| RNA recognition motif. (a.k.a. RRM, RBD, or RNP domain) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | RRM_1 | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00076 | ||||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0221 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000504 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00030 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1sxl / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
RNA recognition motif, RNP-1 is a putative RNA-binding domain of about 90 amino acids that are known to bind single-stranded RNAs. It was found in many eukaryotic proteins. [1] [2] [3]
The largest group of single strand RNA-binding protein is the eukaryotic RNA recognition motif (RRM) family that contains an eight amino acid RNP-1 consensus sequence. [4] [5]
RRM proteins have a variety of RNA binding preferences and functions, and include heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins ( hnRNPs), proteins implicated in regulation of alternative splicing (SR, U2AF2, Sxl), protein components of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (U1 and U2 snRNPs), and proteins that regulate RNA stability and translation ( PABP, La, Hu). [2] [3] [5] The RRM in heterodimeric splicing factor U2 snRNP auxiliary factor appears to have two RRM-like domains with specialised features for protein recognition. [6] The motif also appears in a few single stranded DNA binding proteins.
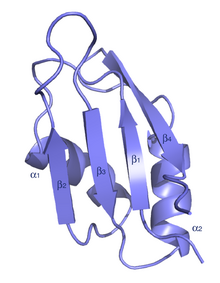
The typical RRM consists of four anti-parallel beta-strands and two alpha-helices arranged in a beta-alpha-beta-beta-alpha-beta fold with side chains that stack with RNA bases. A third helix is present during RNA binding in some cases. [7] The RRM is reviewed in a number of publications. [8] [9] [10]
A2BP1; ACF; BOLL; BRUNOL4; BRUNOL5; BRUNOL6; CCBL2; CGI-96; CIRBP; CNOT4; CPEB2; CPEB3; CPEB4; CPSF7; CSTF2; CSTF2T; CUGBP1; CUGBP2; D10S102; DAZ1; DAZ2; DAZ3; DAZ4; DAZAP1; DAZL; DNAJC17; DND1; EIF3S4; EIF3S9; EIF4B; EIF4H; ELAVL1; ELAVL2; ELAVL3; ELAVL4; ENOX1; ENOX2; EWSR1; FUS; FUSIP1; G3BP; G3BP1; G3BP2; GRSF1; HNRNPL; HNRPA0; HNRPA1; HNRPA2B1; HNRPA3; HNRPAB; HNRPC; HNRPCL1; HNRPD; HNRPDL; HNRPF; HNRPH1; HNRPH2; HNRPH3; HNRPL; HNRPLL; HNRPM; HNRPR; HRNBP1; HSU53209; HTATSF1; IGF2BP1; IGF2BP2; IGF2BP3; LARP7; MKI67IP; MSI1; MSI2; MSSP-2; MTHFSD; MYEF2; NCBP2; NCL; NOL8; NONO; P14; PABPC1; PABPC1L; PABPC3; PABPC4; PABPC5; PABPN1; POLDIP3; PPARGC1; PPARGC1A; PPARGC1B; PPIE; PPIL4; PPRC1; PSPC1; PTBP1; PTBP2; PUF60; RALY; RALYL; RAVER1; RAVER2; RBM10; RBM11; RBM12; RBM12B; RBM14; RBM15; RBM15B; RBM16; RBM17; RBM18; RBM19; RBM22; RBM23; RBM24; RBM25; RBM26; RBM27; RBM28; RBM3; RBM32B; RBM33; RBM34; RBM35A; RBM35B; RBM38; RBM39; RBM4; RBM41; RBM42; RBM44; RBM45; RBM46; RBM47; RBM4B; RBM5; RBM7; RBM8A; RBM9; RBMS1; RBMS2; RBMS3; RBMX; RBMX2; RBMXL2; RBMY1A1; RBMY1B; RBMY1E; RBMY1F; RBMY2FP; RBPMS; RBPMS2; RDBP; RNPC3; RNPC4; RNPS1; ROD1; SAFB; SAFB2; SART3; SETD1A; SF3B14; SF3B4; SFPQ; SFRS1; SFRS10; SFRS11; SFRS12; SFRS15; SFRS2; SFRS2B; SFRS3; SFRS4; SFRS5; SFRS6; SFRS7; SFRS9; SLIRP; SLTM; SNRP70; SNRPA; SNRPB2; SPEN; SR140; SRRP35; SSB; SYNCRIP; TAF15; TARDBP; THOC4; TIA1; TIAL1; TNRC4; TNRC6C; TRA2A; TRSPAP1; TUT1; U1SNRNPBP; U2AF1; U2AF2; UHMK1; ZCRB1; ZNF638; ZRSR1; ZRSR2;
- ^ Swanson MS, Dreyfuss G, Pinol-Roma S (1988). "Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and the pathway of mRNA formation". Trends Biochem. Sci. 13 (3): 86–91. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90046-1. PMID 3072706.
- ^ a b Keene JD, Chambers JC, Kenan D, Martin BJ (1988). "Genomic structure and amino acid sequence domains of the human La autoantigen". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (34): 18043–51. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)81321-2. PMID 3192525.
- ^ a b Davis RW, Sachs AB, Kornberg RD (1987). "A single domain of yeast poly(A)-binding protein is necessary and sufficient for RNA binding and cell viability". Mol. Cell. Biol. 7 (9): 3268–76. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3268. PMC 367964. PMID 3313012.
- ^ Bandziulis RJ, Swanson MS, Dreyfuss G (1989). "RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators". Genes Dev. 3 (4): 431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. PMID 2470643.
- ^ a b Keene JD, Query CC, Bentley RC (1989). "A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein". Cell. 57 (1): 89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-X. PMID 2467746. S2CID 22127152.
- ^ Green MR, Kielkopf CL, Lucke S (2004). "U2AF homology motifs: protein recognition in the RRM world". Genes Dev. 18 (13): 1513–1526. doi: 10.1101/gad.1206204. PMC 2043112. PMID 15231733.
- ^ Kumar S, Birney E, Krainer AR (1993). "Analysis of the RNA-recognition motif and RS and RGG domains: conservation in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing factors". Nucleic Acids Res. 21 (25): 5803–5816. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5803. PMC 310458. PMID 8290338.
- ^ Keene JD, Kenan DJ, Query CC (1991). "RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity". Trends Biochem. Sci. 16 (6): 214–20. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. PMID 1716386.
- ^ Allain FH, Dominguez C, Maris C (2005). "The RNA recognition motif, a plastic RNA-binding platform to regulate post-transcriptional gene expression". FEBS J. 272 (9): 2118–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04653.x. PMID 15853797. S2CID 46680279.
- ^ Teplova M, Yuan YR, Patel DJ, Malinina L, Teplov A, Phan AT, Ilin S (2006). "Structural basis for recognition and sequestration of UUU(OH) 3' temini of nascent RNA polymerase III transcripts by La, a rheumatic disease autoantigen". Mol. Cell. 21 (1): 75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.027. PMC 4689297. PMID 16387655.
- Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource motif class LIG_ULM_U2AF65_1

| RNA recognition motif. (a.k.a. RRM, RBD, or RNP domain) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | RRM_1 | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00076 | ||||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0221 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000504 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00030 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1sxl / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
RNA recognition motif, RNP-1 is a putative RNA-binding domain of about 90 amino acids that are known to bind single-stranded RNAs. It was found in many eukaryotic proteins. [1] [2] [3]
The largest group of single strand RNA-binding protein is the eukaryotic RNA recognition motif (RRM) family that contains an eight amino acid RNP-1 consensus sequence. [4] [5]
RRM proteins have a variety of RNA binding preferences and functions, and include heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins ( hnRNPs), proteins implicated in regulation of alternative splicing (SR, U2AF2, Sxl), protein components of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (U1 and U2 snRNPs), and proteins that regulate RNA stability and translation ( PABP, La, Hu). [2] [3] [5] The RRM in heterodimeric splicing factor U2 snRNP auxiliary factor appears to have two RRM-like domains with specialised features for protein recognition. [6] The motif also appears in a few single stranded DNA binding proteins.
The typical RRM consists of four anti-parallel beta-strands and two alpha-helices arranged in a beta-alpha-beta-beta-alpha-beta fold with side chains that stack with RNA bases. A third helix is present during RNA binding in some cases. [7] The RRM is reviewed in a number of publications. [8] [9] [10]
A2BP1; ACF; BOLL; BRUNOL4; BRUNOL5; BRUNOL6; CCBL2; CGI-96; CIRBP; CNOT4; CPEB2; CPEB3; CPEB4; CPSF7; CSTF2; CSTF2T; CUGBP1; CUGBP2; D10S102; DAZ1; DAZ2; DAZ3; DAZ4; DAZAP1; DAZL; DNAJC17; DND1; EIF3S4; EIF3S9; EIF4B; EIF4H; ELAVL1; ELAVL2; ELAVL3; ELAVL4; ENOX1; ENOX2; EWSR1; FUS; FUSIP1; G3BP; G3BP1; G3BP2; GRSF1; HNRNPL; HNRPA0; HNRPA1; HNRPA2B1; HNRPA3; HNRPAB; HNRPC; HNRPCL1; HNRPD; HNRPDL; HNRPF; HNRPH1; HNRPH2; HNRPH3; HNRPL; HNRPLL; HNRPM; HNRPR; HRNBP1; HSU53209; HTATSF1; IGF2BP1; IGF2BP2; IGF2BP3; LARP7; MKI67IP; MSI1; MSI2; MSSP-2; MTHFSD; MYEF2; NCBP2; NCL; NOL8; NONO; P14; PABPC1; PABPC1L; PABPC3; PABPC4; PABPC5; PABPN1; POLDIP3; PPARGC1; PPARGC1A; PPARGC1B; PPIE; PPIL4; PPRC1; PSPC1; PTBP1; PTBP2; PUF60; RALY; RALYL; RAVER1; RAVER2; RBM10; RBM11; RBM12; RBM12B; RBM14; RBM15; RBM15B; RBM16; RBM17; RBM18; RBM19; RBM22; RBM23; RBM24; RBM25; RBM26; RBM27; RBM28; RBM3; RBM32B; RBM33; RBM34; RBM35A; RBM35B; RBM38; RBM39; RBM4; RBM41; RBM42; RBM44; RBM45; RBM46; RBM47; RBM4B; RBM5; RBM7; RBM8A; RBM9; RBMS1; RBMS2; RBMS3; RBMX; RBMX2; RBMXL2; RBMY1A1; RBMY1B; RBMY1E; RBMY1F; RBMY2FP; RBPMS; RBPMS2; RDBP; RNPC3; RNPC4; RNPS1; ROD1; SAFB; SAFB2; SART3; SETD1A; SF3B14; SF3B4; SFPQ; SFRS1; SFRS10; SFRS11; SFRS12; SFRS15; SFRS2; SFRS2B; SFRS3; SFRS4; SFRS5; SFRS6; SFRS7; SFRS9; SLIRP; SLTM; SNRP70; SNRPA; SNRPB2; SPEN; SR140; SRRP35; SSB; SYNCRIP; TAF15; TARDBP; THOC4; TIA1; TIAL1; TNRC4; TNRC6C; TRA2A; TRSPAP1; TUT1; U1SNRNPBP; U2AF1; U2AF2; UHMK1; ZCRB1; ZNF638; ZRSR1; ZRSR2;
- ^ Swanson MS, Dreyfuss G, Pinol-Roma S (1988). "Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and the pathway of mRNA formation". Trends Biochem. Sci. 13 (3): 86–91. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90046-1. PMID 3072706.
- ^ a b Keene JD, Chambers JC, Kenan D, Martin BJ (1988). "Genomic structure and amino acid sequence domains of the human La autoantigen". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (34): 18043–51. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)81321-2. PMID 3192525.
- ^ a b Davis RW, Sachs AB, Kornberg RD (1987). "A single domain of yeast poly(A)-binding protein is necessary and sufficient for RNA binding and cell viability". Mol. Cell. Biol. 7 (9): 3268–76. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3268. PMC 367964. PMID 3313012.
- ^ Bandziulis RJ, Swanson MS, Dreyfuss G (1989). "RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators". Genes Dev. 3 (4): 431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. PMID 2470643.
- ^ a b Keene JD, Query CC, Bentley RC (1989). "A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein". Cell. 57 (1): 89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-X. PMID 2467746. S2CID 22127152.
- ^ Green MR, Kielkopf CL, Lucke S (2004). "U2AF homology motifs: protein recognition in the RRM world". Genes Dev. 18 (13): 1513–1526. doi: 10.1101/gad.1206204. PMC 2043112. PMID 15231733.
- ^ Kumar S, Birney E, Krainer AR (1993). "Analysis of the RNA-recognition motif and RS and RGG domains: conservation in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing factors". Nucleic Acids Res. 21 (25): 5803–5816. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5803. PMC 310458. PMID 8290338.
- ^ Keene JD, Kenan DJ, Query CC (1991). "RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity". Trends Biochem. Sci. 16 (6): 214–20. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. PMID 1716386.
- ^ Allain FH, Dominguez C, Maris C (2005). "The RNA recognition motif, a plastic RNA-binding platform to regulate post-transcriptional gene expression". FEBS J. 272 (9): 2118–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04653.x. PMID 15853797. S2CID 46680279.
- ^ Teplova M, Yuan YR, Patel DJ, Malinina L, Teplov A, Phan AT, Ilin S (2006). "Structural basis for recognition and sequestration of UUU(OH) 3' temini of nascent RNA polymerase III transcripts by La, a rheumatic disease autoantigen". Mol. Cell. 21 (1): 75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.027. PMC 4689297. PMID 16387655.
- Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource motif class LIG_ULM_U2AF65_1