| Small nucleolar SNORD12/SNORD106 | |
|---|---|
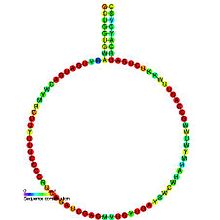 Predicted
secondary structure and
sequence conservation of SNORD12 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SNORD12 |
| Alt. Symbols | SNORD106; snoHBII-99 |
| Rfam | RF00581 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; snRNA; snoRNA; C/D-box |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota |
| GO | GO:0006396 GO:0005730 |
| SO | SO:0000593 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
In molecular biology, the small nucleolar RNAs SNORD106 and SNORD12 (also known as U106 and HBII-99 respectively ) are two related snoRNAs which belongs to the C/D class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs). Both contain the conserved C (UGAUGA) and D (CUGA) box sequence motifs [1]
Human SNORD12 (HBII-99) is the homologue of mouse snoRNA MBII-99. In humans both HB11-99 and U106 snoRNAs share the same host gene. [2] [3]
Most of the members of the box C/D family function in directing site-specific 2'-O- methylation of substrate RNAs. HBII-99 is predicted to guide the 2'O-ribose methylation of 28S rRNA G3878. [4] U106 contains conserved antisense elements which would predict U106 methylates residues G1536 and U1602 of 18S rRNA. [5] However, these targets do not appear to be methylated and U106 might function as an RNA chaperone during rRNA folding. [2] A similar role has been suggested for the H/ACA snoRNAs U17a and U17b [2]
References
- ^ Vitali P, Royo H, Seitz H, Bachellerie JP, Hüttenhofer A, Cavaillé J (November 2003). "Identification of 13 novel human modification guide RNAs". Nucleic Acids Research. 31 (22): 6543–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg849. PMC 275545. PMID 14602913.
- ^ a b c Lestrade L, Weber MJ (January 2006). "snoRNA-LBME-db, a comprehensive database of human H/ACA and C/D box snoRNAs". Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (Database issue): D158-62. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.105.7552. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj002. PMC 1347365. PMID 16381836.
- ^ Askarian-Amiri ME, Crawford J, French JD, Smart CE, Smith MA, Clark MB, Ru K, Mercer TR, Thompson ER, Lakhani SR, Vargas AC, Campbell IG, Brown MA, Dinger ME, Mattick JS (May 2011). "SNORD-host RNA Zfas1 is a regulator of mammary development and a potential marker for breast cancer". RNA. 17 (5): 878–91. doi: 10.1261/rna.2528811. PMC 3078737. PMID 21460236.
- ^ Hüttenhofer A, Kiefmann M, Meier-Ewert S, O'Brien J, Lehrach H, Bachellerie JP, Brosius J (June 2001). "RNomics: an experimental approach that identifies 201 candidates for novel, small, non-messenger RNAs in mouse". The EMBO Journal. 20 (11): 2943–53. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.11.2943. PMC 125495. PMID 11387227.
- ^ Kiss T (April 2002). "Small nucleolar RNAs: an abundant group of noncoding RNAs with diverse cellular functions". Cell. 109 (2): 145–8. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00718-3. PMID 12007400. S2CID 8968788.
External links
| Small nucleolar SNORD12/SNORD106 | |
|---|---|
 Predicted
secondary structure and
sequence conservation of SNORD12 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SNORD12 |
| Alt. Symbols | SNORD106; snoHBII-99 |
| Rfam | RF00581 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; snRNA; snoRNA; C/D-box |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota |
| GO | GO:0006396 GO:0005730 |
| SO | SO:0000593 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
In molecular biology, the small nucleolar RNAs SNORD106 and SNORD12 (also known as U106 and HBII-99 respectively ) are two related snoRNAs which belongs to the C/D class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs). Both contain the conserved C (UGAUGA) and D (CUGA) box sequence motifs [1]
Human SNORD12 (HBII-99) is the homologue of mouse snoRNA MBII-99. In humans both HB11-99 and U106 snoRNAs share the same host gene. [2] [3]
Most of the members of the box C/D family function in directing site-specific 2'-O- methylation of substrate RNAs. HBII-99 is predicted to guide the 2'O-ribose methylation of 28S rRNA G3878. [4] U106 contains conserved antisense elements which would predict U106 methylates residues G1536 and U1602 of 18S rRNA. [5] However, these targets do not appear to be methylated and U106 might function as an RNA chaperone during rRNA folding. [2] A similar role has been suggested for the H/ACA snoRNAs U17a and U17b [2]
References
- ^ Vitali P, Royo H, Seitz H, Bachellerie JP, Hüttenhofer A, Cavaillé J (November 2003). "Identification of 13 novel human modification guide RNAs". Nucleic Acids Research. 31 (22): 6543–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg849. PMC 275545. PMID 14602913.
- ^ a b c Lestrade L, Weber MJ (January 2006). "snoRNA-LBME-db, a comprehensive database of human H/ACA and C/D box snoRNAs". Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (Database issue): D158-62. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.105.7552. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj002. PMC 1347365. PMID 16381836.
- ^ Askarian-Amiri ME, Crawford J, French JD, Smart CE, Smith MA, Clark MB, Ru K, Mercer TR, Thompson ER, Lakhani SR, Vargas AC, Campbell IG, Brown MA, Dinger ME, Mattick JS (May 2011). "SNORD-host RNA Zfas1 is a regulator of mammary development and a potential marker for breast cancer". RNA. 17 (5): 878–91. doi: 10.1261/rna.2528811. PMC 3078737. PMID 21460236.
- ^ Hüttenhofer A, Kiefmann M, Meier-Ewert S, O'Brien J, Lehrach H, Bachellerie JP, Brosius J (June 2001). "RNomics: an experimental approach that identifies 201 candidates for novel, small, non-messenger RNAs in mouse". The EMBO Journal. 20 (11): 2943–53. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.11.2943. PMC 125495. PMID 11387227.
- ^ Kiss T (April 2002). "Small nucleolar RNAs: an abundant group of noncoding RNAs with diverse cellular functions". Cell. 109 (2): 145–8. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00718-3. PMID 12007400. S2CID 8968788.
External links