 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard ( EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NS2 |
| Molar mass | 303.48 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model ( JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 188 to 189 °C (370 to 372 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Piperidylthiambutene (Piperidinohton) is a synthetic [1] opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family, which has around the same potency as morphine. [2] [3] [4] Piperidylthiambutene is structurally distinct from fentanyl, its analogues, and other synthetic opioids previously reported. [1] If sold or obtained for the purpose of human consumption it could be considered a controlled substance analogue in some countries such as the US, Australia and New Zealand. Piperidylthiambutene has been sold as a designer drug, first appearing in late 2018. [5] [6]
Synthesis
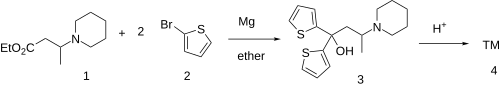
The Grignard reaction between 3-Piperidinobutyric acid ethyl ester, CID:10774378 (1) and 2-Bromothiophene [1003-09-4] (2) gives 3. Dehydration in acid completes the synthesis.
References
- ^ a b "Piperidylthiambutene" (PDF). NMS Labs. Retrieved 2020-09-14.
- ^ Adamson DW, Green AF (January 1950). "A new series of analgesics". Nature. 165 (4186): 122. Bibcode: 1950Natur.165..122A. doi: 10.1038/165122a0. PMID 15409854. S2CID 4190157.
- ^ Adamson DW, Duffin WM, Green AF (January 1951). "Dithienylbutylamines as analgesics". Nature. 167 (4239): 153–4. Bibcode: 1951Natur.167..153A. doi: 10.1038/167153b0. PMID 14806409. S2CID 4280042.
- ^ Green AF (March 1953). "Analgesic and other properties of 3: 3-dithienylalkenylamines". British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy. 8 (1): 2–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1953.tb00739.x. PMC 1509239. PMID 13066683.
- ^ "Analytical report Piperidylthiambutene" (PDF). European Project Response. November 2018.
- ^ Vandeputte MM, Cannaert A, Stove CP (November 2020). "In vitro functional characterization of a panel of non-fentanyl opioid new psychoactive substances". Archives of Toxicology. 94 (11): 3819–3830. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02855-7. hdl: 1854/LU-8687070. PMID 32734307. S2CID 220881657.
- ^ Adamson Donald Wallace, U.S. patent 2,561,899 (1951 to Burroughs Wellcome Co).
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard ( EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NS2 |
| Molar mass | 303.48 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model ( JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 188 to 189 °C (370 to 372 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Piperidylthiambutene (Piperidinohton) is a synthetic [1] opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family, which has around the same potency as morphine. [2] [3] [4] Piperidylthiambutene is structurally distinct from fentanyl, its analogues, and other synthetic opioids previously reported. [1] If sold or obtained for the purpose of human consumption it could be considered a controlled substance analogue in some countries such as the US, Australia and New Zealand. Piperidylthiambutene has been sold as a designer drug, first appearing in late 2018. [5] [6]
Synthesis

The Grignard reaction between 3-Piperidinobutyric acid ethyl ester, CID:10774378 (1) and 2-Bromothiophene [1003-09-4] (2) gives 3. Dehydration in acid completes the synthesis.
References
- ^ a b "Piperidylthiambutene" (PDF). NMS Labs. Retrieved 2020-09-14.
- ^ Adamson DW, Green AF (January 1950). "A new series of analgesics". Nature. 165 (4186): 122. Bibcode: 1950Natur.165..122A. doi: 10.1038/165122a0. PMID 15409854. S2CID 4190157.
- ^ Adamson DW, Duffin WM, Green AF (January 1951). "Dithienylbutylamines as analgesics". Nature. 167 (4239): 153–4. Bibcode: 1951Natur.167..153A. doi: 10.1038/167153b0. PMID 14806409. S2CID 4280042.
- ^ Green AF (March 1953). "Analgesic and other properties of 3: 3-dithienylalkenylamines". British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy. 8 (1): 2–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1953.tb00739.x. PMC 1509239. PMID 13066683.
- ^ "Analytical report Piperidylthiambutene" (PDF). European Project Response. November 2018.
- ^ Vandeputte MM, Cannaert A, Stove CP (November 2020). "In vitro functional characterization of a panel of non-fentanyl opioid new psychoactive substances". Archives of Toxicology. 94 (11): 3819–3830. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02855-7. hdl: 1854/LU-8687070. PMID 32734307. S2CID 220881657.
- ^ Adamson Donald Wallace, U.S. patent 2,561,899 (1951 to Burroughs Wellcome Co).