 | |
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Amlodipine | Calcium channel blocker |
| Benazepril | ACE inhibitor |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Lotrel |
| AHFS/ Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| License data | |
|
Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard ( EPA) | |
| | |
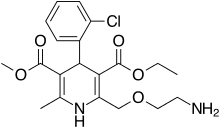
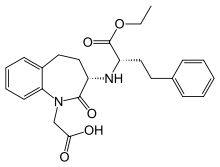
Amlodipine/benazepril, sold under the brand name Lotrel among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication used to treat high blood pressure. [1] It is a combination of amlodipine, as the besilate, a calcium channel blocker, and benazepril, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. [1] It may be used if a single agent is not sufficient. [1] It is taken by mouth. [1]
Common side effects include cough, dizziness, and swelling. [1] Serious side effects may include angioedema, myocardial infarction, high blood potassium, liver problems, and low blood pressure. [1] Use in pregnancy is not recommended. [1] Amlodipine works by increasing the size of arteries while benazepril works by decreasing renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activity. [1]
The combination was approved for medical use in the United States in 1995. [2] It is available as a generic medication. [3] In 2021, it was the 150th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3 million prescriptions. [4] [5]
Medical uses
It is used to treat high blood pressure. [1] It is not a first-line treatment. [6]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Lotrel- amlodipine besylate and benazepril hydrochloride capsule". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 20 June 2021.
- ^ Cerner Multum. "Amlodipine and benazepril Uses, Side Effects & Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- ^ Bope ET, Kellerman RD (2016). Conn's Current Therapy 2017 E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 124. ISBN 978-0-323-44335-7.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2021". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 15 January 2024. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ "Amlodipine; Benazepril - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ Faulkner MA, Hilleman DE (January 2001). "Amlodipine/benazepril: fixed dose combination therapy for hypertension". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 2 (1): 165–178. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2.1.165. PMID 11336577. S2CID 23021242.
 | |
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Amlodipine | Calcium channel blocker |
| Benazepril | ACE inhibitor |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Lotrel |
| AHFS/ Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| License data | |
|
Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard ( EPA) | |
| | |
Amlodipine/benazepril, sold under the brand name Lotrel among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication used to treat high blood pressure. [1] It is a combination of amlodipine, as the besilate, a calcium channel blocker, and benazepril, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. [1] It may be used if a single agent is not sufficient. [1] It is taken by mouth. [1]
Common side effects include cough, dizziness, and swelling. [1] Serious side effects may include angioedema, myocardial infarction, high blood potassium, liver problems, and low blood pressure. [1] Use in pregnancy is not recommended. [1] Amlodipine works by increasing the size of arteries while benazepril works by decreasing renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activity. [1]
The combination was approved for medical use in the United States in 1995. [2] It is available as a generic medication. [3] In 2021, it was the 150th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3 million prescriptions. [4] [5]
Medical uses
It is used to treat high blood pressure. [1] It is not a first-line treatment. [6]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Lotrel- amlodipine besylate and benazepril hydrochloride capsule". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 20 June 2021.
- ^ Cerner Multum. "Amlodipine and benazepril Uses, Side Effects & Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- ^ Bope ET, Kellerman RD (2016). Conn's Current Therapy 2017 E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 124. ISBN 978-0-323-44335-7.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2021". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 15 January 2024. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ "Amlodipine; Benazepril - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ Faulkner MA, Hilleman DE (January 2001). "Amlodipine/benazepril: fixed dose combination therapy for hypertension". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 2 (1): 165–178. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2.1.165. PMID 11336577. S2CID 23021242.