 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| MedlinePlus | a682088 |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 36% |
| Elimination half-life | 17–20 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
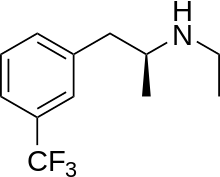
| Formula | C12H16F3N |
| Molar mass | 231.262 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model ( JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dexfenfluramine, marketed as dexfenfluramine hydrochloride under the name Redux, is a serotonergic anorectic drug: it reduces appetite by increasing the amount of extracellular serotonin in the brain. [3] It is the d- enantiomer of fenfluramine and is structurally similar to amphetamine, but lacks any psychologically stimulating effects.
Dexfenfluramine was, for some years in the mid-1990s, approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration for the purposes of weight loss. However, following multiple concerns about the cardiovascular side-effects of the drug, [3] the FDA withdrew the approval in 1997. [4] After it was removed in the US, dexfenfluramine was also pulled out in other global markets. It was later superseded by sibutramine, which, although initially considered a safer alternative to both dexfenfluramine and fenfluramine, [5] [6] [7] was likewise removed from the US market in 2010. [8] [9]
The drug was developed by Interneuron Pharmaceuticals, a company co-founded by Richard Wurtman, aimed at marketing discoveries by Massachusetts Institute of Technology scientists. [10] Interneuron licensed the patent to Wyeth-Ayerst Laboratories. [11] Although at the time of its release, some optimism prevailed that it might herald a new approach, [12] there remained some reservations amongst neurologists, twenty-two of whom petitioned the FDA to delay approval.[ citation needed] Their concern was based on the work of George A. Ricaurte, whose techniques and conclusions were later questioned. [13]
See also
References
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Anvisa (24 July 2023). "RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 25 July 2023). Archived from the original on 27 August 2023. Retrieved 27 August 2023.
- ^ a b Fox SI (2011). Human Physiology (Twelfth ed.). McGraw Hill. p. 665.
- ^ FDA 15 September 1997. FDA Announces Withdrawal Fenfluramine and Dexfenfluramine (Fen-Phen)
- ^ "Dexfenfluramine". PubChem. U.S. Library of Medicine. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ^ Hanotin C, Thomas F, Jones SP, Leutenegger E, Drouin P (July 1998). "A comparison of sibutramine and dexfenfluramine in the treatment of obesity". Obesity Research. 6 (4): 285–291. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1998.tb00351.x. PMID 9688105.
- ^ Lean ME (March 1997). "Sibutramine--a review of clinical efficacy". International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 21 (Suppl 1): S30–6, discussion 37–9. PMID 9130039.
- ^ "Abbott Pulls Diet Drug Meridia Off US Shelves". The Wall Street Journal. 8 October 2010. Archived from the original on 23 October 2010.
- ^ Li MF, Cheung BM (February 2011). "Rise and fall of anti-obesity drugs". World Journal of Diabetes. 2 (2): 19–23. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v2.i2.19. PMC 3083904. PMID 21537456.
- ^ Lemonick MD, Dowell W, Nash JM, Ramirez A, Reid B, Ressner J (23 September 1996). "The New Miracle Drug?". Time. Archived from the original on 6 November 2010. Retrieved 3 October 2010.
- ^ Lemonick MD, Nash JM, Park A, Thompson D (29 September 1997). "The Mood Molecule". Time. Archived from the original on 3 October 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2010.
- ^ Davis R, Faulds D (November 1996). "Dexfenfluramine. An updated review of its therapeutic use in the management of obesity". Drugs. 52 (5): 696–724. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199652050-00007. PMID 9118819. S2CID 261029109.
- ^ Philipkoski K (2 March 2004). "DEA Accedes to Ecstasy Test". Wired. Archived from the original on 10 January 2006.
External links
- Drug description
- Dexfenfluramine hydrochloride
- Questions and Answers about Withdrawal of Fenfluramine (Pondimin) and Dexfenfluramine (Redux)
- Frontline: Dangerous prescriptions—Interview with Leo Lutwak, M.D. in which he discuses the side effects of fenfluramine, its successor Redux, and the Fen-Phen combination
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| MedlinePlus | a682088 |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 36% |
| Elimination half-life | 17–20 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H16F3N |
| Molar mass | 231.262 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model ( JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dexfenfluramine, marketed as dexfenfluramine hydrochloride under the name Redux, is a serotonergic anorectic drug: it reduces appetite by increasing the amount of extracellular serotonin in the brain. [3] It is the d- enantiomer of fenfluramine and is structurally similar to amphetamine, but lacks any psychologically stimulating effects.
Dexfenfluramine was, for some years in the mid-1990s, approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration for the purposes of weight loss. However, following multiple concerns about the cardiovascular side-effects of the drug, [3] the FDA withdrew the approval in 1997. [4] After it was removed in the US, dexfenfluramine was also pulled out in other global markets. It was later superseded by sibutramine, which, although initially considered a safer alternative to both dexfenfluramine and fenfluramine, [5] [6] [7] was likewise removed from the US market in 2010. [8] [9]
The drug was developed by Interneuron Pharmaceuticals, a company co-founded by Richard Wurtman, aimed at marketing discoveries by Massachusetts Institute of Technology scientists. [10] Interneuron licensed the patent to Wyeth-Ayerst Laboratories. [11] Although at the time of its release, some optimism prevailed that it might herald a new approach, [12] there remained some reservations amongst neurologists, twenty-two of whom petitioned the FDA to delay approval.[ citation needed] Their concern was based on the work of George A. Ricaurte, whose techniques and conclusions were later questioned. [13]
See also
References
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Anvisa (24 July 2023). "RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 25 July 2023). Archived from the original on 27 August 2023. Retrieved 27 August 2023.
- ^ a b Fox SI (2011). Human Physiology (Twelfth ed.). McGraw Hill. p. 665.
- ^ FDA 15 September 1997. FDA Announces Withdrawal Fenfluramine and Dexfenfluramine (Fen-Phen)
- ^ "Dexfenfluramine". PubChem. U.S. Library of Medicine. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ^ Hanotin C, Thomas F, Jones SP, Leutenegger E, Drouin P (July 1998). "A comparison of sibutramine and dexfenfluramine in the treatment of obesity". Obesity Research. 6 (4): 285–291. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1998.tb00351.x. PMID 9688105.
- ^ Lean ME (March 1997). "Sibutramine--a review of clinical efficacy". International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 21 (Suppl 1): S30–6, discussion 37–9. PMID 9130039.
- ^ "Abbott Pulls Diet Drug Meridia Off US Shelves". The Wall Street Journal. 8 October 2010. Archived from the original on 23 October 2010.
- ^ Li MF, Cheung BM (February 2011). "Rise and fall of anti-obesity drugs". World Journal of Diabetes. 2 (2): 19–23. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v2.i2.19. PMC 3083904. PMID 21537456.
- ^ Lemonick MD, Dowell W, Nash JM, Ramirez A, Reid B, Ressner J (23 September 1996). "The New Miracle Drug?". Time. Archived from the original on 6 November 2010. Retrieved 3 October 2010.
- ^ Lemonick MD, Nash JM, Park A, Thompson D (29 September 1997). "The Mood Molecule". Time. Archived from the original on 3 October 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2010.
- ^ Davis R, Faulds D (November 1996). "Dexfenfluramine. An updated review of its therapeutic use in the management of obesity". Drugs. 52 (5): 696–724. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199652050-00007. PMID 9118819. S2CID 261029109.
- ^ Philipkoski K (2 March 2004). "DEA Accedes to Ecstasy Test". Wired. Archived from the original on 10 January 2006.
External links
- Drug description
- Dexfenfluramine hydrochloride
- Questions and Answers about Withdrawal of Fenfluramine (Pondimin) and Dexfenfluramine (Redux)
- Frontline: Dangerous prescriptions—Interview with Leo Lutwak, M.D. in which he discuses the side effects of fenfluramine, its successor Redux, and the Fen-Phen combination