1] [31] though in some cases the phenyl ring of the N-benzyl group is replaced by other heterocycles such as thiophene, pyridine, furan, tetrahydrofuran, benzodioxole or naphthalene, among others. [32] [33]
Generally speaking, they have methoxy groups at the 2 and 5 positions of the phenyl ring, a substitution such as a halogen or alkyl group at the 4 position of the phenyl ring, and a methoxy or other substitution (e.g., hydroxyl, fluoro) at the 2 position of the N- benzyl ring. [1] More rarely, other substitution patterns may be present [34] [35] (see e.g. NBOMe-mescaline, 25G-NBOMe, 2CBFly-NBOMe, 25C-NB3OMe). They differ from the 2C series by the presence of the N-benzyl moiety. [1]
Rarely an alpha-methyl group is present making them N-benzyl amphetamines rather than N-benzyl phenethylamines, but this greatly reduces potency and activity. However in some cases where a side chain methyl group is cyclised back to the ring (e.g. in 2CBCB-NBOMe) or links the two alpha positions (e.g. in DMBMPP), this can improve selectivity for the 5-HT2A receptor subtype. [36]
List of 25-NB derivatives
This list includes notable compounds representative of most of the structural variations that have been explored in this series, but is by no means exhaustive. Many derivatives invented for scientific study into the structure-activity relationships of 5-HT2 receptor agonists have never appeared as designer drugs, while conversely some derivatives that have appeared as designer drugs are structurally novel and of unknown pharmacological activity (e.g. C30-NBOMe, 5-APB-NBOMe).
| Chemical structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number | R | R1 | Cyc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
25B-NB | N-benzyl-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 155639-26-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | phenyl |

|
25C-NB | N-benzyl-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391487-65-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | phenyl |

|
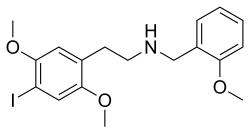
25I-NB | N-benzyl-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-18-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | phenyl |
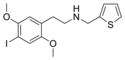
|
25I-NMeTh | N-[(thiophen-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391499-03-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | thiophen-2-yl |

|
25B-NMePyr | N-[(pyridin-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391499-21-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | pyridin-2-yl |

|
25I-NMeFur | N-[(furan-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-93-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | furan-2-yl |

|
25I-NMeTHF | N-[(tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | tetrahydrofuran-2-yl | |

|
25B-NBF | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1539266-17-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-fluorophenyl |

|
25B-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1335331-46-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25B-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1026511-90-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25B-NB23DM | N-(2,3-dimethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391493-68-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,3-dimethoxyphenyl |
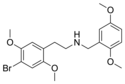
|
25B-NB25DM | N-(2,5-dimethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,5-dimethoxyphenyl | |

|
25B-NMe7BF | N-[(benzofuran-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391492-46-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzofuran-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7DHBF | N-[(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391492-40-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7BT | N-[(benzothiophen-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391492-59-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzothiophen-7-yl |
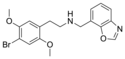
|
25B-NMe7Box | N-[(benzoxazol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-73-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzoxazol-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7Ind | N-[(indol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-28-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | indol-7-yl |
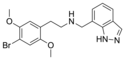
|
25B-NMe7Indz | N-[(indazol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-43-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | indazol-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7Bim | N-[(benzimidazol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-62-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzimidazol-7-yl |

|
FECIMBI-36 | N-[(2-fluoroethoxy)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-(2-fluoroethoxy)phenyl | |
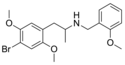
|
DOB-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminopropane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
25C-NB3OMe | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-34-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 3-methoxyphenyl |
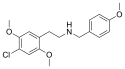
|
25C-NB4OMe | N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-35-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 4-methoxyphenyl |
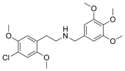
|
C30-NBOMe | N-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1445574-98-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBF | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1539266-21-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-fluorophenyl |
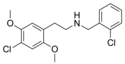
|
25C-NBCl | N-(2-chlorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-chlorophenyl | |

|
25C-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391488-16-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1227608-02-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBOEt | N-(2-ethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-ethoxyphenyl | |
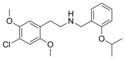
|
25C-NBOiPr | N-(2-isopropoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-isopropoxyphenyl | |

|
25F-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-fluorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1373917-84-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-fluoro | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25CN-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyanophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1539266-32-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyano | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |
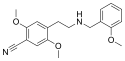
|
25CN-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyanophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-16-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyano | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |
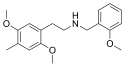
|
25D-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-02-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25D-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391488-44-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25E-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-14-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25E-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391489-79-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethyl | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |
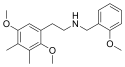
|
25G-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-65-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25H-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-52-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25I-NB34MD | N-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391497-81-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25I-NB3OMe | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-40-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 3-methoxyphenyl |
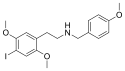
|
25I-NB4OMe | N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-41-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 4-methoxyphenyl |
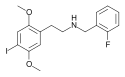
|
25I-NBF | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-21-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-fluorophenyl |
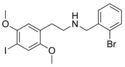
|
25I-NBBr | N-(2-bromobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1648649-98-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-bromophenyl |
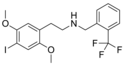
|
25I-NBTFM | N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl | |

|
25I-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-25-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25B-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-19-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
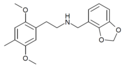
25C-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1373879-26-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |
|
25D-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391488-97-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25I-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-20-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |
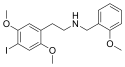
|
25I-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-19-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
DOI-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
25I-NBMeOH | N-[2-(hydroxymethyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391494-71-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl |

|
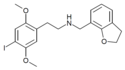
25I-NBAm | N-[2-(carbamoyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391494-85-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-(carbamoyl)phenyl |
|
25I-NMe7DHBF | N-[(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl | |

|
25I-N2Nap1OH | N-[(1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl | |

|
25I-N3MT2M | N-[(3-methoxythiophen-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-66-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 3-methoxythiophen-2-yl |

|
25I-N4MT3M | N-[(4-methoxythiophen-3-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-73-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 4-methoxythiophen-3-yl |
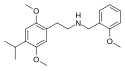
|
25iP-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-isopropylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391487-83-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-isopropyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25N-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-03-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25N-NBOEt [37] | N-(2-ethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 2-ethoxyphenyl | |

|
25N-NB-2-OH-3-Me | N-(2-hydroxy-3-methylbenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 2-hydroxy-3-methylphenyl | |

|
25N-NBOCF2H | N-(2-difluoromethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 2-difluoromethoxyphenyl | |

|
25N-NBPh [38] | N-[(2-phenyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | o-biphenyl | |
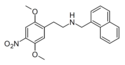
|
25N-N1-Nap | N-[(naphthalen-1-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 1-naphthyl | |
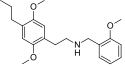
|
25P-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-propylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391489-07-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-propyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25P-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-propylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391490-34-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-propyl | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25TFM-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1027161-33-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25O-NBcP | N-(2-cyclopropylbenzyl)-1-(2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,4,5-trimethoxy | H | 2-cyclopropylphenyl | |

|
25T-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(methylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1539266-47-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(methylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T2-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(ethylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1539266-51-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(ethylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T4-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(isopropylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1354632-17-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(isopropylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T7-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1539266-55-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T7-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1354632-41-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio) | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25AM-NBOMe [39] | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-pentylphenyl]-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(n-pentyl) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
NBOMe-mescaline | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-01-1 | 3,4,5-trimethoxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
NBOMe-escaline | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,5-dimethoxy-4-ethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 3,5-dimethoxy-4-ethoxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
NBOMe-thiobuscaline | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,5-dimethoxy-4-butylthiophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 3,5-dimethoxy-4-(n-butylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
MDPEA-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 3,4-methylenedioxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |
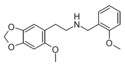
|
2C2-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2-methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2-methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |
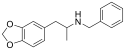
|
MDBZ | N-benzyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane | 65033-29-6 | 3,4-methylenedioxy | methyl | phenyl |
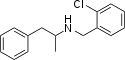
|
Clobenzorex | N-(2-chlorobenzyl)-1-phenyl-2-aminopropane | 13364-32-4 | H | methyl | 2-chlorophenyl |

|
4-EA-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-aminopropane | 4-ethyl | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl | |
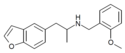
|
5-APB-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(benzofuran-5-yl)-2-aminopropane | benzofuran-5-yl instead of phenyl | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl |
Similar compounds with related structures are also known including;
| Chemical structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|

|
25B-N1POMe | N-[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenethylamine | 1335331-49-1 (R) 1335331-51-5 (S) |

|
2C-B-AN [40] [41] | 2-phenyl-2-[2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)ethylamino]acetonitrile | |
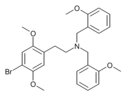
|
25B-N(BOMe)2 | 2-(4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N,N-bis(2-methoxybenzyl)ethan-1-amine | |

|
2CBCB-NBOMe | N-[(3-bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-bicyclo[4,2,0]octa-1,3,5-trien-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2-methoxyphenyl)methanamine | 1354634-09-5 |
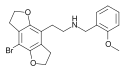
|
2CBFly-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(8-bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane | 1335331-42-4 |
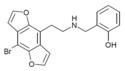
|
2C-B-DRAGONFLY-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(8-bromobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane | 1335331-45-7 |

|
2C-B-FLY-NB2EtO5Cl [42] | N-(2-ethoxy-5-chlorobenzyl)-1-(8-bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane | |
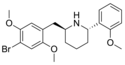
|
DMBMPP | (S,S)-2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromobenzyl)-6-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperidine | 1391499-52-7 |
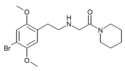
|
25B-NAcPip | 2-{[2-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]amino}-1-(piperidin-1-yl)ethanone | |

|
ZDCM-04 | 1,3-dimethyl-7-{2-[1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)propan-2-ylamino]ethyl}purine-2,6-dione | |
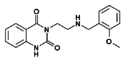
|
RH-34 | 3-[2-(2-methoxybenzylamino)ethyl]-1H-quinazoline-2,4-dione | 1028307-48-3 |
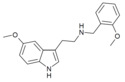
|
5-MeO-T-NBOMe [43] | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-5-methoxytryptamine | 1335331-37-7 |

|
5MT-NB3OMe | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-5-methoxytryptamine | 1648553-42-7 |
Legality
United Kingdom
A large number of substances in the 25-NB class are Class A drugs in the United Kingdom as a result of the N-benzylphenethylamine catch-all clause in the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 [44] or are otherwise covered by the Psychoactive Substances Act 2016. [45]
See also
Notes
- ^ The potency of N-benzylphenethylamines via buccal, sublingual, or nasal absorption is 50-100 greater (by weight) than oral route compared to the parent 2C-x compounds. [22] Researchers hypothesize the low oral metabolic stability of N-benzylphenethylamines is likely causing the low bioavailability on the oral route, although the metabolic profile of this compounds remains unpredictable; therefore researchers state that the fatalities linked to these substances may partly be explained by differences in the metabolism between individuals. [22]
External links
References
- ^ a b c d e f g Adam H (18 January 2017). "Pharmacology and Toxicology of N-Benzylphenethylamine ("NBOMe") Hallucinogens". Neuropharmacology of New Psychoactive Substances. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. Vol. 32. Springer. pp. 283–311. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_64. ISBN 978-3-319-52444-3. PMID 28097528.
- ^ Pertz HH, Rheineck A, Elz S (1999-01-01). "N-Benzylated derivatives of the hallucinogenic drugs mescaline and escaline as partial agonists at rat vascular 5-HT2A receptors". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 359: R29. Archived from the original on September 25, 2015.
- ^ Heim R (February 28, 2010). Synthese und Pharmakologie potenter 5-HT2A-Rezeptoragonisten mit N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Partialstruktur. Entwicklung eines neuen Struktur-Wirkungskonzepts (Thesis) (in German). Berlin: Freie Univ. Retrieved 2013-05-10.
- ^ Silva M (2009). Theoretical study of the interaction of agonists with the 5-HT2A receptor (Ph.D. thesis). Universität Regensburg.
- ^ Hansen M (2011). Design and Synthesis of Selective Serotonin Receptor Agonists for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of the Brain (Ph.D. thesis). University of Copenhagen.
- ^ Silva ME, Heim R, Strasser A, Elz S, Dove S (January 2011). "Theoretical studies on the interaction of partial agonists with the 5-HT2A receptor". Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design. 25 (1): 51–66. Bibcode: 2011JCAMD..25...51S. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.688.2670. doi: 10.1007/s10822-010-9400-2. PMID 21088982. S2CID 3103050.
- ^ Rickli A, Luethi D, Reinisch J, Buchy D, Hoener MC, Liechti ME (December 2015). "Receptor interaction profiles of novel N-2-methoxybenzyl (NBOMe) derivatives of 2,5-dimethoxy-substituted phenethylamines (2C drugs)" (PDF). Neuropharmacology. 99: 546–553. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.034. PMID 26318099. S2CID 10382311.
- ^ Hansen M, Phonekeo K, Paine JS, Leth-Petersen S, Begtrup M, Bräuner-Osborne H, Kristensen JL (March 2014). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of N-benzyl phenethylamines as 5-HT2A/2C agonists". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 5 (3): 243–249. doi: 10.1021/cn400216u. PMC 3963123. PMID 24397362.
- ^ Lipow M, Kaleem SZ, Espiridion E (2022-03-30). "NBOMe Toxicity and Fatalities: A Review of the Literature". Transformative Medicine. 1 (1): 12–18. doi: 10.54299/tmed/msot8578. ISSN 2831-8978. S2CID 247888583.
- ^ a b c Sean I, Joe R, Jennifer S, and Shaun G (28 March 2022). "A cluster of 25B-NBOH poisonings following exposure to powder sold as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)". Clinical Toxicology. 60 (8): 966–969. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2022.2053150. PMID 35343858. S2CID 247764056.
- ^ a b c d Amy E, Katherine W, John R, Sonyoung K, Robert J, Aaron J (December 2018). "Neurochemical pharmacology of psychoactive substituted N-benzylphenethylamines: High potency agonists at 5-HT2A receptors". Biochemical Pharmacology. 158: 27–34. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.09.024. PMC 6298744. PMID 30261175.
- ^ a b c d e Jolanta Z, Monika K, and Piotr A (26 February 2020). "NBOMes–Highly Potent and Toxic Alternatives of LSD". Frontiers in Neuroscience. 14: 78. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00078. PMC 7054380. PMID 32174803.
- ^ a b c d e f Lipow M, Kaleem SZ, Espiridion E (30 March 2022). "NBOMe Toxicity and Fatalities: A Review of the Literature". Transformative Medicine. 1 (1): 12–18. doi: 10.54299/tmed/msot8578. ISSN 2831-8978. S2CID 247888583.
- ^ Micaela T, Sabrine B, Raffaella A, Giorgia C, Beatrice M, Tatiana B, Federica B, Giovanni S, Francesco B, Fabio G, Krystyna G, Matteo M (21 April 2022). "Effect of -NBOMe Compounds on Sensorimotor, Motor, and Prepulse Inhibition Responses in Mice in Comparison With the 2C Analogs and Lysergic Acid Diethylamide: From Preclinical Evidence to Forensic Implication in Driving Under the Influence of Drugs". Front Psychiatry. 13: 875722. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.875722. PMC 9069068. PMID 35530025.
- ^ a b Cristina M, Matteo M, Nicholas P, Maria C, Micaela T, Raffaella A, Maria L (12 December 2019). "Neurochemical and Behavioral Profiling in Male and Female Rats of the Psychedelic Agent 25I-NBOMe". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 10: 1406. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01406. PMC 6921684. PMID 31915427.
- ^ a b c Anna R, Dino L, Julia R, Daniele B, Marius H, Matthias L (December 2015). "Receptor interaction profiles of novel N-2-methoxybenzyl (NBOMe) derivatives of 2,5-dimethoxy-substituted phenethylamines (2C drugs)". Neuropharmacology. 99: 546–553. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.034. ISSN 1873-7064. PMID 26318099. S2CID 10382311.
- ^ a b David W, Roumen S, Andrew C, Paul D (6 February 2015). "Prevalence of use and acute toxicity associated with the use of NBOMe drugs". Clinical Toxicology. 53 (2): 85–92. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2015.1004179. PMID 25658166. S2CID 25752763.
- ^ Humston C, Miketic R, Moon K, Ma P, Tobias J (2017-06-05). "Toxic Leukoencephalopathy in a Teenager Caused by the Recreational Ingestion of 25I-NBOMe: A Case Report and Review of Literature". Journal of Medical Cases. 8 (6): 174–179. doi: 10.14740/jmc2811w. ISSN 1923-4163.
- ^ Justin P, Stephen R, Kylin A, Alphonse P, Michelle P (2015). "Analysis of 25I-NBOMe, 25B-NBOMe, 25C-NBOMe and Other Dimethoxyphenyl-N-[(2-Methoxyphenyl) Methyl]Ethanamine Derivatives on Blotter Paper". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 39 (8): 617–623. doi: 10.1093/jat/bkv073. PMC 4570937. PMID 26378135.
- ^ Morini L, Bernini M, Vezzoli S, Restori M, Moretti M, Crenna S, et al. (October 2017). "Death after 25C-NBOMe and 25H-NBOMe consumption". Forensic Science International. 279: e1–e6. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.08.028. PMID 28893436.
- ^ Byard RW, Cox M, Stockham P (November 2016). "Blunt Craniofacial Trauma as a Manifestation of Excited Delirium Caused by New Psychoactive Substances". Journal of Forensic Sciences. 61 (6): 1546–1548. doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.13212. PMID 27723094. S2CID 4734566.
- ^ a b Sabastian LP, Christoffer B, Martin H, Martin AC, Jan K, Jesper LK (14 February 2014). "Correlating the Metabolic Stability of Psychedelic 5-HT2A Agonists with Anecdotal Reports of Human Oral Bioavailability". Neurochemical Research. 39 (10): 2018–2023. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1253-y. PMID 24519542. S2CID 254857910.
- ^ Boris D, Cristian C, Marcelo K, Edwar F, Bruce KC (August 2016). "Analysis of 25 C NBOMe in Seized Blotters by HPTLC and GC–MS". Journal of Chromatographic Science. 54 (7): 1153–1158. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmw095. PMC 4941995. PMID 27406128.
- ^ Francesco SB, Ornella C, Gabriella A, Giuseppe V, Rita S, Flaminia BP, Eduardo C, Pierluigi S, Giovanni M, Guiseppe B, Fabrizio S (3 July 2014). "25C-NBOMe: preliminary data on pharmacology, psychoactive effects, and toxicity of a new potent and dangerous hallucinogenic drug". BioMed Research International. 2014: 734749. doi: 10.1155/2014/734749. PMC 4106087. PMID 25105138.
- ^ Adam JP, Simon HT, Simon LH (September 2021). "Pharmacology and toxicology of N-Benzyl-phenylethylamines (25X-NBOMe) hallucinogens". Novel Psychoactive Substances: Classification, Pharmacology and Toxicology (2 ed.). Academic Press. pp. 279–300. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-818788-3.00008-5. ISBN 978-0-12-818788-3. S2CID 240583877.
- ^ Rothman RB, Baumann MH, Savage JE, Rauser L, McBride A, Hufeisen SJ, Roth BL (Dec 2000). "Evidence for possible involvement of 5-HT(2B) receptors in the cardiac valvulopathy associated with fenfluramine and other serotonergic medications". Circulation. 102 (23): 2836–41. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.23.2836. PMID 11104741.
- ^ Fitzgerald LW, Burn TC, Brown BS, Patterson JP, Corjay MH, Valentine PA, Sun JH, Link JR, Abbaszade I, Hollis JM, Largent BL, Hartig PR, Hollis GF, Meunier PC, Robichaud AJ, Robertson DW (Jan 2000). "Possible role of valvular serotonin 5-HT(2B) receptors in the cardiopathy associated with fenfluramine". Molecular Pharmacology. 57 (1): 75–81. PMID 10617681.
- ^ Roth BL (Jan 2007). "Drugs and valvular heart disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 356 (1): 6–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp068265. PMID 17202450.
- ^ Xu P, Qiu Q, Li H, Yan S, Yang M, Naman CB, et al. (26 February 2019). "25C-NBOMe, a Novel Designer Psychedelic, Induces Neurotoxicity 50 Times More Potent Than Methamphetamine In Vitro". Neurotoxicity Research. 35 (4): 993–998. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-0012-x. PMID 30806983. S2CID 255763701.
- ^ Álvarez-Alarcón N, Osorio-Méndez JJ, Ayala-Fajardo A, Garzón-Méndez WF, Garavito-Aguilar ZV (2021). "Zebrafish and Artemia salina in vivo evaluation of the recreational 25C-NBOMe drug demonstrates its high toxicity". Toxicology Reports. 8: 315–323. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.01.010. ISSN 2214-7500. PMC 7868744. PMID 33598409.
- ^ Poulie CB, Jensen AA, Halberstadt AL, Kristensen JL (December 2020). "DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: NBOMes". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 11 (23): 3860–3869. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00528. PMC 9191638. PMID 31657895. S2CID 204952449.
- ^ Michael Robert Braden (2007). "Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action". Dissertation: 1–176.
- ^ Nichols DE (2012). "Structure-activity relationships of serotonin 5-HT2A agonists". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Membrane Transport and Signaling. 1 (5): 559–579. doi: 10.1002/wmts.42.
- ^ Leth-Petersen S, Petersen IN, Jensen AA, Bundgaard C, Bæk M, Kehler J, Kristensen JL (November 2016). "5-HT2A/5-HT2C Receptor Pharmacology and Intrinsic Clearance of N-Benzylphenethylamines Modified at the Primary Site of Metabolism". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 7 (11): 1614–1619. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00265. PMID 27564969.
- ^ Prabhakaran J, Solingapuram Sai KK, Zanderigo F, Rubin-Falcone H, Jorgensen MJ, Kaplan JR, et al. (January 2017). "In vivo evaluation of [18F]FECIMBI-36, an agonist 5-HT2A/2C receptor PET radioligand in nonhuman primate". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 27 (1): 21–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.11.043. PMC 5348621. PMID 27889455.
- ^ Juncosa JI, Hansen M, Bonner LA, Cueva JP, Maglathlin R, McCorvy JD, Marona-Lewicka D, Lill MA, Nichols DE (January 2013). "Extensive rigid analogue design maps the binding conformation of potent N-benzylphenethylamine 5-HT2A serotonin receptor agonist ligands". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 4 (1): 96–109. doi: 10.1021/cn3000668. PMC 3547484. PMID 23336049.
- ^ Wallach J, et al. Selective, Partial and Arrestin-Biased 5-HT2A Agonists with Utility in Various Disorders. Patent WO 2022/241006
- ^ Wallach J, Cao AB, Calkins MM, Heim AJ, Lanham JK, Bonniwell EM, Hennessey JJ, Bock HA, Anderson EI, Sherwood AM, Morris H, de Klein R, Klein AK, Cuccurazzu B, Gamrat J, Fannana T, Zauhar R, Halberstadt AL, McCorvy JD. Identification of 5-HT2A Receptor Signaling Pathways Responsible for Psychedelic Potential. bioRxiv 2023 Jul 31:2023.07.29.551106. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.29.551106 PMID 37577474
- ^ Kruegel AC. Phenalkylamines and Methods of Making and Using the Same. Patent WO 2022/192781
- ^ Trachsel D, Lehmann D, Enzensperger C (2013). Phenethylamine Von der Struktur zur Funktion. Nachtschatten Verlag AG. p. 843. ISBN 978-3-03788-700-4.
- ^ Elliott SP, Holdbrook T, Brandt SD (May 2020). "Prodrugs of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS): A New Challenge" (PDF). Journal of Forensic Sciences. 65 (3): 913–920. doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.14268. PMID 31943218. S2CID 210335207.
- ^ Richter LH, Menges J, Wagmann L, Brandt SD, Stratford A, Westphal F, et al. (2020). "In vitro toxicokinetics and analytical toxicology of three novel NBOMe derivatives: Phase I and II metabolism, plasma protein binding, and detectability in standard urine screening approaches studied by means of hyphenated mass spectrometry" (PDF). Forensic Toxicology. 38: 141–159. doi: 10.1007/s11419-019-00498-7. S2CID 202879918.
- ^ Nichols DE, Sassano MF, Halberstadt AL, Klein LM, Brandt SD, Elliott SP, Fiedler WJ (July 2015). "N-Benzyl-5-methoxytryptamines as Potent Serotonin 5-HT2 Receptor Family Agonists and Comparison with a Series of Phenethylamine Analogues". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 6 (7): 1165–1175. doi: 10.1021/cn500292d. PMC 4505863. PMID 25547199.
- ^ "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Ketamine etc.) (Amendment) Order 2014". www.legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ "Psychoactive Substances Act 2016". www.legislation.gov.uk.

The 25-NB (25x-NBx) series, sometimes alternatively referred to as the NBOMe compounds, is a family of serotonergic psychedelics. [1] They are substituted phenethylamines and were derived from the 2C family. [1] They act as selective agonists of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor. [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] The 25-NB family is unique relative to other classes of psychedelics in that they are, generally speaking, extremely potent and relatively selective for the 5-HT2A receptor. [1] Use of NBOMe series drugs has caused many deaths and hospitalisations since the drugs popularisation in the 2010s. This is primarily due to their high potency, unpredictable pharmacokinetics, and sellers passing off the compounds in the series as LSD. [9]
Toxicity and harm potential
NBOMe compounds are often associated with life-threatening toxicity and death. [10] [11] Studies on NBOMe family of compounds demonstrated that the substance exhibit neurotoxic and cardiotoxic activity. [12] Reports of autonomic dysfunction remains prevalent with NBOMe compounds, with most individuals experiencing sympathomimetic toxicity such as vasoconstriction, hypertension and tachycardia in addition to hallucinations. [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] Other symptoms of toxidrome of include agitation or aggression, seizure, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, hypertonia, rhabdomyolysis, and death. [13] [17] [11] Researchers report that NBOMe intoxication frequently display signs of serotonin syndrome. [18] The likelihood of seizure is higher in NBOMes compared to other psychedelics. [12]
NBOMe and NBOHs are regularly sold as LSD in blotter papers, [11] [19] which have a bitter taste and different safety profiles. [13] [10] Despite high potency, recreational doses of LSD have only produced low incidents of acute toxicity. [10] Fatalities involved in NBOMe intoxication suggest that a significant number of individuals ingested the substance which they believed was LSD, [15] and researchers report that "users familiar with LSD may have a false sense of security when ingesting NBOMe inadvertently". [13] While most fatalities are due to the physical effects of the drug, there have also been reports of death due to self-harm and suicide under the influence of the substance. [20] [21] [13]
Given limited documentation of NBOMe consumption, the long-term effects of the substance remain unknown. [13] NBOMe compounds are not active orally, [a] and are usually taken sublingually. [1]: 3 When NBOMes are administered sublingually, numbness of the tongue and mouth followed by a metallic chemical taste was observed, and researchers describe this physical side effect as one of the main discriminants between NBOMe compounds and LSD. [23] [24] [25]
Neurotoxic and cardiotoxic actions
Many of the NBOMe compounds have high potency agonist activity at additional 5-HT receptors and prolonged activation of 5-HT2B can cause cardiac valvulopathy in high doses and chronic use. [11] [16] 5-HT2B receptors have been strongly implicated in causing drug-induced valvular heart disease. [26] [27] [28] The high affinity of NBOMe compounds for adrenergic α1 receptor has been reported to contribute to the stimulant-type cardiovascular effects. [16]
In vitro studies, 25C-NBOMe has been shown to exhibit cytotoxicity on neuronal cell lines SH-SY5Y, PC12, and SN471, and the compound was more potent than methamphetamine at reducing the visibility of the respective cells; the neurotoxicity of the compound involves activation of MAPK/ERK cascade and inhibition of Akt/PKB signaling pathway. [12] 25C-NBOMe, including the other derivative 25D-NBOMe, reduced the visibility of cardiomyocytes H9c2 cells, and both substances downregulated expression level of p21 (CDC24/RAC)-activated kinase 1 (PAK1), an enzyme with documented cardiac protective effects. [12]
Preliminary studies on 25C-NBOMe have shown that the substance is toxic to development, heart health, and brain health in zebrafish, rats, and Artemia salina, a common organism for studying potential drug effects on humans, but more research is needed on the topic, the dosages, and if the toxicology results apply to humans. Researchers of the study also recommended further investigation of the drug's potential in damaging pregnant women and their fetus due to the substance's damaging effects to development. [29] [30]
Emergency treatment
At present, there are no specific antidotes for NBOMes, and all acute intoxication is managed by symptomatic treatments, such as administration of benzodiazepines, antipsychotic drugs, and antiarrhythmic agents, such as beta blockers; some emergency interventions are intended to specifically treat rhabdomyolysis, which may lead to critical complications such as metabolic acidosis and acute kidney injury. [12]
Chemical structure
The 25-NB compounds are mostly N-benzylphenethylamines, [1] [31] though in some cases the phenyl ring of the N-benzyl group is replaced by other heterocycles such as thiophene, pyridine, furan, tetrahydrofuran, benzodioxole or naphthalene, among others. [32] [33]
Generally speaking, they have methoxy groups at the 2 and 5 positions of the phenyl ring, a substitution such as a halogen or alkyl group at the 4 position of the phenyl ring, and a methoxy or other substitution (e.g., hydroxyl, fluoro) at the 2 position of the N- benzyl ring. [1] More rarely, other substitution patterns may be present [34] [35] (see e.g. NBOMe-mescaline, 25G-NBOMe, 2CBFly-NBOMe, 25C-NB3OMe). They differ from the 2C series by the presence of the N-benzyl moiety. [1]
Rarely an alpha-methyl group is present making them N-benzyl amphetamines rather than N-benzyl phenethylamines, but this greatly reduces potency and activity. However in some cases where a side chain methyl group is cyclised back to the ring (e.g. in 2CBCB-NBOMe) or links the two alpha positions (e.g. in DMBMPP), this can improve selectivity for the 5-HT2A receptor subtype. [36]
List of 25-NB derivatives

This list includes notable compounds representative of most of the structural variations that have been explored in this series, but is by no means exhaustive. Many derivatives invented for scientific study into the structure-activity relationships of 5-HT2 receptor agonists have never appeared as designer drugs, while conversely some derivatives that have appeared as designer drugs are structurally novel and of unknown pharmacological activity (e.g. C30-NBOMe, 5-APB-NBOMe).
| Chemical structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number | R | R1 | Cyc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
25B-NB | N-benzyl-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 155639-26-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | phenyl |

|
25C-NB | N-benzyl-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391487-65-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | phenyl |

|
25I-NB | N-benzyl-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-18-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | phenyl |

|
25I-NMeTh | N-[(thiophen-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391499-03-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | thiophen-2-yl |

|
25B-NMePyr | N-[(pyridin-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391499-21-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | pyridin-2-yl |

|
25I-NMeFur | N-[(furan-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-93-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | furan-2-yl |

|
25I-NMeTHF | N-[(tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | tetrahydrofuran-2-yl | |

|
25B-NBF | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1539266-17-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-fluorophenyl |

|
25B-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1335331-46-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25B-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1026511-90-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25B-NB23DM | N-(2,3-dimethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391493-68-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,3-dimethoxyphenyl |

|
25B-NB25DM | N-(2,5-dimethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,5-dimethoxyphenyl | |

|
25B-NMe7BF | N-[(benzofuran-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391492-46-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzofuran-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7DHBF | N-[(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391492-40-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7BT | N-[(benzothiophen-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391492-59-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzothiophen-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7Box | N-[(benzoxazol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-73-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzoxazol-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7Ind | N-[(indol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-28-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | indol-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7Indz | N-[(indazol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-43-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | indazol-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7Bim | N-[(benzimidazol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-62-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzimidazol-7-yl |

|
FECIMBI-36 | N-[(2-fluoroethoxy)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-(2-fluoroethoxy)phenyl | |

|
DOB-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminopropane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
25C-NB3OMe | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-34-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 3-methoxyphenyl |

|
25C-NB4OMe | N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-35-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 4-methoxyphenyl |

|
C30-NBOMe | N-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1445574-98-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBF | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1539266-21-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-fluorophenyl |

|
25C-NBCl | N-(2-chlorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-chlorophenyl | |

|
25C-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391488-16-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1227608-02-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBOEt | N-(2-ethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-ethoxyphenyl | |

|
25C-NBOiPr | N-(2-isopropoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-isopropoxyphenyl | |

|
25F-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-fluorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1373917-84-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-fluoro | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25CN-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyanophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1539266-32-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyano | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25CN-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyanophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-16-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyano | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25D-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-02-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25D-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391488-44-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25E-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-14-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25E-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391489-79-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethyl | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25G-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-65-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25H-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-52-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25I-NB34MD | N-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391497-81-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25I-NB3OMe | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-40-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 3-methoxyphenyl |

|
25I-NB4OMe | N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-41-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 4-methoxyphenyl |

|
25I-NBF | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-21-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-fluorophenyl |

|
25I-NBBr | N-(2-bromobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1648649-98-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-bromophenyl |

|
25I-NBTFM | N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl | |

|
25I-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-25-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25B-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-19-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1373879-26-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25D-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391488-97-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25I-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-20-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25I-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-19-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
DOI-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
25I-NBMeOH | N-[2-(hydroxymethyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391494-71-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl |

|
25I-NBAm | N-[2-(carbamoyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391494-85-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-(carbamoyl)phenyl |

|
25I-NMe7DHBF | N-[(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl | |

|
25I-N2Nap1OH | N-[(1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl | |

|
25I-N3MT2M | N-[(3-methoxythiophen-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-66-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 3-methoxythiophen-2-yl |

|
25I-N4MT3M | N-[(4-methoxythiophen-3-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-73-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 4-methoxythiophen-3-yl |

|
25iP-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-isopropylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391487-83-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-isopropyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25N-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-03-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25N-NBOEt [37] | N-(2-ethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 2-ethoxyphenyl | |

|
25N-NB-2-OH-3-Me | N-(2-hydroxy-3-methylbenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 2-hydroxy-3-methylphenyl | |

|
25N-NBOCF2H | N-(2-difluoromethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 2-difluoromethoxyphenyl | |

|
25N-NBPh [38] | N-[(2-phenyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | o-biphenyl | |

|
25N-N1-Nap | N-[(naphthalen-1-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 1-naphthyl | |

|
25P-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-propylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391489-07-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-propyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25P-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-propylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391490-34-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-propyl | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25TFM-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1027161-33-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25O-NBcP | N-(2-cyclopropylbenzyl)-1-(2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,4,5-trimethoxy | H | 2-cyclopropylphenyl | |

|
25T-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(methylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1539266-47-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(methylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T2-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(ethylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1539266-51-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(ethylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T4-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(isopropylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1354632-17-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(isopropylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T7-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1539266-55-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T7-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1354632-41-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio) | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25AM-NBOMe [39] | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-pentylphenyl]-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(n-pentyl) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
NBOMe-mescaline | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-01-1 | 3,4,5-trimethoxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
NBOMe-escaline | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,5-dimethoxy-4-ethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 3,5-dimethoxy-4-ethoxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
NBOMe-thiobuscaline | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,5-dimethoxy-4-butylthiophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 3,5-dimethoxy-4-(n-butylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
MDPEA-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 3,4-methylenedioxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
2C2-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2-methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2-methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
MDBZ | N-benzyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane | 65033-29-6 | 3,4-methylenedioxy | methyl | phenyl |

|
Clobenzorex | N-(2-chlorobenzyl)-1-phenyl-2-aminopropane | 13364-32-4 | H | methyl | 2-chlorophenyl |

|
4-EA-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-aminopropane | 4-ethyl | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
5-APB-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(benzofuran-5-yl)-2-aminopropane | benzofuran-5-yl instead of phenyl | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl |
Similar compounds with related structures are also known including;
| Chemical structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|

|
25B-N1POMe | N-[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenethylamine | 1335331-49-1 (R) 1335331-51-5 (S) |

|
2C-B-AN [40] [41] | 2-phenyl-2-[2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)ethylamino]acetonitrile | |

|
25B-N(BOMe)2 | 2-(4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N,N-bis(2-methoxybenzyl)ethan-1-amine | |

|
2CBCB-NBOMe | N-[(3-bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-bicyclo[4,2,0]octa-1,3,5-trien-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2-methoxyphenyl)methanamine | 1354634-09-5 |

|
2CBFly-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(8-bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane | 1335331-42-4 |

|
2C-B-DRAGONFLY-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(8-bromobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane | 1335331-45-7 |

|
2C-B-FLY-NB2EtO5Cl [42] | N-(2-ethoxy-5-chlorobenzyl)-1-(8-bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane | |

|
DMBMPP | (S,S)-2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromobenzyl)-6-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperidine | 1391499-52-7 |

|
25B-NAcPip | 2-{[2-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]amino}-1-(piperidin-1-yl)ethanone | |

|
ZDCM-04 | 1,3-dimethyl-7-{2-[1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)propan-2-ylamino]ethyl}purine-2,6-dione | |

|
RH-34 | 3-[2-(2-methoxybenzylamino)ethyl]-1H-quinazoline-2,4-dione | 1028307-48-3 |

|
5-MeO-T-NBOMe [43] | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-5-methoxytryptamine | 1335331-37-7 |

|
5MT-NB3OMe | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-5-methoxytryptamine | 1648553-42-7 |
Legality
United Kingdom
A large number of substances in the 25-NB class are Class A drugs in the United Kingdom as a result of the N-benzylphenethylamine catch-all clause in the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 [44] or are otherwise covered by the Psychoactive Substances Act 2016. [45]
See also
Notes
- ^ The potency of N-benzylphenethylamines via buccal, sublingual, or nasal absorption is 50-100 greater (by weight) than oral route compared to the parent 2C-x compounds. [22] Researchers hypothesize the low oral metabolic stability of N-benzylphenethylamines is likely causing the low bioavailability on the oral route, although the metabolic profile of this compounds remains unpredictable; therefore researchers state that the fatalities linked to these substances may partly be explained by differences in the metabolism between individuals. [22]
External links
References
- ^ a b c d e f g Adam H (18 January 2017). "Pharmacology and Toxicology of N-Benzylphenethylamine ("NBOMe") Hallucinogens". Neuropharmacology of New Psychoactive Substances. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. Vol. 32. Springer. pp. 283–311. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_64. ISBN 978-3-319-52444-3. PMID 28097528.
- ^ Pertz HH, Rheineck A, Elz S (1999-01-01). "N-Benzylated derivatives of the hallucinogenic drugs mescaline and escaline as partial agonists at rat vascular 5-HT2A receptors". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 359: R29. Archived from the original on September 25, 2015.
- ^ Heim R (February 28, 2010). Synthese und Pharmakologie potenter 5-HT2A-Rezeptoragonisten mit N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Partialstruktur. Entwicklung eines neuen Struktur-Wirkungskonzepts (Thesis) (in German). Berlin: Freie Univ. Retrieved 2013-05-10.
- ^ Silva M (2009). Theoretical study of the interaction of agonists with the 5-HT2A receptor (Ph.D. thesis). Universität Regensburg.
- ^ Hansen M (2011). Design and Synthesis of Selective Serotonin Receptor Agonists for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of the Brain (Ph.D. thesis). University of Copenhagen.
- ^ Silva ME, Heim R, Strasser A, Elz S, Dove S (January 2011). "Theoretical studies on the interaction of partial agonists with the 5-HT2A receptor". Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design. 25 (1): 51–66. Bibcode: 2011JCAMD..25...51S. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.688.2670. doi: 10.1007/s10822-010-9400-2. PMID 21088982. S2CID 3103050.
- ^ Rickli A, Luethi D, Reinisch J, Buchy D, Hoener MC, Liechti ME (December 2015). "Receptor interaction profiles of novel N-2-methoxybenzyl (NBOMe) derivatives of 2,5-dimethoxy-substituted phenethylamines (2C drugs)" (PDF). Neuropharmacology. 99: 546–553. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.034. PMID 26318099. S2CID 10382311.
- ^ Hansen M, Phonekeo K, Paine JS, Leth-Petersen S, Begtrup M, Bräuner-Osborne H, Kristensen JL (March 2014). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of N-benzyl phenethylamines as 5-HT2A/2C agonists". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 5 (3): 243–249. doi: 10.1021/cn400216u. PMC 3963123. PMID 24397362.
- ^ Lipow M, Kaleem SZ, Espiridion E (2022-03-30). "NBOMe Toxicity and Fatalities: A Review of the Literature". Transformative Medicine. 1 (1): 12–18. doi: 10.54299/tmed/msot8578. ISSN 2831-8978. S2CID 247888583.
- ^ a b c Sean I, Joe R, Jennifer S, and Shaun G (28 March 2022). "A cluster of 25B-NBOH poisonings following exposure to powder sold as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)". Clinical Toxicology. 60 (8): 966–969. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2022.2053150. PMID 35343858. S2CID 247764056.
- ^ a b c d Amy E, Katherine W, John R, Sonyoung K, Robert J, Aaron J (December 2018). "Neurochemical pharmacology of psychoactive substituted N-benzylphenethylamines: High potency agonists at 5-HT2A receptors". Biochemical Pharmacology. 158: 27–34. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.09.024. PMC 6298744. PMID 30261175.
- ^ a b c d e Jolanta Z, Monika K, and Piotr A (26 February 2020). "NBOMes–Highly Potent and Toxic Alternatives of LSD". Frontiers in Neuroscience. 14: 78. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00078. PMC 7054380. PMID 32174803.
- ^ a b c d e f Lipow M, Kaleem SZ, Espiridion E (30 March 2022). "NBOMe Toxicity and Fatalities: A Review of the Literature". Transformative Medicine. 1 (1): 12–18. doi: 10.54299/tmed/msot8578. ISSN 2831-8978. S2CID 247888583.
- ^ Micaela T, Sabrine B, Raffaella A, Giorgia C, Beatrice M, Tatiana B, Federica B, Giovanni S, Francesco B, Fabio G, Krystyna G, Matteo M (21 April 2022). "Effect of -NBOMe Compounds on Sensorimotor, Motor, and Prepulse Inhibition Responses in Mice in Comparison With the 2C Analogs and Lysergic Acid Diethylamide: From Preclinical Evidence to Forensic Implication in Driving Under the Influence of Drugs". Front Psychiatry. 13: 875722. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.875722. PMC 9069068. PMID 35530025.
- ^ a b Cristina M, Matteo M, Nicholas P, Maria C, Micaela T, Raffaella A, Maria L (12 December 2019). "Neurochemical and Behavioral Profiling in Male and Female Rats of the Psychedelic Agent 25I-NBOMe". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 10: 1406. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01406. PMC 6921684. PMID 31915427.
- ^ a b c Anna R, Dino L, Julia R, Daniele B, Marius H, Matthias L (December 2015). "Receptor interaction profiles of novel N-2-methoxybenzyl (NBOMe) derivatives of 2,5-dimethoxy-substituted phenethylamines (2C drugs)". Neuropharmacology. 99: 546–553. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.034. ISSN 1873-7064. PMID 26318099. S2CID 10382311.
- ^ a b David W, Roumen S, Andrew C, Paul D (6 February 2015). "Prevalence of use and acute toxicity associated with the use of NBOMe drugs". Clinical Toxicology. 53 (2): 85–92. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2015.1004179. PMID 25658166. S2CID 25752763.
- ^ Humston C, Miketic R, Moon K, Ma P, Tobias J (2017-06-05). "Toxic Leukoencephalopathy in a Teenager Caused by the Recreational Ingestion of 25I-NBOMe: A Case Report and Review of Literature". Journal of Medical Cases. 8 (6): 174–179. doi: 10.14740/jmc2811w. ISSN 1923-4163.
- ^ Justin P, Stephen R, Kylin A, Alphonse P, Michelle P (2015). "Analysis of 25I-NBOMe, 25B-NBOMe, 25C-NBOMe and Other Dimethoxyphenyl-N-[(2-Methoxyphenyl) Methyl]Ethanamine Derivatives on Blotter Paper". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 39 (8): 617–623. doi: 10.1093/jat/bkv073. PMC 4570937. PMID 26378135.
- ^ Morini L, Bernini M, Vezzoli S, Restori M, Moretti M, Crenna S, et al. (October 2017). "Death after 25C-NBOMe and 25H-NBOMe consumption". Forensic Science International. 279: e1–e6. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.08.028. PMID 28893436.
- ^ Byard RW, Cox M, Stockham P (November 2016). "Blunt Craniofacial Trauma as a Manifestation of Excited Delirium Caused by New Psychoactive Substances". Journal of Forensic Sciences. 61 (6): 1546–1548. doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.13212. PMID 27723094. S2CID 4734566.
- ^ a b Sabastian LP, Christoffer B, Martin H, Martin AC, Jan K, Jesper LK (14 February 2014). "Correlating the Metabolic Stability of Psychedelic 5-HT2A Agonists with Anecdotal Reports of Human Oral Bioavailability". Neurochemical Research. 39 (10): 2018–2023. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1253-y. PMID 24519542. S2CID 254857910.
- ^ Boris D, Cristian C, Marcelo K, Edwar F, Bruce KC (August 2016). "Analysis of 25 C NBOMe in Seized Blotters by HPTLC and GC–MS". Journal of Chromatographic Science. 54 (7): 1153–1158. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmw095. PMC 4941995. PMID 27406128.
- ^ Francesco SB, Ornella C, Gabriella A, Giuseppe V, Rita S, Flaminia BP, Eduardo C, Pierluigi S, Giovanni M, Guiseppe B, Fabrizio S (3 July 2014). "25C-NBOMe: preliminary data on pharmacology, psychoactive effects, and toxicity of a new potent and dangerous hallucinogenic drug". BioMed Research International. 2014: 734749. doi: 10.1155/2014/734749. PMC 4106087. PMID 25105138.
- ^ Adam JP, Simon HT, Simon LH (September 2021). "Pharmacology and toxicology of N-Benzyl-phenylethylamines (25X-NBOMe) hallucinogens". Novel Psychoactive Substances: Classification, Pharmacology and Toxicology (2 ed.). Academic Press. pp. 279–300. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-818788-3.00008-5. ISBN 978-0-12-818788-3. S2CID 240583877.
- ^ Rothman RB, Baumann MH, Savage JE, Rauser L, McBride A, Hufeisen SJ, Roth BL (Dec 2000). "Evidence for possible involvement of 5-HT(2B) receptors in the cardiac valvulopathy associated with fenfluramine and other serotonergic medications". Circulation. 102 (23): 2836–41. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.23.2836. PMID 11104741.
- ^ Fitzgerald LW, Burn TC, Brown BS, Patterson JP, Corjay MH, Valentine PA, Sun JH, Link JR, Abbaszade I, Hollis JM, Largent BL, Hartig PR, Hollis GF, Meunier PC, Robichaud AJ, Robertson DW (Jan 2000). "Possible role of valvular serotonin 5-HT(2B) receptors in the cardiopathy associated with fenfluramine". Molecular Pharmacology. 57 (1): 75–81. PMID 10617681.
- ^ Roth BL (Jan 2007). "Drugs and valvular heart disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 356 (1): 6–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp068265. PMID 17202450.
- ^ Xu P, Qiu Q, Li H, Yan S, Yang M, Naman CB, et al. (26 February 2019). "25C-NBOMe, a Novel Designer Psychedelic, Induces Neurotoxicity 50 Times More Potent Than Methamphetamine In Vitro". Neurotoxicity Research. 35 (4): 993–998. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-0012-x. PMID 30806983. S2CID 255763701.
- ^ Álvarez-Alarcón N, Osorio-Méndez JJ, Ayala-Fajardo A, Garzón-Méndez WF, Garavito-Aguilar ZV (2021). "Zebrafish and Artemia salina in vivo evaluation of the recreational 25C-NBOMe drug demonstrates its high toxicity". Toxicology Reports. 8: 315–323. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.01.010. ISSN 2214-7500. PMC 7868744. PMID 33598409.
- ^ Poulie CB, Jensen AA, Halberstadt AL, Kristensen JL (December 2020). "DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: NBOMes". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 11 (23): 3860–3869. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00528. PMC 9191638. PMID 31657895. S2CID 204952449.
- ^ Michael Robert Braden (2007). "Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action". Dissertation: 1–176.
- ^ Nichols DE (2012). "Structure-activity relationships of serotonin 5-HT2A agonists". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Membrane Transport and Signaling. 1 (5): 559–579. doi: 10.1002/wmts.42.
- ^ Leth-Petersen S, Petersen IN, Jensen AA, Bundgaard C, Bæk M, Kehler J, Kristensen JL (November 2016). "5-HT2A/5-HT2C Receptor Pharmacology and Intrinsic Clearance of N-Benzylphenethylamines Modified at the Primary Site of Metabolism". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 7 (11): 1614–1619. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00265. PMID 27564969.
- ^ Prabhakaran J, Solingapuram Sai KK, Zanderigo F, Rubin-Falcone H, Jorgensen MJ, Kaplan JR, et al. (January 2017). "In vivo evaluation of [18F]FECIMBI-36, an agonist 5-HT2A/2C receptor PET radioligand in nonhuman primate". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 27 (1): 21–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.11.043. PMC 5348621. PMID 27889455.
- ^ Juncosa JI, Hansen M, Bonner LA, Cueva JP, Maglathlin R, McCorvy JD, Marona-Lewicka D, Lill MA, Nichols DE (January 2013). "Extensive rigid analogue design maps the binding conformation of potent N-benzylphenethylamine 5-HT2A serotonin receptor agonist ligands". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 4 (1): 96–109. doi: 10.1021/cn3000668. PMC 3547484. PMID 23336049.
- ^ Wallach J, et al. Selective, Partial and Arrestin-Biased 5-HT2A Agonists with Utility in Various Disorders. Patent WO 2022/241006
- ^ Wallach J, Cao AB, Calkins MM, Heim AJ, Lanham JK, Bonniwell EM, Hennessey JJ, Bock HA, Anderson EI, Sherwood AM, Morris H, de Klein R, Klein AK, Cuccurazzu B, Gamrat J, Fannana T, Zauhar R, Halberstadt AL, McCorvy JD. Identification of 5-HT2A Receptor Signaling Pathways Responsible for Psychedelic Potential. bioRxiv 2023 Jul 31:2023.07.29.551106. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.29.551106 PMID 37577474
- ^ Kruegel AC. Phenalkylamines and Methods of Making and Using the Same. Patent WO 2022/192781
- ^ Trachsel D, Lehmann D, Enzensperger C (2013). Phenethylamine Von der Struktur zur Funktion. Nachtschatten Verlag AG. p. 843. ISBN 978-3-03788-700-4.
- ^ Elliott SP, Holdbrook T, Brandt SD (May 2020). "Prodrugs of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS): A New Challenge" (PDF). Journal of Forensic Sciences. 65 (3): 913–920. doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.14268. PMID 31943218. S2CID 210335207.
- ^ Richter LH, Menges J, Wagmann L, Brandt SD, Stratford A, Westphal F, et al. (2020). "In vitro toxicokinetics and analytical toxicology of three novel NBOMe derivatives: Phase I and II metabolism, plasma protein binding, and detectability in standard urine screening approaches studied by means of hyphenated mass spectrometry" (PDF). Forensic Toxicology. 38: 141–159. doi: 10.1007/s11419-019-00498-7. S2CID 202879918.
- ^ Nichols DE, Sassano MF, Halberstadt AL, Klein LM, Brandt SD, Elliott SP, Fiedler WJ (July 2015). "N-Benzyl-5-methoxytryptamines as Potent Serotonin 5-HT2 Receptor Family Agonists and Comparison with a Series of Phenethylamine Analogues". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 6 (7): 1165–1175. doi: 10.1021/cn500292d. PMC 4505863. PMID 25547199.
- ^ "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Ketamine etc.) (Amendment) Order 2014". www.legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ "Psychoactive Substances Act 2016". www.legislation.gov.uk.