| This is an archive of past discussions. Do not edit the contents of this page. If you wish to start a new discussion or revive an old one, please do so on the current talk page. |
| Archive 5 | ← | Archive 9 | Archive 10 | Archive 11 |
Date of index case?
There has been wikidiscussions on what is the established date of the Wuhan index case in mainstream scientific reports. The current version of the page does not include any information on the index case. Previous to this lack of information the article said the index case emerged on Dec 1 2020, based on a a non-ideal RS (a book from a non-specialist that tangentially deals with the index case). The "Dec 1"-source was dicussed here, where I reasonably argued that it was a weak source with a consensus that it was not ideal.
There are two MEDRS that say the index case happened on Dec 8 2020, which coincidentally is a late date that goes against the lab leak hypothesis (I've been accused of POV editing and this edit is a counterexample). The MEDRS are Hu et al (2020), and the WHO report. RandomCanadian please stop disrupting the inclusion of this fact, there are DS sanctions in place for this page, I believe you are aware of them. I propose we use this two MEDRS supplemented by citing also the Washington post recent article on it, as long as it goes in the same direction and MEDRS does allow to cite RS along MEDRS in this case.
Forich (
talk) 20:15, 9 July 2021 (UTC)
- There is considerable disagreement among experts in MEDRSes about this December index case, and some
agreementMEDRSes suggest that there likely is no single index case. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] The considerable pre-Huanan seafood market circulation of the virus in Wuhan, and the existence of the A and B variant clades, both point to multiple introductions of the virus into the human population. See also this very illuminating episode of This Week in Virology, which reviews much of this evidence. (Episode mp3 and transcript). The good stuff starts around 18 minutes in.-- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 21:02, 9 July 2021 (UTC)(edited 03:48, 10 July 2021 (UTC)) - Forich: the WaPo (the one source you cited - and to which you attributed the statement -
not my job to go hunting through the other ones) is not a MEDRS, so I don`t see why you`re objecting to me removing it and content based on it (if you're referring to my recent edit - otherwise I have no clue what it could be) and then arguing for including content based on MEDRS (I note that there doesn't appear to be a consensus amongst these that the index case happened on 8 December - in fact, the more recent ones seems to argue it happened at least a couple of weeks earlier, and that it likely hasn't been identified yet). I note that the
COVID-19 pandemic section already seems to have all the relevant information for that aspect, we should maybe copy and expand from there.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 02:44, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- @
Shibboleth:, I believe we have a miscommunication here and I'd like to invite you to read again the definition of
index case. It is by definition the first documented patient. With key emphasis on documented. It need not coincide with the person where the spillover event happened, which may be what the evidence you are citing seem to be referring to. I have further comments, but they may not matter if the source of our disagreement is semantic.
Forich (
talk) 20:41, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- @
RandomCanadian:, I am sorry you are absolutely right, your removal is not a violation of any rules and seems reasonably well-explained. I will strikethrough your name and I apologize again. I'll need to check the history to see who was the editor reverting all those edits, they do deserve a warning not you.
Forich (
talk) 20:46, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- Hi, Forich, you don't need to explain to me what an index case is. The sources I provided above demonstrate there is controversy about the first documented case of SARS-COV-2, and indeed one of the provided sources points to the December 1st case, which has no association with the wet market. I believe this controversy about which case Dec 1st or 8th or an earlier November case of an elderly man in the outer province (I believe first reported in the SCMP) counts as "Patient Zero" is why we basically have three options:
- @
RandomCanadian:, I am sorry you are absolutely right, your removal is not a violation of any rules and seems reasonably well-explained. I will strikethrough your name and I apologize again. I'll need to check the history to see who was the editor reverting all those edits, they do deserve a warning not you.
Forich (
talk) 20:46, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- @
Shibboleth:, I believe we have a miscommunication here and I'd like to invite you to read again the definition of
index case. It is by definition the first documented patient. With key emphasis on documented. It need not coincide with the person where the spillover event happened, which may be what the evidence you are citing seem to be referring to. I have further comments, but they may not matter if the source of our disagreement is semantic.
Forich (
talk) 20:41, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- There is considerable disagreement among experts in MEDRSes about this December index case, and some
- A) Declare an index case, disregarding the entire controversy.
- B) Report the entirety of this controversy, weighted as it is in secondary RSes and MEDRSes. With appropriate wording "purported" "claimed" etc. Per WP:RSUW. We kinda already do this in the Epidemiology section of this article, I just noticed. And I think it's actually done quite well.
- C) Wait for the dust to settle a bit more, and for more serology/blood sample PCRs to be described in the literature that help establish if there was an earlier index case. In the meantime, remove all the current coverage of it that we have, and don't add any more. Per WP:RECENTISM.
- Personally I vote for Option B. It would be inappropriate for us to remove the coverage we have, but I think it would also be inappropriate for us to "declare" an index case when we know controversy exists.-- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 17:06, 11 July 2021 (UTC)
- I have read again all the sources you provided (primary sources, not MEDRS, btw) and none of them suggest controversy on the first documented case, ergo, index case in Wuhan. They do suggest controversy on the date of first cases, plainly, which are currently undocumented (unfortunately). If my interpretation of no controversy on index case is true, your proposals, as they are now, are out of place. If we are to slightly modify them to make more sense with de index/documented/undocumented terminology, it would be something like this:
- A) Declare that the exact or approximate date of the first case is known, disregarding the entire controversy.
- B) Report the entirety of this controversy, weighted as it is in secondary RSes and MEDRSes. With appropriate wording "purported" "claimed" etc. Per WP:RSUW. We kinda already do this in the Epidemiology section of this article, I just noticed. And I think it's actually done quite well.
- C) Wait for the dust to settle a bit more, and for more serology/blood sample PCRs to be described in the literature that help establish if there was an earlier first case. In the meantime, remove all the current coverage of it that we have, and don't add any more. Per WP:RECENTISM.
- I'd propose option D): describe what the currently earliest known cases are ("earliest known" is not the same thing as "index" case), attributing uncertainty and doubts about these where necessary, and adding that the scientific literature currently suggests that the real index case (which likely isn't known at this time) was at some point between October and November 2019. Or, basically, take the following from COVID-19 pandemic#Epidemiology:
The earliest known person with symptoms was later discovered to have fallen ill on 1 December 2019, and that person did not have visible connections with the later wet market cluster.[43][44] However, an earlier case of infection could have occurred on 17 November.[45] Of the early cluster of cases reported that month, two-thirds were found to have a link with the market.[46][47][48] Molecular clock analysis suggests that the index case is likely to have been infected with the virus between mid-October and mid-November 2019.[49][50]
- And expand as needed to cover more detail. This will also help updating in the other direction (back into the pandemic article) once we've ironed it out here. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:55, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- Option B. And I think we could slightly modify what
Shibbolethink said above and just use that in the article. He provided citations and everything.
There is considerable disagreement among experts in MEDRSes about this December index case, and some agreement MEDRSes suggest that there likely is no single index case.[1][2][3][4][5][6] The considerable pre-Huanan seafood market circulation of the virus in Wuhan, and the existence of the A and B variant clades, both point to multiple introductions of the virus into the human population.
– Novem Linguae ( talk) 02:10, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
TWIV transcript on date of index case
The following text is from a podcast (This Week in Virology #760, may 26th 2021) with three members of the WHO team.
-Marion Koopmans: "a lot of the work tried, the epi work, really aimed at trying to dig back, so what was the earliest case, that is recognized. That was the process. Now the earliest confirmed recognized case is a person that survived, a person that we also met, but the epi work suggest that there have been many more cases that have not been recognized, there is also no sequence data for those. And that's part of the digging back that you would want to do."
-Rich Kondit: "So what were the earliest cases and to what extent or not do they have any association with the market?"
-Thea Kolsen Fischer: "So the first, the earliest now recognized case had an onset date of December 8th with no contact with neither the Huanan wet market or other markets. The closest kind of market contact was a mother who had cooked for the [first] case and who has bought some of her cooking ingredients at an unnamed market. But the [first] person had no contact with markets."
The WHO report, our best source on the matter, says there were three alleged cases from befor Dec 8th, but they qualify them as "excludable on the basis of the clinical features of their illnesses".
So according to this information, again, the best source we have, a tweaked version that follows the one from RandomCanadian would look like:
The earliest known person with symptoms was later discovered to have fallen ill on
18 December 2019, and that person did not have visible connections with the later wet market cluster. However,anat leastonethree earlier cases of infection could have occurred before the 8th of december. Of the early cluster of cases reported that month, two-thirds were found to have a link with the market. Molecular clock analysis suggests that the index case is likely to have been infected with the virus between mid-October and mid-November 2019
Forich ( talk) 21:18, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- @ Forich: What about just dropping the precise dates? That seems wiser than documenting a controversy over whether the first known case was on the 1st or the 8th of December, which, 1 1/2 year after the events in question, doesn't seem a particularly important, encyclopedic distinction. So:
The earliest known person with symptoms was later discovered to have fallen ill in early December 2019, and that person did not have visible connections with the later wet market cluster. However, a few earlier cases of infection could have occurred.[45] Of the early cluster of cases reported that month, two-thirds were found to have a link with the market.[46][47][48] Molecular clock analysis suggests that the index case is likely to have been infected with the virus between mid-October and mid-November 2019.[49][50]
- And then we can work on expanding that here with more details where/if needed. Also, I note that MEDRS is not required for everything. A newspaper (with attribution, if necessary) is enough to say "there were reports of earlier cases", although we should then use proper SCHOLARSHIP to determine how to describe those reports RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:43, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
- @ RandomCanadian:, I can see how that is reasonable if there actually was a controversy on the documented earliest case. But in MEDRS, there is no controversy on that, just the uncertainty of earlier undocumented cases from the molecular clock start-date. Here is the temporal sequence of the coverage of the earliest known case:
- The Lancet article said the first patient presented an onset of symptoms on Dec 1st (not MEDRS). The point of having a MEDRS check the facts on a primary source is to have more solid confirmation that the basic fact holds when scrutinized by a second set of expert eyes.
- Sciencemag news report verbatim the result from Lancet on Dec 1. Neither are MEDRS.
- A SCMP reporter alleged having seen in government reports a Nov 17th case. Not MEDRS. If we had no MEDRS, I'd go for an attributed inclusion of this, for sure. But we have MEDRS that say different.
- Allam (2020), admittedly doing a better job than Sciencemag and SCMP, documents the Dec 1st from Lancet together with the alleged Nov case from SCMP. But, still he is not an expert, he is an architect who wrote a non-MEDRS book about the political economy of the pandemic, and the first chapter included a timeline of events as a preface to the main chapters of the book. He is not qualified to say, for example, whether the Dec 1st case symptoms were from a coincidental flu or from COVID-19. The publisher is very reputable (Elsevier) so we can use the facts from the main subject of the book (political economy of the pandemic) in Wikipedia, not the tangential time of the earliest case that he researched
- The WHO report comes out, saying that the first confirmed case had onset of symptoms on Dec 8th, clarifies that the Dec 1st case was excluded "on the basis of the clinical features of its illness". The experts from the WHO-team (maybe the international members, we don't know) took a closer look at the Dec 1st case and said that he was determined to have suffered other illness in early December, contracting the coronavirus later that month with his wife in a family cluster. This is an important correction that leaves no space for controversy, until another MEDRS challenges it.
- By saying that Dec 8th was the earliest known case, inserted in a paragraph with the whole context, I believe we are good. Should the paragraph include the SMCP allegation? Only if it gets repeated in a MEDRS. Allam repeated it, but I don't consider it a MEDRS for the reasons stated already. The WHO team was probably aware of the SCMP allegations when they investigated the early cases in Wuhan, and after having contrasted notes and corroborated sequences and paperwork with the Chinese members, they did not include the SCMP Nov case as a confirmed one. I don't see why we should not trust them on that conclusion.
- On your point that we can use Bryner, 2020; Davidson, 2020, the sources cited in Allam (2020), I don't know them, but of course we can check them out. I'll try to do it if I find the time later.
Forich (
talk) 21:39, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
- This recent-ish paper (primary for its results, but secondary for the "Introduction" section) states that
- On your point that we can use Bryner, 2020; Davidson, 2020, the sources cited in Allam (2020), I don't know them, but of course we can check them out. I'll try to do it if I find the time later.
Forich (
talk) 21:39, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
"Uncertainty still persists around the origin of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the resulting COVID-19 disease. While an origin as a zoonotic spillover in the Huanan Seafood Market, Wuhan, sometime during early December, 2019, has been proposed [1], this has been called into question [2–4]. This uncertainty arises due to both the presence of earlier potential COVID-19 cases, and the fact that most phylogenetic analyses put the most recent ancestor at between mid-November and early December, 2019 [5].
- So the earlier cases are "potential". I say "recent-ish" 'cause the paper was submitted for publication back in September last year, well before the WHO report. @
Shibbolethink: Is such a long delay unusual? The paper does seem to have been picked up by the news, ex.
[1]
[2]. Whether that is a good or bad thing
is another question...
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 02:59, 21 July 2021 (UTC)
- RandomCanadian, I would say....no not that unusual, especially for PLOS Pathogens.
- The higher in impact you go, the longer the review process. And PLOS Pathogens in the medium-to-high range as far as topic-specific virology journals go at ~6. Anecdotally, the Zika paper we published in Science during grad school was submitted in the middle of November of one year and accepted in the middle of March of the next [3], and that was considered "fast."
- This study by Huisman and Smits in 2017 [4] says around 85-90% of natural science/medicine papers are accepted by about 6 months post-submission.
- So I would say Roberts et al (that PLOS Path paper) is on the long end of normal. I bolded "accepted" because that's what really matters. It's kind of irrelevant when they "fit" the paper into their publication queue, that's all on the paper's logistics re: how many papers they fit into each "issue" and how overworked the layout staff are. Roberts et al submitted at the end of September of 2020 and got accepted at the beginning of May 2021. So around 7 months.
- That could easily be explained by a persnickety or delinquent reviewer who sat on the paper too long, while frantically working on their own pandemic-relevant work, or an editor who wanted to wait and see how other similar research shook out before finally saying "yes"... Like I said, long end of normal. If you showed me a paper that took more than a year, I would be more concerned. But also could mean that paper is even more squeaky clean after even closer eyes.
- But overall I think this is a good paper worth using for this purpose, in their intro and their findings eventually when/if they get cited by reviews. In their intro, they cite many of the same sources that we have discussed re: November spread of the virus ( [5] [6] [7]) and, importantly, this paper has also been covered in a few news-based RSes in its few weeks of existence, lending credibility to it as, at the very least, likely not a maligned or fringe viewpoint ( [8] [9] [10] (newsweek))
- I don't think this should be our only source for this, but I think in the context of the other sources discussed, it does start to mount for the inclusion of a sentence on "early pre-market spread" in my opinion...-- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 03:48, 21 July 2021 (UTC)
- So the earlier cases are "potential". I say "recent-ish" 'cause the paper was submitted for publication back in September last year, well before the WHO report. @
Shibbolethink: Is such a long delay unusual? The paper does seem to have been picked up by the news, ex.
[1]
[2]. Whether that is a good or bad thing
is another question...
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 02:59, 21 July 2021 (UTC)
The Sciencemag news extract
The paper, written by a large group of Chinese researchers from several institutions, offers details about the first 41 hospitalized patients who had confirmed infections with what has been dubbed 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). In the earliest case, the patient became ill on 1 December 2019 and had no reported link to the seafood market, the authors report. “No epidemiological link was found between the first patient and later cases,” they state. Their data also show that, in total, 13 of the 41 cases had no link to the marketplace. “That’s a big number, 13, with no link,” says Daniel Lucey, an infectious disease specialist at Georgetown University.
This is not MEDRS. Forich ( talk) 21:20, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- This is a lay-summary of this, which wasn't particularly hard to find - so we can cite both. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:43, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
The SCMP extract
According to the government data seen by the Post, a 55 year-old from Hubei province could have been the first person to have contracted Covid-19 on November 17. From that date onwards, one to five new cases were reported each day. By December 15, the total number of infections stood at 27 – the first double-digit daily rise was reported on December 17 – and by December 20, the total number of confirmed cases had reached 60.
SCMP is not MEDRS. Forich ( talk) 21:32, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- See my post above about not requiring MEDRS for everything. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:43, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
The Allam (2020) book chapter
The earliest date of symptoms for COVID-19, according to a study performed by Huang et al. (2020) and published in the Lancet journal, was December 1, 2019. However, there are other sources (Bryner, 2020; Davidson, 2020) claiming that individuals with similar symptoms may have presented themselves to hospital as early as November. According to the report, by South China Morning Post (Ma, 2020), the first person who presented similar cases was a male patient of 55-year old from the province of Hubei. However, Chinese doctors only came to realize that they were dealing with a new and serious virus late December, when similar symptoms continued to increase every day, and mostly originating from Wuhan. According to the article in Lancet, the first patient, and whom they insist may be the first case, was reported on December 1, 2019, and whom did not have direct link with the Wuhan Seafood Market that has been associated with the origin of the virus. This finding interestingly matches with Ma (2020) who also argues that the November 2019 case was not from Wuhan. The story as to the origin of the virus has fueled much political and social divides and is expected to evolve as further efforts are poured into understanding this crisis.
This source is not a MEDRS because Zaheer Allam, the author of the chapter and book, is an architect that specializes in political economy. He is neither a virologist nor an epidemiologist. The book itself is about the political economy of the pandemic. Forich ( talk) 21:37, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- What about using the sources given by Allam? The full chapter is here, with refs at the bottom. I note that, despite misgivings about the author's credentials, he seems to have done a decent enough job: "The earliest date of symptoms for COVID-19, according to a study performed by Huang et al. (2020) and published in the Lancet journal, was December 1, 2019. However, there are other sources (Bryner, 2020, Davidson, 2020) claiming that individuals with similar symptoms may have presented themselves to hospital as early as November." isn't that different from our current wording, either. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:43, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
I just went WP:Bold and fixed the information. The burden is on editors trying to use different information or with a history of reverting my edit (@ RandomCanadian:, @ Shibbolethink:, @ Alexbrn:) to find MEDRS sources, otherwise please abstain from reverting. Forich ( talk) 21:33, 26 July 2021 (UTC)
- The burden is on those making a change to get consensus for it, per WP:ONUS. Or, as in this case, where the "D" part of BRD appears to have stalled, there's no reason to get stuck in it, and we can just keep making bold edits, assuming that they will not be the final version, until we get to a satisfactory conclusion for everyone. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 00:37, 27 July 2021 (UTC)
- Our current information, which speaks of early cases that pre-date the official Chinese date of 8th December, I believe favors the lab leak a bit, because it puts a stab on one of the alternatives (the Huanan Seafood Market hypothesis). I tried my best to fix the date (I must have tried 10 attempts, including talk page interactions) with no successs, and I guess the Bold, Edit, Discuss cycle has led to this equilibrium of vagueness ("early December" can be anything between 1 to 14). RandomCanadian has answered to an inquiry in his User talk page that he is not cherry picking his uses of MEDRS so I am gonna have to trust him and let this discussion go. We can archive this discussion any time now.
Forich (
talk) 20:31, 5 August 2021 (UTC)
- I think that's a stretch, and would require an RS to back up. Got one? Because we've got other RS that make no link between earlier circulation and the WIV. Bakkster Man ( talk) 21:16, 5 August 2021 (UTC)
- Our current information, which speaks of early cases that pre-date the official Chinese date of 8th December, I believe favors the lab leak a bit, because it puts a stab on one of the alternatives (the Huanan Seafood Market hypothesis). I tried my best to fix the date (I must have tried 10 attempts, including talk page interactions) with no successs, and I guess the Bold, Edit, Discuss cycle has led to this equilibrium of vagueness ("early December" can be anything between 1 to 14). RandomCanadian has answered to an inquiry in his User talk page that he is not cherry picking his uses of MEDRS so I am gonna have to trust him and let this discussion go. We can archive this discussion any time now.
Forich (
talk) 20:31, 5 August 2021 (UTC)
Sources
|
|---|
|
- Not sure why I was pinged here, the proposed source seems unproblematic. What I think we need to avoid is exceptional/fringe claims that the virus was at large in Italy/California/wherever much earlier, and/or that CV19 is just a rebranding of an existing prior disease. Alexbrn ( talk) 02:33, 27 July 2021 (UTC)
- @ Alexbrn:, In your edit comment for your revert of March 29 of 2021 you said: "Rvt. primary research; would need WP:MEDRS" The diff is here, it seems you opposed Pekar et al (2021) then, and now you find it unproblematic. Maybe you made a mistake back then? Forich ( talk) 19:11, 6 August 2021 (UTC)
FCS
FCS : furin-like cleavage site -- 92.184.104.9 ( talk) 18:18, 7 August 2021 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 12 August 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Please add Template:Outdated to the "Infection and transmission" section. It reports only 2020 information. The idea of aerosol transmission is presented as not-yet-confirmed. There are 47 citations before the start of the "Reinfection" subsection: 1 dates from 2010, 41 date from 2020, and just 5 date from 2021. And of those 5, 2 are a case study of a specific person, 1 talks about animals that can get infected, and 2 talk about particles emitted during talking. Most or all items in this section should be relying on 2021 data, because the science is getting updated so fast through extensive research. 174.206.39.24 ( talk) 11:15, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
 Done. will do, but I will also say that these statements probably need better
WP:MEDRS, as "etiology" is explicitly covered under
WP:BMI. To be plain, the statements may require a higher level of sourcing commiserate with scientific journal review articles published in topic-relevant venues. We may not be able to move as fast as the science does as a result. Of course this also means some of these sentences are definitely poorly sourced as it is, even the ones from the past. Appreciate you pointing this out, thank you.--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:55, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
Done. will do, but I will also say that these statements probably need better
WP:MEDRS, as "etiology" is explicitly covered under
WP:BMI. To be plain, the statements may require a higher level of sourcing commiserate with scientific journal review articles published in topic-relevant venues. We may not be able to move as fast as the science does as a result. Of course this also means some of these sentences are definitely poorly sourced as it is, even the ones from the past. Appreciate you pointing this out, thank you.--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:55, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
here are some links to find high quality MEDRS about this topic (SARS-CoV-2 transmission): Find medical sources: Source guidelines · PubMed · Cochrane · DOAJ · Gale · OpenMD · ScienceDirect · Springer · Trip · Wiley · TWL -- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 23:06, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
Typo "Demark"
I'm sorry, if I'm using the talk page the wrong way, but since the article is protected and I couldn't make the edit myself, I would appreciate it, if an experienced member could just fix this little typo.
It's really self-explanatory, there's just a missing "n" in "Demark" that needs to be added. It's in the last sentence of the paragraph in chapter 4.1.1 (Phylogenetics -> Variants).
Thank you very much!
XLix ( talk) 22:18, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
-
 Fixed. thanks--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 22:20, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
Fixed. thanks--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 22:20, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
First paragraph in Epidemiology section
The first paragraph in the Epidemiology section is a near-duplicate to the previous paragraph (in the previous section). I believe it should be removed.— Preceding unsigned comment added by WhamboMPS ( talk • contribs) 15:27, 28 August 2021 (UTC)
Typo in "Epidemiology" section
The "epidemiology" section start with "xVery few drugs" (erroneous "x") Technicolour-dreamboat ( talk) 12:09, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
 Done. Thanks for the heads up.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 18:55, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
Done. Thanks for the heads up.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 18:55, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
Featured picture scheduled for POTD
Hello! This is to let editors know that the featured picture File:Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.jpg, which is used in this article, has been selected as the English Wikipedia's picture of the day (POTD) for September 3, 2021. A preview of the POTD is displayed below and can be edited at Template:POTD/2021-09-03. For the greater benefit of readers, any potential improvements or maintenance that could benefit the quality of this article should be done before its scheduled appearance on the Main Page. If you have any concerns, please place a message at Wikipedia talk:Picture of the day. Thank you! Cwmhiraeth ( talk) 09:45, 20 August 2021 (UTC)
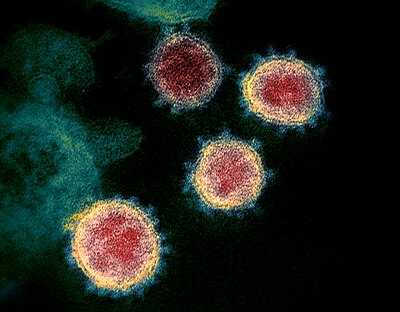
|
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is the virus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Like other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 has four structural proteins, known by the letters S ( spike), E ( envelope), M ( membrane), and N ( nucleocapsid); the N protein holds the RNA genome, and the S, E, and M proteins together create the viral envelope. This colourised transmission electron micrograph shows SARS-CoV-2 virus particles emerging from the surface of cells cultured in a laboratory. The crown-like spikes on the outer edge of the virus particles give coronaviruses their name, derived from Latin corona, 'crown'. Photograph credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Rocky Mountain Laboratories
Recently featured:
|
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 9 September 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
In the lead, replace Virus with Emergent virus. 79.70.190.198 ( talk) 08:30, 9 September 2021 (UTC)
 Not done for now: please establish a
consensus for this alteration
before using the
Not done for now: please establish a
consensus for this alteration
before using the {{ edit extended-protected}}template. I think it's better to link to the actual virus article. ScottishFinnishRadish ( talk) 13:35, 9 September 2021 (UTC)
Global Viral Mass
AFAIK there have been no estimations of the global viral mass of SARS‑CoV‑2, or the mass of a single virion for that matter. What are we dealing with here, a few kilos or what? kencf0618 ( talk) 03:39, 6 September 2021 (UTC)
- There is this estimation, but I'm unsure how relevant and meaningful the estimate is for the article. Bakkster Man ( talk) 14:45, 7 September 2021 (UTC)
References
- ^ "The total number and mass of SARS-CoV-2 virions". www.pnas.org. National Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 29 September 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
X... Coronaviruses infect humans, other mammals, and avian species, including livestock and companion animals.
Y... Coronaviruses infect humans, other mammals, including livestock and companion animals, and avian species.
NOTE: This is a trivial edit. The string 'livestock and companion animals' relates to 'other mammals', not 'avian species'. Cheers. Kevbo ( talk) 04:09, 29 September 2021 (UTC)
 Done
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 10:53, 29 September 2021 (UTC)
Done
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 10:53, 29 September 2021 (UTC)
The Laos' bats pre print
Why are we allowing the use of the Laos bats preprint? It was inserted in this edit . I suggest we remove it until it passes peer review. Forich ( talk) 04:43, 9 October 2021 (UTC)
- I agree, we need to at least wait for it to be peer reviewed, if not waiting for a secondary source. Bakkster Man ( talk) 12:17, 9 October 2021 (UTC)
- Yes I would agree. Although we do already have secondary sources about this: [11] (among others). I would just rather wait for the PRIMARY to be peer reviewed before jumping to use any secondary sources. The good news is that it's under consideration and likely fast tracked at a Nature-family journal, so this interim shouldn't last long. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 17:57, 9 October 2021 (UTC)
Mad props to all contributors
I love how roughly half the length of this article comprises carefully cited and documented references. Thank you to everyone who has contributed to this article; every Wikipedia article should be this good — PowerPCG5 ( talk) 09:35, 12 October 2021 (UTC)
Wiki link to viral shedding
This
edit request has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
In the second paragraph of the section titled “Infection and transmission,” please make the text “RNA shedding” into a wiki link that points to Viral shedding.
Tylercrompton ( talk) 23:50, 11 October 2021 (UTC)
 Done
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 10:50, 12 October 2021 (UTC)
Done
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 10:50, 12 October 2021 (UTC)
NIH grant
I'm not an expert on this subject, so I cannot judge the completeness and veracity of this report from the US government itself. I leave it to others to decide if a digest of this should be included in the article, or if a footnote should be added.
The expert summary by a geneticist: https://merogenomics.ca/blog/en/145/Understanding-the-Risk-of-Bat-Coronavirus-Emergence-a-Merogenomics-NIH-grant-review
The actual documents from the NIH: https://www.documentcloud.org/documents/21055989-understanding-risk-bat-coronavirus-emergence-grant-notice access seems faster here: https://s3.documentcloud.org/documents/21055989/understanding-risk-bat-coronavirus-emergence-grant-notice.pdf
The actual document is 528 pages, but you can start by doing a search for the 24 occurrences of hACE2, reading the accompanying paragraphs, and seeing if you feel it worth your time to delve deeper.
My understanding is that, if true, the USA's NIH sponsored contractor EcoHealth and its principal investigator Dr. Peter Daszak to create versions of bat corona viruses that can infect cells via human ACE2 receptors (hACE2 receptors). This was an outgrowth of an innocent experiment to see if there were wild bat corona viruses that can infect humans.
The hACE2 work was apparently done in Wuhan, China.
Presumably the release was totally accidental. (Possibly, the lab was certified as BCL3 instead of BCL4, as it should have been for airborne viruses lethal to humans.)
I'm not an expert on this subject, so I cannot judge the completeness and veracity of this report from the US government itself. I leave it to others to decide if a digest of this should be included in the article, or if a footnote should be added. — Preceding unsigned comment added by 2604:3D09:A57B:9870:C550:BE5:2934:91E7 ( talk) 05:07, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
- 1) we do not write encyclopedia articles based on primary sources (such as opinion blogs or grant requests) 2) This is clearly the grant referred to here ("The alliance's grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, titled "Understanding the risk of bat coronavirus emergence," was launched in 2014 and renewed for 5 years in 2019 after receiving an outstanding peer-review score. "); and clearly it's nothing new, and the section title is misleading. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 05:14, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
Note below diagram is wrong.
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
The diagram depicting the structure of SARS-COVID-19 has an error in the note beneath the diagram. It claims the picture is an “atom”. It is a virus made of molecules. 2600:100C:B017:9372:C27:BC92:5330:9DE3 ( talk) 13:00, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
 Not done That is a 3D model based on the location of atoms in crystallography/spectroscopy. It does not claim the picture is of an atom, it claims that each sphere in the model is an atom.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 13:13, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
Not done That is a 3D model based on the location of atoms in crystallography/spectroscopy. It does not claim the picture is of an atom, it claims that each sphere in the model is an atom.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 13:13, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
Banal preprint is still being used
I see we are still quoting directly from the research square preprint of the BANAL strains found in Laos. This was discussed in previous archived threads of this talk page, and several editors agreed that it was best to pause any mention of the information from the preprint until and if the paper passes peer review properly. The diff that uses the preprint is this one. By the way I could not verify the 96.8% figure anywhere in the preprint, so it means that we are incurring in two breaches of policy here by allowing that sentence. Forich ( talk) 04:31, 28 October 2021 (UTC)
- Agreed, the BANAL information should be removed pending peer review. Unfortunately, it's a fair number of diffs to remove it (including the phylogenetic tree), but I'll take a look as I have opportunity. Anyone else available should feel free as well. Bakkster Man ( talk) 13:49, 28 October 2021 (UTC)
COVID Moonshot
Would it be appropriate to mention COVID Moonshot in the "Treatment and drug development" section? I just released a Wikipedia article on the initiative: They are particularly interesting as an alternative (international collaborative crowd-sourced open-science open data no patents) approach to drug development, but they aren't yet doing clinical trials. I was thinking of something like the following, if it is acceptable to mention them. -- MaryMO (AR) ( talk) 20:11, 5 November 2021 (UTC)
- COVID Moonshot is an international collaborative open-science project started in March 2020 with the goal of developing an un- patented oral antiviral drug for treatment of SARS-CoV-2. [1]
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 12 August 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Please add Template:Outdated to the "Infection and transmission" section. It reports only 2020 information. The idea of aerosol transmission is presented as not-yet-confirmed. There are 47 citations before the start of the "Reinfection" subsection: 1 dates from 2010, 41 date from 2020, and just 5 date from 2021. And of those 5, 2 are a case study of a specific person, 1 talks about animals that can get infected, and 2 talk about particles emitted during talking. Most or all items in this section should be relying on 2021 data, because the science is getting updated so fast through extensive research. 174.206.39.24 ( talk) 11:15, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
 Done. will do, but I will also say that these statements probably need better
WP:MEDRS, as "etiology" is explicitly covered under
WP:BMI. To be plain, the statements may require a higher level of sourcing commiserate with scientific journal review articles published in topic-relevant venues. We may not be able to move as fast as the science does as a result. Of course this also means some of these sentences are definitely poorly sourced as it is, even the ones from the past. Appreciate you pointing this out, thank you.--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:55, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
Done. will do, but I will also say that these statements probably need better
WP:MEDRS, as "etiology" is explicitly covered under
WP:BMI. To be plain, the statements may require a higher level of sourcing commiserate with scientific journal review articles published in topic-relevant venues. We may not be able to move as fast as the science does as a result. Of course this also means some of these sentences are definitely poorly sourced as it is, even the ones from the past. Appreciate you pointing this out, thank you.--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:55, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
here are some links to find high quality MEDRS about this topic (SARS-CoV-2 transmission): Find medical sources: Source guidelines · PubMed · Cochrane · DOAJ · Gale · OpenMD · ScienceDirect · Springer · Trip · Wiley · TWL -- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 23:06, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
Typo "Demark"
I'm sorry, if I'm using the talk page the wrong way, but since the article is protected and I couldn't make the edit myself, I would appreciate it, if an experienced member could just fix this little typo.
It's really self-explanatory, there's just a missing "n" in "Demark" that needs to be added. It's in the last sentence of the paragraph in chapter 4.1.1 (Phylogenetics -> Variants).
Thank you very much!
XLix ( talk) 22:18, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
-
 Fixed. thanks--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 22:20, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
Fixed. thanks--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 22:20, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
Featured picture scheduled for POTD
Hello! This is to let editors know that the featured picture File:Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.jpg, which is used in this article, has been selected as the English Wikipedia's picture of the day (POTD) for September 3, 2021. A preview of the POTD is displayed below and can be edited at Template:POTD/2021-09-03. For the greater benefit of readers, any potential improvements or maintenance that could benefit the quality of this article should be done before its scheduled appearance on the Main Page. If you have any concerns, please place a message at Wikipedia talk:Picture of the day. Thank you! Cwmhiraeth ( talk) 09:45, 20 August 2021 (UTC)

|
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is the virus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Like other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 has four structural proteins, known by the letters S ( spike), E ( envelope), M ( membrane), and N ( nucleocapsid); the N protein holds the RNA genome, and the S, E, and M proteins together create the viral envelope. This colourised transmission electron micrograph shows SARS-CoV-2 virus particles emerging from the surface of cells cultured in a laboratory. The crown-like spikes on the outer edge of the virus particles give coronaviruses their name, derived from Latin corona, 'crown'. Photograph credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Rocky Mountain Laboratories
Recently featured:
|
Typo in "Epidemiology" section
The "epidemiology" section start with "xVery few drugs" (erroneous "x") Technicolour-dreamboat ( talk) 12:09, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
 Done. Thanks for the heads up.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 18:55, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
Done. Thanks for the heads up.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 18:55, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
Global Viral Mass
AFAIK there have been no estimations of the global viral mass of SARS‑CoV‑2, or the mass of a single virion for that matter. What are we dealing with here, a few kilos or what? kencf0618 ( talk) 03:39, 6 September 2021 (UTC)
- There is this estimation, but I'm unsure how relevant and meaningful the estimate is for the article. Bakkster Man ( talk) 14:45, 7 September 2021 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 9 September 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
In the lead, replace Virus with Emergent virus. 79.70.190.198 ( talk) 08:30, 9 September 2021 (UTC)
 Not done for now: please establish a
consensus for this alteration
before using the
Not done for now: please establish a
consensus for this alteration
before using the {{ edit extended-protected}}template. I think it's better to link to the actual virus article. ScottishFinnishRadish ( talk) 13:35, 9 September 2021 (UTC)
Higher mortality risk for COVID survivors?
NEWS (3 December 2021): Apparently - there's a significantly *higher mortality risk* for COVID survivors after 1-year of onset. [2] [3] - QUESTION: Worth considering for the main article? - in any case - Stay Safe and Healthy !! - Drbogdan ( talk) 18:45, 3 December 2021 (UTC)
References
- ^ Whipple, Tom (October 23, 2021). "Moonshot is the spanner in the Covid-19 works the country needs". The Times. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ Flynn, Hannah (3 December 2021). "COVID-19 survivors have an increased risk of death 12 months post infection". Medical News Today. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
-
^ Mainous III, Arch G.; et al. (1 December 2021).
"COVID-19 Post-acute Sequelae Among Adults: 12 Month Mortality Risk".
Frontiers in Medicine. 8 (778434).
doi:
10.3389/fmed.2021.778434. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
{{ cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI ( link)
Epidemiological tracing of early cases
Time for a major rewrite of this section:
The first known infections from SARS‑CoV‑2 were discovered in Wuhan, China. The original source of viral transmission to humans remains unclear, as does whether the virus became pathogenic before or after the spillover event. Because many of the early infectees were workers at the Huanan Seafood Market, it has been suggested that the virus might have originated from the market. However, other research indicates that visitors may have introduced the virus to the market, which then facilitated rapid expansion of the infections. A March 2021 WHO-convened report stated that human spillover via an intermediate animal host was the most likely explanation, with direct spillover from bats next most likely. Introduction through the food supply chain and the Huanan Seafood Market was considered another possible, but less likely, explanation. An analysis in December 2021, however, said that the index case had been misidentified and that the preponderance of early cases linked to the Huanan Market, specifically a section where raccoon dogs were caged, argued for it being the source.
Major points of improvement:
- There are two "however" that redirect the reader in confusing directions.
- The text messes information of the place of origin (i.e. wuhan market) with the pathway of transmission (direct spillover vs intermediate spillover vs food supply chain vs unmentioned lab leak)
- "The first known infections from SARS-CoV-2 were discovered in Wuhan, China" is too vague, given that we have this from the NYTimes, for example, "Toward the end of December 2019, doctors at several Wuhan hospitals noticed mysterious cases of pneumonia arising in people who worked at the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, a dank and poorly ventilated space where seafood, poultry, meat and wild animals were sold." It gives more specific locations than ours (wuhan hospitals vs wuhan the city), and expands on key characteristics of the market (e.g. dank place where wild animals were sold).
- Our paraphrase of Worobey's results ("An analysis in December 2021, however, said that the index case had been misidentified and that the preponderance of early cases linked to the Huanan Market, specifically a section where raccoon dogs were caged, argued for it being the source.") is too strong, in my opinion. I propose we moderate it to something like this:
Forich ( talk) 03:35, 22 November 2021 (UTC)Michael Worobey, an expert on the origins of influenza and H.I.V., has traced the epidemiological origin of the early cases in Wuhan, suggesting that the index case (i.e. the first known case) was a vendor at the Huanan Seafood Market, which contrast with other public accounts that register as the index case an accountant who lived many miles from it.
- I agree with 1 and 2. A rewording for clarity is deserved, now that things are a bit more settled and there's less edit warring in general dividing our attention. For 3, I think I'd prefer to word it as "first confirmed infections", rather than replacing it with speculation about "mysterious cases of pneumonia" especially if paired with "dank and poorly ventilated" that I'd consider WP:WTW (particularly 'dank'). Along with 4, I'd suggest splitting the paragraph into things we know (first confirmed cases, Huanan Seafood Market being early epicenter) and the major areas of investigation (spillover event at seafood market, unidentified pneumonia, etc) to help clarify the certainty. Bakkster Man ( talk) 14:36, 22 November 2021 (UTC)
- Would there also be any relevance in including this NPR report somewhere in this section? It concerns findings of coronavirus antibodies in American blood samples from December 2019, and here is the DOI. Would it be extraneous to discuss the possible spread of the disease prior to the Wuhan outbreak? Wuhan is a well-documented outbreak and there are no other similar candidates at that time, but mentioning these findings in the rewrite may better reflect how there are several other unknown factors around the origins. Mewnst ( talk) 10:00, 23 December 2021 (UTC)
References
Restoring two discussions that were deleted by a random IP
Two discussions here, the "Epidemiological tracing of early cases" and "Higher mortality risk for COVID survivors?" were removed by a random IP address in this edit and were thus not properly archived or examined for further discussion. I have brought them back and something should be done about that annoying IP in the meantime. Mewnst ( talk) 11:32, 6 January 2022 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 12 January 2022
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Please change:
It mainly enters human cells by
To:
It enters human cells by
According to the two citations provided [1] [2], while SARS‑CoV‑2 viral entry depends on multiple factors, binding to ACE2 is the only way it enters human cells. -- Xarm Endris ( talk) 17:56, 12 January 2022 (UTC)
 Done
SpinningCeres (
talk) 01:46, 13 January 2022 (UTC)
Done
SpinningCeres (
talk) 01:46, 13 January 2022 (UTC)
unsubstantiated factoid about virus particle diameter
I don't seem to be able to edit, so am commenting here: The section Virology / Structure gives a diameter of the particles as 50-200 nm, and cites a reference. However, that reference just says they viruss "envelop" particles of that size range (which doesn't even make sense) and then cites a single reference for that, which doesn't support that in any way. So my suggestion would be to either remove the diameter range or else find a reference to support it. I'm looking but haven't found one yet. Thanks! Joe Betts-LaCroix ( talk) 22:10, 8 January 2022 (UTC)
- I've added a reference from somewhere else on the page and changed the bounds of the size. SpinningCeres ( talk) 15:55, 13 January 2022 (UTC)
Typo in total virus mass range
In section Virology/Structure a total virus mass of 0.1-1kg is stated. The given reference [142] (Sender et al., 2020) however states a mass range of 0.1-10kg. 89.160.8.66 ( talk) 11:24, 4 February 2022 (UTC)
Featured picture scheduled for POTD
Hello! This is to let editors know that File:SARS-CoV-2 scanning electron microscope image.jpg, a featured picture used in this article, has been selected as the English Wikipedia's picture of the day (POTD) for February 22, 2022. A preview of the POTD is displayed below and can be edited at Template:POTD/2022-02-22. For the greater benefit of readers, any potential improvements or maintenance that could benefit the quality of this article should be done before its scheduled appearance on the Main Page. If you have any concerns, please place a message at Wikipedia talk:Picture of the day. Thank you! Cwmhiraeth ( talk) 11:26, 13 February 2022 (UTC)

|
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory disease responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. This scanning electron micrograph shows SARS-CoV-2 virions (gold) emerging from the surface of cells cultured in a laboratory. The virus particles depicted were isolated from a patient in the United States. Photograph credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Recently featured:
|
Out of date part of article?
"Preliminary research indicates that the virus may remain viable on plastic (polypropylene) and stainless steel (AISI 304) for up to three days, but it does not survive on cardboard for more than one day or on copper for more than four hours." appears well out-of-date(?) as I thought I saw a journal article relating to research in Australia, now itself quite a while ago but several months later than this 'preliminary' research that suggested the virus could survive for up to 28 days on steel, perhaps in a dark environment undisturbed and in cold winter weather. I also think it could be on plastic for up to 5 or 7 days - virus in one piece of research I seem to remember (no idea where any of it is now) could not be detected on the seventh day. It appears to me the initial research is no longer the position that we know now and, in short, is likely out-of-date. However I do not know whether the extended time periods necessarily showed that the virus, where it was still found, was viable. In addition though, I haven't seen any evidence as to whether the time periods of survival of viable virus are different, possibly longer, with Omicron etc. (logic to me as a layperson might suggest that perhaps it could last longer on surfaces when Omicron appears to be able to remain present in unventilated indoor spaces in the air for quite a lot longer than the original virus (in excess of 2 1/2 days as opposed to up to 16 hours originally) but I suspect with SARS-CoV-2 it might confound what I think might be logical, as it usually turns out to do things 'unexpected' by (some) scientists that I expect it will do because it will be unusual and different to what has been previously encountered - I think, if anyone has assumptions, the assumptions are usually wrong). aspaa ( talk) 03:36, 19 February 2022 (UTC)
- 1) We would need secondary sources on this, not a primary research article.
2) It is important to emphasize that such studies must be based in virus isolation and culture rather than nucleic acid amplification in order to be useful for this question. The latter, often referred to as "PCR-based methods" can have false positives when nucleic acids are still present, but no viable virus remains. Similarly, some patients continue to test "PCR-positive" for several months after clearing the infection.
3) It is overall unlikely that this virus would remain viable for that long, as it is a lipid-membrane-enveloped virus. Such lipid bilayers break down relatively quickly in the open air, on the order of 3-4 days to zero viable particles. [12] [13] We don't have much reason to believe SARS-CoV-2 would be much different. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 11:36, 19 February 2022 (UTC)
misisleading to refer to SARS-CoV2 as the "successor" to SARS-CoV1
The last sentence of the first paragraph:
"As described by the US National Institutes of Health, it is the successor to SARS-CoV-1, the virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak.[16]"
is misleading and should be removed.
Although the cited reference does use the word "successor", the usage seems to imply that SARS-CoV2 is derived from SARS-CoV1. There is no evidence for this and substantial reason to believe that it is false (chiefly, that SARS-CoV1 was eradicated in 2004 and hasn't been seen anywhere in the world since then).
I suggest simply erasing this sentence, or, if it is deemed necessary to refer to SARS-CoV1, substituting:
"An unrelated coronavirus, now designated SARS-CoV1, caused the SARS epidemic of 2002-2004 and was eradicated in 2004." References for this information (refs 4 and 5 copied from the Wikipedia article on SARS1):
Chan-Yeung M, Xu RH (November 2003). "SARS: epidemiology". Respirology. 8 Suppl (s1): S9-14. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1843.2003.00518.x. PMC 7169193. PMID 15018127.
"SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome)". NHS Choices. UK National Health Service. 3 October 2014. Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 8 March 2016. Since 2004, there haven't been any known cases of SARS reported anywhere in the world.
— Preceding unsigned comment added by 108.52.207.45 ( talk) 16:11, 7 March 2022 (UTC)
- I moved this sentence to the following sentence. The word 'successor' seemed to refer to the timing of the outbreaks, rather than direct descendance. But the idea the two are 'unrelated' is also incorrect, as is evident in the name
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus.
Bakkster Man (
talk) 16:57, 7 March 2022 (UTC)
- Politically, it is the successor. All corona viruses descend from some common ancestor billions of years ago. As with other organisms, there is much mixing, so you can't draw a nice tree. I have run into this descending question before in microprocessors, where it can also be misleading, but is used anyway. Even there, things get mixed such that you can't draw a nice tree. Gah4 ( talk) 20:31, 7 March 2022 (UTC)
Number of virions needed for infection
During human-to-human transmission, between 200 and 800 infectious SARS‑CoV‑2 virions are thought to initiate a new infection.
What variant is this talking about? None of the references is recent: source #1 is from 11 May 2020 (very early), source #2 is from 9 December 2020 (early), and source #3 is from 20 May 2010 (what is this even doing here?). I don't understand the charts in #2, so I don't know if it means the original variant or the Alpha variant, but none of these sources can possibly be talking about Delta, Omicron, or lesser-known variants. Since this information is very much outdated, reliant on sources that are too old to reflect current research, and probably not applicable to the variants that are all over the place now, I think it ought to be removed completely. 49.198.51.54 ( talk) 07:58, 5 April 2022 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 3 May 2022
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
You can’t affirm that the virus came from China without prove, so that information is wrong 191.183.196.31 ( talk) 15:33, 3 May 2022 (UTC)
 Not done: it's not clear what changes you want to be made. Please mention the specific changes in a "change X to Y" format and provide a
reliable source if appropriate. The article states the first identified cases were in China. Is that untrue?
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 15:39, 3 May 2022 (UTC)
Not done: it's not clear what changes you want to be made. Please mention the specific changes in a "change X to Y" format and provide a
reliable source if appropriate. The article states the first identified cases were in China. Is that untrue?
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 15:39, 3 May 2022 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 14 May 2022
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Infection and Transmission:
The degree to which the virus is infectious during the
incubation period is uncertain, but research has indicated that the
pharynx reaches peak
viral load approximately four days after infection
Source:
Pharyngeal virus shedding was very high during the first week of symptoms, with a peak at 7.11 × 108 RNA copies per throat swab on day 4. ...
The earliest swabs were taken on day 1 of symptoms, which were often very mild or prodromal.
Current text indicates pharyngeal viral load peaks 4 days after infection rather than onset of symptoms.
Suggested change:
The degree to which the virus is infectious during the
incubation period is uncertain, but research has indicated that the
pharynx reaches peak
viral load approximately four days after the onset of symptoms
Peaceandlonglife (
talk) 14:54, 14 May 2022 (UTC)
cauldron of virus mixing
OK, I didn't explain it will before, and didn't have references. Virologists have been worried about Chinese farms as sources of new viruses for years. The discussion about zoonotic vs. lab misses the fact that farms are not close to natural, and not supposed to be labs. A quick Google search find a Nature article that calls a Chinese farm a cauldron of virus mixing. [3] This was the first one that came up, and from September 2019, so barely before Covid-19. I am not writing this as a WP:SOAPBOX, and no suggestions regarding lab origins or not, but for better understanding of virus origins. In 2019, there was much interest in pandemic flu viruses, but not (yet) corona viruses. Gah4 ( talk) 04:14, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
- Viral recombinance among farm animals is still zoonotic, and the WIV's primary research goals have been coronaviruses with pandemic potential since that was the source of SARS. Bakkster Man ( talk) 15:47, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
References
- ^ Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, et al. (April 2020). "SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor". Cell. 181 (2): 271–280.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. PMC 7102627. PMID 32142651.
- ^ Zhao P, Praissman JL, Grant OC, Cai Y, Xiao T, Rosenbalm KE, et al. (October 2020). "Virus-Receptor Interactions of Glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Human ACE2 Receptor". Cell Host & Microbe. 28 (4): 586–601.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.08.004. PMC 7443692. PMID 32841605.
- ^ Willyard, Cassandra (18 September 2019). "Flu on the farm" (PDF). Nature (573, S62-S63 (2019)). Retrieved 27 May 2022.
What constitutes certifiable facts
Regardless of one's views about the merits of the zoonotic hypothesis for SARS-COV2 the fact that some prominent scientists think the issue is unresolved is a fact. Facts like this, with appropriate documentation, are suitable for noting in an article about the virus. Does anyone disagree with this? StN ( talk) 18:12, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
-
WP:DROPTHESTICK. This has already been explained enough times that I can't really be bothered to keep arguing at length over it, but in short,
WP:FALSEBALANCE is clear enough that
Wikipedia policy does not state or imply that every minority view or extraordinary claim needs to be presented along with commonly accepted mainstream scholarship as if they were of equal validity.
andWe do not take a stand on these issues as encyclopedia writers, for or against; we merely omit this information where including it would unduly legitimize it
. Given that, besides a few opinion letters, most secondary sources (i.e. reviews and the like) by experts in the topic area overwhelmingly favour a zoonotic origin (many sources take it for granted, and the few sources that focus specifically on the origins of the virus are rather unambiguous as well), then this would indeed appear to be a prime casewhere including [the opposing theory] would unduly legitimize it
. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 18:21, 27 May 2022 (UTC)- Agreed. Having looked over the discussion above, it's clear to me that it is now time for StN to drop the stick and move on.
Generalrelative (
talk) 23:10, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
- Also agree. StN is writing at the wrong level. They may well observe some dissenting voices and decide in their view this constitutes enough to say "the jury is out" - but Wikipedia cannot reflect such a view unless it is explicitly said in reliable sources. Instead, we must just reflect what the WP:BESTSOURCES say - and they assert zoonotic origin, so far as I can see. Alexbrn ( talk) 04:45, 28 May 2022 (UTC)
- Agreed. Having looked over the discussion above, it's clear to me that it is now time for StN to drop the stick and move on.
Generalrelative (
talk) 23:10, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
I edited this article to reflect the fact that the unequivocal assertion that the SARS_Cov2 virus is of zoonotic origin is not universally accepted by experts in the field. I did not mention any other theory, but only cited letters and commentaries by some of those experts in the most respected scientific journals in the world. I was accused of advancing conspiracy theories, but although my edits each time were to different respected sources (each time with no alternative theory mentioned by me) other editors requested that I be banned from editing the article, and I was for 48 hours. After the ban expired, I edited the article again, this time linking to another Wikipedia article that indicated that the conclusion in this one was controversial. That article is already linked to in this one, but in a context that conceals the controversy that is its main subject. An editor used that innocuous edit to get me banned for a week, this time from editing Wikipedia at all. Since then, the World Health Organization has issued a report saying a laboratory manipulation and leak of the virus remains a viable scenario for the virus. Since the most active editors on the page consider this a conspiracy theory, I am reluctant to cite the WHO report, since I don't wish to get banned again. The blanket assertion, with no qualification, that the virus is of natural origin is itself a POV. Any advice User:Bbb23? StN ( talk) 18:32, 10 June 2022 (UTC)
- For reference this is the SAGO report being mentioned. On a quick scan, the following two quotes seem most relevant here:
- In the executive summary:
At the present time, currently available epidemiological and sequencing data suggest ancestral strains to SARS-CoV-2 have a zoonotic origin with the closest genetically related viruses being beta coronaviruses, identified in Rhinolophus bats in China in 2013 (96.1%) and Laos in 2020 (96.8%). However, so far neither the virus progenitors nor the natural/intermediate hosts or spill-over event to humans have been identified.
- Among the recommendations for further study:
Determine the occupational hazards intrinsic to laboratories working with SARS-like CoV and the nature of the studies performed before the first reported COVID-19 cases in Wuhan and whether they involved reverse engineering or gain-of-function, genetic manipulation or animal studies with strains of SARS-like CoV.
- I'll note that your ban came as a result of edit warring, not the content of your edit. Learn to edit collaboratively, (ie, continue discussing on the talk page, without making it a
WP:BATTLEGROUND) and you should be fine.
Bakkster Man (
talk) 19:33, 10 June 2022 (UTC)
- The keyword there is
suggest
. I think it supports StN and Palpable's proposed changes. According to high-quality sources, the natural reservoir is most likely bats, and the spillover was most likely a natural occurrence, but the intermediate host and time and place of the first spillover are far from certain and there is a minority view that the spillover was research related. ScrumptiousFood ( talk) 17:41, 11 June 2022 (UTC)
- The keyword there is
Zoonotic origins
The references provided for the assertion that the virus is of zoonontic origin were from 2020, and the removal of this unequivocal statement was reverted twice based on those old, controversial papers. A recent review in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2202769119 indicates that this view is not the consensus. Leaving out the assertion does not commit to either side. StN ( talk) 23:47, 23 May 2022 (UTC)
- Do you have a stronger source than the unreviewed opinion article you cited here?
Bakkster Man (
talk) 02:14, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Investigate the origins of COVID-19 - PubMed (nih.gov)
StN (
talk) 02:22, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33986172/
StN (
talk) 02:22, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33574591/
StN (
talk) 02:24, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- An unreviewed letter, and a news posting. Neither are stronger sources. Bakkster Man ( talk) 22:41, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33574591/
StN (
talk) 02:24, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33986172/
StN (
talk) 02:22, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Investigate the origins of COVID-19 - PubMed (nih.gov)
StN (
talk) 02:22, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
I have reverted assertions that the virus is of zoonotic origins since there is no consensus about this. I have not proposed an alternative. It is inaccurate to say that there is a consensus. I have cited a paper that indicates there is not a consensus. Please don't change this unless an authoritative paper stating that zoonoses is generally accepted can be cited. StN ( talk) 01:36, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
The statement that "It has been suggested to be of zoonotic origins, but some experts consider this unsettled" is uncontroversial and well supported by articles in Science and Nature. Removing it from the article is unwarranted and contrary to Wikipedia policy. StN ( talk) 19:01, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- No, you've just made that up.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:05, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Made up that virologists like Jesse Bloom and Richard Ebright consider it unsettled, or that reports about this from reputable sources are allowed in Wikipedia articles?
StN (
talk) 19:10, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Made up in that it's editorial invention. "One virologist disagreed" would at least be honest, but undue. There are always some fringe guys, don't amp them up.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:16, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Your comment would have some merit if there were a single article that showed evidence of zoonotic origins. There was more than one skeptical virologist who signed on to those letters. I have not advocated any alternative theory in my edits, so the allegation of "fringe" is inapplicable. I don't think you have familiarized yourself with the subject, but you and others are adept at using Wikipedia to keep readers from knowing that this is an unsettled subject among legitimate scientists.
StN (
talk) 19:31, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Follow the sources, and stop making stuff up, and we'll make progress.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:38, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- To recount the history of this: I started by removing a sentence that I considered speculative (i.e., making stuff up). It was reverted. I put it back, citing a recent review in one of the most esteemed journals in science, PNAS. I was reverted again with the comment that the people whose review was published by PNAS had no authority. I put it back with other sources of the kind that are cited all the time in Wikipedia. I was reverted again, with threats to be blocked and reporting to Wiki administration. At no time did I propound any fringe theories or any alternatives at all, but cited people raising questions about the zoonotic theory. The SARS virologist Ralph Baric was among these. At no point did I make anything up, which is dishonest of you to claim. If you knew anything about the subject, you would recognize that zoonoses is not established and that even the authors of the 2020 Andersen paper had doubts about it 2 days before they published the assertion that it was the only possibility. That's in the public record. If you knew anything about science, you would realize that claims require evidence and until that's available they remain controversial. Citing reports of doubts by reputable scientists in prime outlets is not indulging in fringe science. I always wonder about the kind of educational background or life experiences that produce reply guys like you, ready with the "nopes" or "stop making things up." Why don't you try to educate yourself and learn what a source is.
StN (
talk) 20:44, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- I think WP:CIR applies. You seem blinded by your own POV and sense of self-righteousness. Here, things need to be backed up by sources - reliable sources. Your own view and how well you consider yourself "self-educated" don't matter. Alexbrn ( talk) 20:53, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Unless you con find sources of similar quality to those listed
here (or even
those here, although they may be slightly outdated); then it doesn't matter. I also don't understand why the bollocks about the Andersen et al. emails is still circulating on the misinformation-net. Scientists had initial doubts (expressed via a private email, which is not a reliable source), then they investigated it more thoroughly, and found that those doubts were not backed up by evidence (as the published paper - the actual reliable source - clearly says). Random opinion pieces are nowhere near the level of sourcing required.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 22:37, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- The sources cited [refs. 9 and 17] present descriptions of the viral genome, but the suggestions of zoonotic origin are purely speculative. They are both from early 2020. The reliability of the sequence data does not transfer to the speculations about the origin. There is no evidence in those sources about the origins. The statements of uncertainly that I cited are just that, not evidence of an alternative. Anyone not committed to the zoonotic hypothesis would recognize that a statement that "some virologists think that the question is open" is appropriately sourced by a published statement by virologists that they think that the question is open. But we seem to be dealing with ideologues here.
StN (
talk) 22:51, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Obviously you want to waste other people's time without investing any of your own. The cited sources on the first page I linked (even quoted for your convenience, so you didn't even have to go read the whole papers!) are clear enough and I'm not going to bother repeating what they say. They are also all very much not "from early 2020"...
This, from September 2021, is very much recommended reading.
the suggestions of zoonotic origin are purely speculative
is not to be found in any of them, and appears very much to be your own opinion. Sadly for you, Wikipedia doesn't care about your (or my) opinion. It cares about what is published in reputable reliable sources. If you think it isn't true, too bad, but that is not Wikipedia's problem. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 23:34, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Obviously you want to waste other people's time without investing any of your own. The cited sources on the first page I linked (even quoted for your convenience, so you didn't even have to go read the whole papers!) are clear enough and I'm not going to bother repeating what they say. They are also all very much not "from early 2020"...
This, from September 2021, is very much recommended reading.
- The sources cited [refs. 9 and 17] present descriptions of the viral genome, but the suggestions of zoonotic origin are purely speculative. They are both from early 2020. The reliability of the sequence data does not transfer to the speculations about the origin. There is no evidence in those sources about the origins. The statements of uncertainly that I cited are just that, not evidence of an alternative. Anyone not committed to the zoonotic hypothesis would recognize that a statement that "some virologists think that the question is open" is appropriately sourced by a published statement by virologists that they think that the question is open. But we seem to be dealing with ideologues here.
StN (
talk) 22:51, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- To recount the history of this: I started by removing a sentence that I considered speculative (i.e., making stuff up). It was reverted. I put it back, citing a recent review in one of the most esteemed journals in science, PNAS. I was reverted again with the comment that the people whose review was published by PNAS had no authority. I put it back with other sources of the kind that are cited all the time in Wikipedia. I was reverted again, with threats to be blocked and reporting to Wiki administration. At no time did I propound any fringe theories or any alternatives at all, but cited people raising questions about the zoonotic theory. The SARS virologist Ralph Baric was among these. At no point did I make anything up, which is dishonest of you to claim. If you knew anything about the subject, you would recognize that zoonoses is not established and that even the authors of the 2020 Andersen paper had doubts about it 2 days before they published the assertion that it was the only possibility. That's in the public record. If you knew anything about science, you would realize that claims require evidence and until that's available they remain controversial. Citing reports of doubts by reputable scientists in prime outlets is not indulging in fringe science. I always wonder about the kind of educational background or life experiences that produce reply guys like you, ready with the "nopes" or "stop making things up." Why don't you try to educate yourself and learn what a source is.
StN (
talk) 20:44, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Follow the sources, and stop making stuff up, and we'll make progress.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:38, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Your comment would have some merit if there were a single article that showed evidence of zoonotic origins. There was more than one skeptical virologist who signed on to those letters. I have not advocated any alternative theory in my edits, so the allegation of "fringe" is inapplicable. I don't think you have familiarized yourself with the subject, but you and others are adept at using Wikipedia to keep readers from knowing that this is an unsettled subject among legitimate scientists.
StN (
talk) 19:31, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Made up in that it's editorial invention. "One virologist disagreed" would at least be honest, but undue. There are always some fringe guys, don't amp them up.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:16, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Made up that virologists like Jesse Bloom and Richard Ebright consider it unsettled, or that reports about this from reputable sources are allowed in Wikipedia articles?
StN (
talk) 19:10, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
There is absolutely no conclusion as of yet to the origins of COVID-19. You should not be stated that it zoonotic in origin. Wikiwowie ( talk) 01:32, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- I think even the remaining "lab leakers" agree on "zoonotic in origin" (though through lab accident rather than in the wild). Or are you saying other ideas are still plausibly entertained in reliable sources?
Alexbrn (
talk) 07:09, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- You are using "lab leakers" as a pejorative. This is not about people who are 100% sure there was a leak, those people can be safely ignored. The point is that there is still doubt among reasonable people, because there just isn't enough evidence either way.
- Despite intensive searching the closest known natural relatives of SARS-CoV-2 lack the furin cleavage site - but there were gain of function research proposals with the explicit intent of adding this feature to other bat viruses, in Wuhan no less. This remains a viable hypothesis, and no reasonable person would consider laboratory gain of function research to be "zoonotic origin", whether it occurred through splicing or just by hosting sick animals together.
- The article
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 is much more balanced. It states that the majority of scientists favor a zoonotic origin, without attempting to present the matter as settled.
Palpable (
talk) 16:06, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Wikipedia tends to reflect what scientists think. Relevant sources, as cited, flat-out assert zoonotic origin and elsewhere the bio-engineered scenario is called a conspiracy theory (do we really need to go into that again here?) There's no option but to follow the sources.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:13, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- You have a bad habit of equating people who haven't made up their minds with conspiracy theorists. There is more ideology than evidence, on both sides of the debate, and in the absence of a known natural reservoir, the article should not present the matter as settled.
- Again,
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 has a pretty balanced view on things.
Palpable (
talk) 16:20, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- It's not me, it's the relevant sources. You have a bad habit of personalizing things.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:22, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- You're the one throwing around the "consipiracy theorist" and "lab leaker" pejoratives.
- The burden of proof for a dogmatic statement is higher than for one that expresses doubt. The sources you consider relevant are not actually that strong.
-
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 has plenty of relevant sources. Given the lack of strong evidence on either side, attempting to make a definitive statement about the origins is misguided. It is sufficient to say that the majority of scientists favor a zoonotic origin.
Palpable (
talk) 16:38, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Sorry what source do you consider "not actually that strong"? In contrast you have produced zero sourcing. Sure, the
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 is the right place to go into all the conspiracy theories in detail. This article isn't the right place for that. If we just mirror high-quality sources, it's job done.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:45, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The lead makes the unverified statement "It is of zoonotic origins". This statement is not actually sourced; the subsequent statement that it has close similarity to bat coronaviruses is sourced to an article that refers to a likely spillover from bats. Note that the scientific source uses the word "likely" which has been promoted to certainty in the article text. Shouldn't "likely" be in the article?
Palpable (
talk) 17:01, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- quote: "its unprecedented global societal and economic disruptive impact has marked the third zoonotic introduction of a highly pathogenic coronavirus into the human population" [my emphasis]. To repeat: what source is "not actually that strong"?
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:07, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The statement in the paper is not as strong as the statement in the article.
- If "zoonotic" merely means that the virus was not sequenced from scratch, then sure, it's obviously zoonotic. But you know as well as I do that in the context of SARS-CoV-2 origins, zoonotic implies "without lab involvement" which is by no means settled.
Palpable (
talk) 17:24, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The assertion here faithfully mirrors the assertion in the source. Helpfully it glosses "Zoonotic pathogens" as "Animal pathogens that can infect and replicate in humans". Any argument to the contrary would seem to be extreme
WP:FRINGE and need super sourcing for an
WP:EXCEPTIONAL claim, expecially since we have strong sources calling the "bio-engineered" origin idea a conspiracy theory.
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:31, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Again with the pejoratives. As you know, there are numerous letters by non-fringe scientists who think the question of lab involvement is still open; you and others seem to think that science doesn't have room for disagreement so you eliminate these opinions from the article.
- I think this manufactured certainty weakens Wikipedia's credibility, but obviously you have more time to spend on this than I do. I give up.
Palpable (
talk) 17:41, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Letters are not reliable sources for sci/med assertions, and the fact that stuff is published in letters and not peer-reviewed scholarly sources strongly indicates its
WP:FRINGE status. Bottom line: Wikipedia mirrors reliable sources.
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:57, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Dissenting letters from notable scientists are a reliable indication that consensus has not been reached. Despite my best efforts here, it seems that you can't see the difference between confidently asserting a lab leak (conspiracy theory) and expressing uncertainty about a natural origin (waiting for evidence). It sounds like you are not a scientist yourself. Palpable ( talk) 18:27, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Letters are not reliable sources for sci/med assertions, and the fact that stuff is published in letters and not peer-reviewed scholarly sources strongly indicates its
WP:FRINGE status. Bottom line: Wikipedia mirrors reliable sources.
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:57, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The assertion here faithfully mirrors the assertion in the source. Helpfully it glosses "Zoonotic pathogens" as "Animal pathogens that can infect and replicate in humans". Any argument to the contrary would seem to be extreme
WP:FRINGE and need super sourcing for an
WP:EXCEPTIONAL claim, expecially since we have strong sources calling the "bio-engineered" origin idea a conspiracy theory.
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:31, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- quote: "its unprecedented global societal and economic disruptive impact has marked the third zoonotic introduction of a highly pathogenic coronavirus into the human population" [my emphasis]. To repeat: what source is "not actually that strong"?
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:07, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The lead makes the unverified statement "It is of zoonotic origins". This statement is not actually sourced; the subsequent statement that it has close similarity to bat coronaviruses is sourced to an article that refers to a likely spillover from bats. Note that the scientific source uses the word "likely" which has been promoted to certainty in the article text. Shouldn't "likely" be in the article?
Palpable (
talk) 17:01, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Sorry what source do you consider "not actually that strong"? In contrast you have produced zero sourcing. Sure, the
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 is the right place to go into all the conspiracy theories in detail. This article isn't the right place for that. If we just mirror high-quality sources, it's job done.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:45, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- It's not me, it's the relevant sources. You have a bad habit of personalizing things.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:22, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Wikipedia tends to reflect what scientists think. Relevant sources, as cited, flat-out assert zoonotic origin and elsewhere the bio-engineered scenario is called a conspiracy theory (do we really need to go into that again here?) There's no option but to follow the sources.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:13, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Note there has been off-wiki recruiting on this matter. [14] I have added a template at the head of the page accordingly. Alexbrn ( talk) 16:02, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- New sources support
StN and
Palpable's proposed changes. Zoonotic origin and lab origin aren't mutually exclusive, as the Wuhan CDC was doing field research with bat viruses. Some scientists (including the WHO) have also raised concerns about experiments done by the Wuhan Institute of Virology, possibly supported by ECA and the NIH. Certainty will only come with China's cooperation with the WHO, according to SAGO report, and secondary sources writing about it
[15]
[16]
[17]
[18]
[19]
[20]
[21]
[22]
[23].
ScrumptiousFood (
talk) 17:32, 11 June 2022 (UTC)
- You'd think so, but you will be reverted, accused of edit-warring, and ultimately be banned for trying to rectify this. The editors who have taken hold of this page will not accept letters in Science and Nature from prominent virologists who don't agree that the issue is settled to support -- not an alternative hypothesis -- but the factual statement "Not all prominent virologists consider the issue settled." Yes, Wikipedia's credibility is undermined by such maneuvers, but it seems that little can be done about it. StN ( talk) 19:05, 11 June 2022 (UTC)
- Best to cite the SAGO report [24] directly rather than the press coverage. In particular, page 11 of the report draws a distinction between "origin" and "source" which clarifies that a zoonotic origin does not rule out a lab accident somewhere in the chain.
- That said, some of the fringe crusaders here have gone full battleground. Logical argument is stalled with strawmanning and wikilawyering. You might have more luck with the actual doctors and scientists at
Wikipedia Talk:WikiProject Medicine. -
Palpable (
talk) 22:17, 11 June 2022 (UTC)
- I can get to this eventually if no one else does, but I have already been banned twice. If you want to try, I am more than happy to step aside for a while. StN ( talk) 00:20, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- Citing WHO reports directly was how we changed the previous 'don't even mention the lab' consensus, so we have precedent there. And I agree, the above is already over the line of battleground and aspersions, if it continues it's likely to end with another ban.
Bakkster Man (
talk) 00:29, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- Totally agree. I'd like to see if the stance in the reports is backed up by a change of stance in other sources (is there? I can't find that much, to begin with -
1, from May this year, simply says
The subgenus Sarbecovirus of beta-CoVs, such as SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, had spread to humans, most likely via intermediate hosts.
). Also agree thatThat said, some of the fringe crusaders here have gone full battleground. Logical argument is stalled with strawmanning and wikilawyering.
is quite over the line. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 00:48, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- Totally agree. I'd like to see if the stance in the reports is backed up by a change of stance in other sources (is there? I can't find that much, to begin with -
1, from May this year, simply says
Requested move 21 June 2022
- The following is a closed discussion of a requested move. Please do not modify it. Subsequent comments should be made in a new section on the talk page. Editors desiring to contest the closing decision should consider a move review after discussing it on the closer's talk page. No further edits should be made to this discussion.
The result of the move request was: Moved. CollectiveSolidarity ( non-admin closure) ( talk) 00:41, 28 June 2022 (UTC)
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 → SARS-CoV-2
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 → SARS-CoV-1
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus → SARSr-CoV
- Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus → MERS-CoV
There are many good reasons why these pages should be moved to their widely used abbreviations. To start with the obvious, these are their
WP:COMMONNAMEs universally used by reliable sources and the public, which should replace the extremely lengthy and rarely-used
WP:OFFICIALNAMEs per
WP:CONCISE,
WP:RECOGNIZABILITY, and
WP:ACROTITLE. It's hard to imagine that any reader would take the time to type in Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
(5 words) or Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus
(6 words) into the search bar. Before any members of
WP:COVID-19 jump in and point me to {{
Current COVID-19 Project Consensus}}, rest assured I have read that page and understand that the current consensus of the WikiProject is to use the full name. But
WP:CONSENSUSCANCHANGE, and I see
the last RM discussion was over a year ago. Most editors who objected to a page move there did so on the grounds of
WP:CONSISTENT, so to address that concern I'm requesting any related pages to be moved as well. This also makes them consistent with
COVID-19,
SARS, and
MERS, all of which were moved following successful RMs with similar arguments (
Talk:COVID-19/Archive 17 § Requested move 1 March 2021,
Talk:SARS § Requested move 8 December 2021, and
Talk:MERS § Requested move 15 December 2021).
InfiniteNexus (
talk) 00:02, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Note: WikiProject COVID-19 and WikiProject Viruses have been notified of this discussion. InfiniteNexus ( talk) 00:03, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support per nom. The abbreviated titles clearly meet the WP:TITLE criteria. Ajpolino ( talk) 00:19, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Oppose I presume there are redirects from all the possible other names. To me, it is nice to see the official name, even though I will probably use the redirect. But that is why we have redirects! (Well, one reason.) Gah4 ( talk) 01:42, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Redirects are for names that are less common than the article title, not the other way round. When a redirect's title is more commonly used than the article's title, then that should be the name of the article. InfiniteNexus ( talk) 03:00, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- I just notice in my watchlist, the pages Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Superheterodyne receiver. In both cases, shorter forms are commonly used, and might be the WP:COMMONNAME. I can probably find many more. The shorter names are like slang, you use them when convenient, but the right name when it is important, as WP:TONE indicates. Gah4 ( talk) 20:01, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- I may have agreed with you if these article's current titles weren't 5 or 6 words long. InfiniteNexus ( talk) 20:16, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Hmmm. Does the article still start with the whole name? (Especially since that is where WP:TONE applies.) If so, then I probably go to Neutral. Gah4 ( talk) 22:31, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Yes they do, and they should continue to do so after they are moved. InfiniteNexus ( talk) 02:58, 22 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support, at least for SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1, and MERS-CoV, for which the short forms are much more recognizable and more commonly used. I am less sure about SARSr-CoV; I'll defer to others on that one. — Mx. Granger ( talk · contribs) 10:36, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support per nom. Consider the consistency with
SARS and
MERS and the arguments put forth in their RM discussions. Also consider
WP:SHORTFORM. However, I suggest to move
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus to
SARS-related coronavirus, as that seems more generally recognizable than
SARSr-CoV. —
BarrelProof (
talk) 12:15, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- In fact, to help readers WP:RECOGNIZE the topics, I further suggest:
- — BarrelProof ( talk) 02:30, 23 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support per nom. While I personally prefer the longer full article title, I can't make a compelling argument that the contractions aren't indeed the WP:COMMONNAME. There are some other viruses which don't have this kind of title shortening, they seem to be the exception where the abbreviation isn't nearly as common ( A/H1N1 for Influenza A virus subtype H1N1, for instance). Bakkster Man ( talk) 13:45, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support, principally per the thorough arguments laid out by the nominator. "SARS-CoV-2" has become a widely used acronym and, based on my experience, the definite WP:COMMONNAME for the virus; it's also substantially more WP:CONCISE than the spelled-out title. My feelings on the other requested moves are less strong, but I think the same underlying principles hold for all of the titles in question, and it makes sense to be WP:CONSISTENT about the move. ModernDayTrilobite ( talk • contribs) 14:19, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support per nom, at least for SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1, and MERS-CoV. I'm not sure if SARSr-CoV is the undisputed common name for Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus, but I think it's common enough for WP:CONSISTENT to apply. ~ BappleBusiness [talk] 22:32, 27 June 2022 (UTC)
Requested move 17 August 2022
- The following is a closed discussion of a requested move. Please do not modify it. Subsequent comments should be made in a new section on the talk page. Editors desiring to contest the closing decision should consider a move review after discussing it on the closer's talk page. No further edits should be made to this discussion.
The result of the move request was: Withdrawn. No support and several opposed after nearly three days. This proposal doesn't have traction. — BarrelProof ( talk) 20:15, 19 August 2022 (UTC)
– Please see the similar just-closed RMs at Talk:SARS-related coronavirus#Requested move 9 July 2022 and Talk:MERS-related coronavirus#Requested move 19 July 2022. These two articles were recently renamed (from titles different from what I am suggesting here). However, I suggest that the names that I propose would be more WP:RECOGNIZEable for most readers. I previously made these same title suggestions in the recent RM at Talk:SARS-CoV-2#Requested move 21 June 2022, but there was no reaction to my suggestions at the time, as the focus of that discussion was about whether to abbreviate SARS and MERS or not. I think the current titles are now overly abbreviated to a degree that makes them difficult for many readers to recognize. — BarrelProof ( talk) 00:54, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- I've heard Dr. Fauci say "Sars Co Vee Two" on TV. Gives me the impression that despite being a complex abbreviation, that this has entered the spoken vernacular and could be somewhat common. I won't cast a bolded !vote since this is just an anecdote, but figured I'd mention this. – Novem Linguae ( talk) 01:06, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- I supported the MERS request, but while "SARS coronavirus 2" is more attractive visually, I believe that
SARS-CoV-2 is more recognizable as well as being considerably more common than the proposed title.
Dekimasu
よ! 07:38, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- Agreed, "SARS-CoV-2" gets three orders of magnitude more search results than "SARS coronavirus 2". We're currently using the common name, no need to move. Bakkster Man ( talk) 13:24, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- After the previous move discussion, I heard SARS coronavirus 2 in some news discussion. I would have voted for it in the previous move discussion if it was offered. (I ended up neutral in the actual discussion.) Not overly long like the previous name, but not too short, either. Gah4 ( talk) 08:22, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- Oppose per WP:COMMONNAME. Ngrams won't be applicable here because its corpus only goes up to 2019, but Google Search and Google Scholar results both suggest that SARS-CoV-2 is a substantially more widely used term than SARS coronavirus 2. Not only does SARS-CoV-2 receive more search results on either metric ( 1.85 million Google Scholar results and 717 million Google Search results, vs. 1.38 million and 282 million respectively for "SARS coronavirus 2"), but most of the results listed under "SARS coronavirus 2" also go on to use the term "SARS-CoV-2" extensively throughout the body text. Further, authoritative sources typically use "SARS-CoV-2" as the name of the virus, with little or no discussion of its longer names: for instance, see the World Health Organization, the US Centers for Disease Control and the US National Cancer Institute. ModernDayTrilobite ( talk • contribs) 14:50, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- Oppose per COMMONNAME. And I would disagree on what readers will find "recognizable." These abbreviations "CoV" etc. are now in the popular lexicon, in news stories, and in the mouths of many of our most trusted public health officials. I've heard it as "SARS -Cove-Two" and as "SARS-Coh-Vee-2", but it is the same acronym. If somebody doesn't recognize the name, I don't think changing it to "coronavirus" will help all that much. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 16:40, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
Lead
Considering the fact that the WHO has called the lab leak a possibility, it is completely ridiculous to dismiss it as a fringe minority opinion. Aren't we supposed to trust and cite what the experts have to say? BTW, the article on the COVID-19 disease itself mentions the lab leak as a possibility. X-Editor ( talk) 03:46, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- 1) There's an ongoing talk page discussion and short-cutting it to include text is not productive 2) The change of stance of WHO's latest report does not appear to be reflected by the existing sources 3) We should probably wait to see how exactly this turns out per
WP:NORUSH
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 03:48, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- I'll also note that singling out the lab-leak from the SAGO report seems unhelpful. It doesn't focus solely on that; and in fact, in the nearly 2-page long summary which begins the document, it only dedicates one short paragraph, the following, to the lab-leak:
The SAGO notes that there has not been any new data made available to evaluate the laboratory as a pathway of SARS-CoV-2 into the human population and recommends further investigations into this and all other possible pathways. The SAGO will remain open to any and all scientific evidence that becomes available in the future to allow for comprehensive testing of all reasonable hypotheses.
- Thus the recent addition failed both
WP:FALSEBALANCE (when compared to other sources) but also
WP:DUE (when compared to the source it was coming from)
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 03:52, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- WP:NORUSH is an essay, not a guideline or rule. The SAGO report is also only one report. There is also a difference between adding the lab leak to the lede and adding it to the body of the article. Would you be fine if it was added to the body? X-Editor ( talk) 03:57, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- Now that I think about it, the best course of action would be consensus through voting. I've started a discussion
here regarding that.
X-Editor (
talk) 04:02, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- WP:NOTAVOTE is a better suggestion. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:06, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- (
edit conflict)The more I read the SAGO report the more I'm disappointed at the news sources being cited which seem to unduly focus on one clickbaity aspect (as is only too usual). The report suggests a whole litany of studies (
3.1.1 Early investigation studies
, with a few suggestions;3.1.2 Human studies
with over half a dozen suggestions;3.1.3 Animal and environmental studies
similarly;3.1.4 Genomics and phylogenetics studies
; and then, yes, finally;3.1.5 The possibility of a breach in biosafety or biosecurity measures
). A call for further studies (without all of the "increasingly active consideration" editorialising) seems really all there is to it. Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 would probably be the correct article to summarise this. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:06, 12 June 2022 (UTC)- I have stayed out of these discussions so far except to object to edit warring, but just a small point: even if this were to be added to the article, I agree that "increasingly active consideration" is not the wording we would use, per WP:SYNTH, MOS:REALTIME, and MOS:WTW. Dekimasu よ! 04:17, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- N.B. I've rewritten the mention in the Investigations article as
In June 2022, the WHO released an additional report advocating for more investigations in the various possible pathways of emergence.
, as per the bit quoted above (and the rest of the initial summary), to avoid a silly-game of chinese telephone between what the original report is saying and what the news are click-baiting from it. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:18, 12 June 2022 (UTC)- @
X-Editor: "most important one" - is it really? It's the last one to be listed, has the least amount of text devoted to it; and basically is not much of a departure from the known stance of the WHO director-general (who said that it was
"premature" for the WHO's report to rule out a potential link between a laboratory leak
and called on China to provide additional data). We don't need to emphasise stuff which hasn't really changed. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:23, 12 June 2022 (UTC)- To be fair the current wording seems reasonable enough where it is (minor nitpicking about the extra-emphasis final words aside). I'm however very much not sure if we need to copy it to other articles. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:25, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- @
X-Editor: "most important one" - is it really? It's the last one to be listed, has the least amount of text devoted to it; and basically is not much of a departure from the known stance of the WHO director-general (who said that it was
- Best not to get hung up on the news coverage. It has been sensationalized, but that should not reflect on the report itself.
- Rather than adding more about the lab leak, what about saying less? The current wording lends itself to misinterpretation because it sounds like a "no lab leak" claim. But as the SAGO report states, zoonotic "origin" does not preclude a lab "source". Why not remove the "it is of zoonotic origins" sentence in the current lead and refer all discussion of the origin to the Investigations article?
- The article has plenty to say about what the virus actually is without trying to make a short summary of the complicated/uncertain/political origins debate, and that debate is already linked in the next sentence. -
Palpable (
talk) 20:52, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- A reasonable proposal. ScrumptiousFood ( talk) 16:21, 13 June 2022 (UTC)
- I'm in favor of saying less in the lede to discuss more in the origin section and article. I'm not sure we need to make quite so large a cut as to remove the entire sentence. Particularly if the concerns are the words 'zoonotic' and 'origin'. I propose the following change:
It
This still sets up the following sentence with its link to the Investigations article, and mirrors the language used by SAGO. Bakkster Man ( talk) 17:08, 13 June 2022 (UTC)is of zoonotic origins andhas close genetic similarity to bat coronaviruses, suggestingit emerged froma bat-borne virus ancestor.- I agree, that is better than just removing the sentence. - Palpable ( talk) 22:58, 13 June 2022 (UTC)
- Except that's not even what the SAGO report says, let alone all of the other high-quality RS we have on the matter.
At the present time, currently available epidemiological and sequencing data suggest ancestral strains to SARS-CoV-2 have a zoonotic origin with the closest genetically related viruses being beta coronaviruses, identified in Rhinolophus bats in China in 2013 (96.1%) and Laos in 2020 (96.8%). However, so far neither the virus progenitors nor the natural/intermediate hosts or spill-over event to humans have been identified.
- A more legitimate rewriting of the sentence in the lead (taking into account what other sources say) might be
Available evidence indicates that the virus is of zoonotic origin, and has close genetic similarity to bat coronaviruses, suggesting a bat-borne viral ancestor.
RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 23:13, 13 June 2022 (UTC)- Or heck, even simpler, just replace
It is of zoonotic origins [...]
withAvailable evidence indicates that it is of zoonotic origin [...]
. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 23:19, 13 June 2022 (UTC)- yeah agreed re: "Available evidence." — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 00:12, 15 June 2022 (UTC)
- But the SAGO report explains what they mean by "origin" with two full paragraphs on page 11. Without that context, "origin" is easily misinterpreted to mean "immediate parent". -
Palpable (
talk) 00:19, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Wikipedia articles should ideally, as much as possible be written in non-technical, plain English. This applies even more so in the lead, where one would expect that an adequate summary can be made without going into technical distinctions. "Origin", in plain English like in the SAGO report (the explanation given is IMHO very close to the definition given by the
Cambridge dict as
the thing from which something comes, or the place where it began:
), does not mean "immediate parent", else we would be writing this differently. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 00:37, 14 June 2022 (UTC)- In the context of this report, the “origin” can be understood as the ancestral host from where the pathogen has evolved.
- Surely that implies a distinction between "the context of this report" and plain English. -
Palpable (
talk) 01:37, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Why must I repeat? Per Cambridge dictionary;
origins [plural] - used to describe the particular way in which something started to exist or someone started their life: The story has obscure origins
- Or the other very similar definition of the singular form
the thing from which something comes, or the place where it began:
- This seems to me just like researchers being thorough and making clear it is not the "immediate origin" they are referring to. But the current text in the article here is not referring to an immediate origin or to a direct/immediate ancestor, so we should be fine.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 01:46, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Ok, let's try this another way.
- Four people have come to this Talk page recently, objecting that the current text in the lead strongly implies "no lab leak". I can't speak for the other three, but I am a native English speaker and voracious reader with a respectable university degree. You appear to be saying that all three of us have misinterpreted the lead, but at the same time you deny that it lends itself to misinterpretation.
- -
Palpable (
talk) 02:31, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- "no lab leak"; or more accurately "lab leak very unlikely, no or very little evidence to support it, and not seriously considered by most scientists", is the correct interpretation, of both this and other articles and of the sources, so, yeah, there has been no misinterpretation here.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 04:12, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- There must be a clear distinction between "no lab leak" and "no or very little evidence to support a lab leak". While the second claim is valid, it is just as valid to say that there is no or very little evidence to deny a lab leak. The ability to distinguish between ontology and epistemology should be table stakes for participating in this debate.
- If we agree that "it is of zoonotic origin" implies "no lab leak" to many reasonable English speakers, but it clearly means something more nuanced to WHO and other scientific sources, then that phrasing is misleading. It should be removed - or bogged down with a bunch of text clarifying that the technical meaning of "zoonotic origin" does not rule out a lab.
- The next revision of the COVID-19 origins consensus should also be more careful about the meaning of "origin". It seems to be causing a great deal of confusion and, as seen above, some people appear to be exploiting this confusion to push the NOLABLEAK POV. -
Palpable (
talk) 16:12, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
it is just as valid to say that there is no or very little evidence to deny a lab leak.
I think that's the textbook example of affirming a disjunct. Something not being proven false does not mean that there is no evidence against it, only that the evidence against it does not allow to make a definitive conclusion on the premises. Both the SAGO report and other sources (the Holmes et al. critical review; other recent sources like the papers I mentioned earlier, for ex. [25]) say that what evidence we do have (as SAGO phrases it, " epidemiological and sequencing data"; the evidence that Sars-COV-2 was circulating outside of China earlier than thought presented in other sources; the fact that the first detected outbreak in Wuhan was not near the lab but likely involved or was amplified by the wildlife market, ...) suggests an origin with no lab involved. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 00:59, 15 June 2022 (UTC)- Thanks for the reading suggestions. Reading papers is certainly a breath of fresh air after the polemic stench here.
- I am not employing the logical fallacy you mention, I'm pointing to a real lack of evidence. 2.5 years later, we are not much closer to the source than RaTG13. Holmes et al provides very persuasive arguments against the virus being engineered, based on a presumably comprehensive knowledge of available techniques. But many of their claims are still based on absence of evidence. If they had complete documentation of the lab's activities, the closed-world assumption would apply making it possible to reason from the absence of evidence. Unfortunately, access to the full evidence has been severely restricted, the open-world assumption applies instead, and any conclusions from lack of evidence must be taken with a grain of salt.
- I hope I won't be accused of cherry-picking for pointing out that the conclusion to Holmes et al hedges their position with "the possibility of a laboratory accident cannot be entirely dismissed". That's what good science communication looks like: uncertainty comes with the territory, and balance is not considered a sign of weakness. But here on Wikipedia, a small clique of non-scientists can use this careful paper to justify accusations like "fringe", "conspiracy theory", "lab-leaker", and "wingnuttery". Have a nice day. -
Palpable (
talk) 15:25, 15 June 2022 (UTC)
- Basically the SAGO source only says that there's no new information that could provide evidence for the leak theory. This means that nothing changed and that the fully natural origin continues to be the most plausible... —
Paleo
Neonate – 08:20, 16 June 2022 (UTC)
- Most plausible is not the same as absolutely true. We currently say that "It is of zoonotic origins" which is not the same as saying that a zoonotic origin is the most plausible. Would you support a change to the lede so that it reads something to the effect of Available evidence indicates that it is of zoonotic origin" or most likely of zoonotic origin or something to that effect? Bonewah ( talk) 15:00, 16 June 2022 (UTC)
- Basically the SAGO source only says that there's no new information that could provide evidence for the leak theory. This means that nothing changed and that the fully natural origin continues to be the most plausible... —
Paleo
Neonate – 08:20, 16 June 2022 (UTC)
- "no lab leak"; or more accurately "lab leak very unlikely, no or very little evidence to support it, and not seriously considered by most scientists", is the correct interpretation, of both this and other articles and of the sources, so, yeah, there has been no misinterpretation here.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 04:12, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Wikipedia articles should ideally, as much as possible be written in non-technical, plain English. This applies even more so in the lead, where one would expect that an adequate summary can be made without going into technical distinctions. "Origin", in plain English like in the SAGO report (the explanation given is IMHO very close to the definition given by the
Cambridge dict as
- Or heck, even simpler, just replace
- This content has been censored from this article for months. Agree it should be included for NPOV and obviously the FRINGE tag on it is just for the purpose of excluding it. But you will face very active editors who have time to banter this position endlessly attempting to push the local consensus here. You probably should run an RFC if you want it looked again by more mainstream editors. As you point out the broader consensus changes over time in the RS and at wikipedia we will follow that (eventually). There is no requirement that we follow MEDRS on all the articles (such as the pandemic) but this article about the disease I wonder if it will fall towards MEDRS (making it harder to go with mainstream view which probably recognizes that there is a decent chance it came from the lab in China). Thanks
Jtbobwaysf (
talk) 02:28, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- I support changing the lead to read that "Available evidence indicates that it is of zoonotic origin" or most likely of zoonotic origin. If tons of official sources hold open the possibility that it is not of zoonotic origin then so should we.
Bonewah (
talk) 12:46, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- The SAGO report unpacks "zoonotic origin", saying the natural reservoir of the virus is most likely zoonotic, and on that I don't think there is any disagreement between experts in sources or editors here. On how the virus was introduced to humans (spillover), and if it was a natural occurrence, the report says it is uncertain.
ScrumptiousFood (
talk) 18:42, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- I think this is probably mostly correct on the level of agreement. I picked up on the word 'ancestry' in the SAGO report, since it seems to do a very good job of leaving the spillover and any evolution between the closest ancestral bat virus and the initial lineage sequenced in humans open ended. Whether direct spillover to humans, intermediate spillover through another animal, or a sample collected in a lab, the ultimate ancestry of some bat beta coronavirus seems fundamentally agreed to. I also think it's probably more clear to an average reader that if/when we find that bat virus, it may not be the exact same virus as SARS-CoV-2, just a direct ancestor. Bakkster Man ( talk) 18:57, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Agree with this change. "Available evidence" is the only necessary hedging, and it is precisely what our best available consensus source (the SAGO report) currently says. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 00:13, 15 June 2022 (UTC)
- I also support this wording. Bakkster Man ( talk) 17:43, 16 June 2022 (UTC)
- I agree, this wording improves the lead. = Palpable ( talk) 20:59, 17 June 2022 (UTC)
- The SAGO report unpacks "zoonotic origin", saying the natural reservoir of the virus is most likely zoonotic, and on that I don't think there is any disagreement between experts in sources or editors here. On how the virus was introduced to humans (spillover), and if it was a natural occurrence, the report says it is uncertain.
ScrumptiousFood (
talk) 18:42, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- I support changing the lead to read that "Available evidence indicates that it is of zoonotic origin" or most likely of zoonotic origin. If tons of official sources hold open the possibility that it is not of zoonotic origin then so should we.
Bonewah (
talk) 12:46, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
"Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origins..." What evidence is that? Identifying infected humans in a seafood market where no infected animals have been found does not constitute such evidence, as many commentators in citable sources have noted. Evidence for zoonotic origins requires identifying infected nonlaboratory animals. StN ( talk) 15:07, 18 October 2022 (UTC)
- Please see the discussion above, which references the SAGO report. Bakkster Man ( talk) 16:05, 18 October 2022 (UTC)
Spike protein of the sars-cov-2
I propose we create a new article on the Spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus as it has become notable by itself. The Spike protein has been discussed as vital for the entry process of the cell, vital for the fabrication of vaccines across platforms, and vital to understand possible effects on the immune system because of its shedding. One natural starting point can be the virology sections from this entry, which I can use to write a draft in user space. Opinions? Forich ( talk) 21:10, 20 October 2022 (UTC)
- You mean like Coronavirus spike protein as we have linked in the info box? Bakkster Man ( talk) 16:53, 21 October 2022 (UTC)
Work towards A-Class status
I propose we consciously embark on making this an A-Class article. The criteria are:
Provides a well-written, clear and complete description of the topic, as described in Wikipedia:Article development. It should be of a length suitable for the subject, appropriately structured, and be well referenced by a broad array of reliable sources. It should be well illustrated, with no copyright problems. Only minor style issues and other details need to be addressed before submission as a featured article candidate
. Do any of the wikiprojects involved in this entry have an A-Class assessment departments? Forich ( talk) 16:49, 27 November 2022 (UTC)
- I think A-class is a very uncommon rating. Perhaps WP:GA would be a good goal. – Novem Linguae ( talk) 17:43, 27 November 2022 (UTC)
Caption for the bottom image accompanying article lead
'Atomic model of the external structure of the SARS-CoV-2 virion. Each "ball" is an atom.'
Despite the rather confusing description of the source stating this also: Each "ball" depicted is not an individual Atom but rather a Chemical compound consisting of multiple different chemically bonded atoms.
I have never seen the individual structures of the viral envelope referred to as 'atoms' before, though it it possible that is simply an archaic convention among virologists that I am unaware of.
At any rate though, the link in the caption for this image does direct to the Wikipedia article for atoms.
Would anyone mind correcting for the above? I believe that I am unable to do so myself given the (understandable) protected status of this article. 2A02:A443:AF4E:1:D5A2:151D:A66C:5A5 ( talk) 20:29, 28 December 2022 (UTC)
- Agreed, each "ball" is actually a specific amino acid, which the source image discusses in depth in its description. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 23:54, 28 December 2022 (UTC)
In the "Phylogenetics and taxonomy" section, the claim is made: "The furin cleavage site PRRAR↓ is identical to that of the feline coronavirus, an alphacoronavirus 1 strain." However, the source cited for this statement contradicts this claim. According to the source, there are two variants of feline coronavirus. FECV, which is milder, and FIPV which can be fatal, and that the mild variant has an optimized furin cleavage site, whereas the severe variant has a mutated or even missing furin cleavage site:
For example, the feline enteric coronavirus (FECV), responsible for a milder and localized form of enteric infection in the infected cat, carried a highly optimized furin cleavage site at S1/S2. In contrast, in the spike protein of the feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV), that caused systemic infection and death of the infected cat, the polybasic insert was either completely lost or found mutated.
It goes on to state that the mild form (FECV) has a furin cleavage site with the sequence RRARR↓ (note that this does not match the sequence PRRAR↓ which the Wikipedia article claims is identical):
The presence of a furin cleavage site RRARR↓S in the feline spike protein of the less infectious strain FECV and the presence of PRRAR↓S in the SARS-CoV-2 prompted us to analyse the sequences more carefully.
It also states that of the two feline coronavirus variants, SARS-CoV-2's cleavage site is more similar to the mild variant's site (which as shown above does not have an identical furin cleavage site):
Thus the polybasic insert of CoV-2 spike protein is closer to that of the spike protein of the milder feline coronavirus but carries crucial substitutions that are either uncommon or are disfavored in classical Furin substrates.
This clearly shows that the cited paper does not support the claim made in this article that the PRRAR↓ furin cleavage site present in SARS-CoV-2 is identical to the furin cleavage site in the feline coronavirus. It even appears that not only is the claim not supported by that source, but that the claim may even be incorrect (according to the statements from the source). Moulding ( talk) 21:11, 31 January 2023 (UTC)
- Why don't we just say "nearly identical" since it's only one proline off? And other source say they're very similar:
[26]
[27]Indeed, the second source there says:
For instance, a similar P-R-R-A-R motif in the spike of a feline CoV has been observed to be encoded with a CGG-CGA for the double Arginine (Bank-Wolf et al. 2014). In this case, a single mutation could change the CGG-CGA to a CGG-CGG.
— Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 21:54, 31 January 2023 (UTC)- The second source refers only to the general PRRAR motif found in some FIPV sequences, not the entire cleavage sequece. As can be seen in the original source graphic, the entire cleavage sequence that matched that motif in FIPV was PRRARM↓S, which still is not identical to PRRAR↓S. It also shows that the consensus sequence appears to be SRRSRR↓S (which is not at all similar to SARS-CoV-2's sequence, and it may be misleading for this Wikipedia article to suggest otherwise).
- Original source graphic:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3713968/figure/F2/
Moulding (
talk) 23:06, 31 January 2023 (UTC)
- I'm just gonna change the text to be "highly similar" to, since they are quite similar in the sense of BLOSUM similarity. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 01:57, 1 February 2023 (UTC)
Airborne
I changed the lead to clarify that SARS-CoV-2 is airborne. Sparkie82 ( t• c) 23:46, 22 February 2023 (UTC)
small correction
Pardon the newb comment but I’m used to making small edits as I read Wikipedia articles, but it looks like this article isn’t editable to me.
In Origins it says “… published on Nature …”, should be “in”. Hambolger ( talk) 14:57, 9 March 2023 (UTC)
 Done thanks for the help —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:07, 9 March 2023 (UTC)
Done thanks for the help —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:07, 9 March 2023 (UTC)
Edit request: Addition of {{Update section}} template to variants section
This
edit request to
SARS-CoV-2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Please add "{{Update section|date=April 2023}}" after "{{Main|Variants of SARS-CoV-2}}"
Why? The variants section is very much out of date. The statement "Nextstrain divides the variants into five clades (19A, 19B, 20A, 20B, and 20C), while GISAID divides them into seven (L, O, V, S, G, GH, and GR)." is out of date since at least March 2021 when there were already new GISAID clades GV and GRV, see https://gisaid.org/resources/statements-clarifications/clade-and-lineage-nomenclature-aids-in-genomic-epidemiology-of-active-hcov-19-viruses/ AncientWalrus ( talk) 20:14, 24 April 2023 (UTC)
 Done
Actualcpscm (
talk) 20:39, 24 April 2023 (UTC)
Done
Actualcpscm (
talk) 20:39, 24 April 2023 (UTC)
Edit request: Incorrect reference for WHO origin report
This
edit request to
SARS-CoV-2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Reference 87 is not correct to support the following statement: Introduction through the food supply chain and the Huanan Seafood Market was considered another possible, but less likely, explanation.
. The provided reference is Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) but should be WHO-convened Global Study of Origins of SARS-CoV-2: China Part.
Please replace the reference with this one: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-convened-global-study-of-origins-of-sars-cov-2-china-part-joint-report.pdf AncientWalrus ( talk) 11:55, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
 Done
[28] —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 12:21, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Done
[28] —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 12:21, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Origin update?...
From the article's intro: "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin and has close genetic similarity to bat coronaviruses, suggesting it emerged from a bat-borne virus."
The citation provided there though (#18) is dated 2020, when the pandemic was still quite new, and our understanding of the virus and its origins were much more limited. We now have US government agencies, like the Energy Dept in the recent report, saying that a lab leak origin is more likely. So I would suggest that this part of the intro be updated, rewritten, and much newer citations used. - 2003:CA:871C:D28:77AA:E11E:9B4:E4E6 ( talk) 11:32, 28 February 2023 (UTC)
- See: COVID-19 lab leak theory and Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 where this discussion is more appropriately placed. I'll bring the consensus wording from those pages. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 13:28, 28 February 2023 (UTC)
Early origin
Found a review of early detections, including viral DNA from a skin sample in Italy November 12, 2019. https://gh.bmj.com/content/7/3/e008386.long Sennalen ( talk) 21:27, 5 March 2023 (UTC)
- The authors themselves describe how much false positives likely impacted these results:
So yes, it's certainly possible these are real, but they are also very far from proven. The sequencing data does also predict an emergence into humans in late October/early November based on mutation rates: [29] [30] [31] — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 22:38, 5 March 2023 (UTC)laboratory evidence for early circulation is often dismissed and labelled as a result of false-positive testing. Antibody detection results can indeed be affected by the presence in sera of antibodies which, although able to recognise SARS-CoV-2 antigens, were induced by other agents.12 However, the presence of SARS-CoV-2 neutralising activity in these sera and the fact that several patients presented more than one class of antibodies recognising SARS-CoV-2 suggest that, although some cross-reactivity should be taken into account, at least some of the sera could contain antibodies induced by a prior SARS-CoV-2 infection... PCR-based methods are highly sensitive and, therefore, more prone to false-positive results.
- That's one mode of testing. Evidence was found in sera antibodies and RNA skin samples from November and sewage two weeks later. There were no positives in June-August. It's not an isolated false positive, but a body of evidence consistent with the same timeline. Sennalen ( talk) 23:28, 5 March 2023 (UTC)
- @
Shibbolethink: No real harm in reastating it, but the part you added wasn't missing.
Sennalen (
talk) 20:50, 10 March 2023 (UTC)
- I think wikipedia policy makes it clear that we should always put mainstream criticisms of things next to their mention whenever possible, and not separate them so as to de-emphasize or isolate criticism. That's why I made the edit I did, even if I do think the addition is a good one to the article. I think it should probably be integrated more with that paragraph, though, as it currently reads weird wrt the later sentences about December of 2019... Given that most sources place the beginning of the pandemic in late November, early December. I am happy to help fix it but I also think you are well-equipped to do so — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 20:55, 10 March 2023 (UTC)
- As a subject matter expert, early detections outside of China before 2019 are not taken seriously. Everything starting from "The Lombardy region..." until "..and RNA sequencing" should in my opinion be removed as WP:UNDUE. One single review "Waiting for the truth" is used almost exclusively for the whole paragraph. It has only been cited 10 times in more than a year, which is very little for a review in general and in particular on the hot topic of COVID. AncientWalrus ( talk) 21:50, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
Paragraph on early detections outside of China
The whole paragraph about putative early detections of SARS-CoV-2 genome fragments in Italy in the autumn of 2019 should be removed. It is entirely based on primary research. While it may appear that the most cited reference is a review, that review article was written by the same authors who did the original research the review is reviewing.
For a topic with such extensive secondary and tertiary coverage in reputable science journalism, such a not-widely cited review does not justify a paragraph in this article.
I already touched on this briefly in the higher up topic
Early origin. Thanks @
Bon courage for getting started on this
here but I think we should go much further by removing it altogether. If at all, it should get a minor mention in the separate origins article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:14, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I agree, if anything it deserves a very short mention, but we probably overemphasize the research here. Any mention of it requires heavy context about it being speculative and possible false positives, but that would create an overall too-long mention. So I agree with your suggestion to cut it. —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 12:16, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- There does seem to be a review cited, but it's an
WP:EXCEPTIONAL claim given way too much credence here.
Bon courage (
talk) 12:36, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- The review didn't get much traction at all. I couldn't find any mention of the early detection theory in any Science journal news article, which is a good proxy for what is considered reasonable by the science community. The
Lancet Commission gives it one sentence
Whether identifiable cases appeared earlier than December, 2019, is unknown.
in a long article. None of the reports were published in top journals either. The best independent coverage I could find is Wired which closes withBut it’s clear that the evidence so far isn’t the most robust. “Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence,” says Jonathan Stoye, a virologist at the Francis Crick Institute. “I’m not convinced that a dodgy piece of data on top of another dodgy piece of data on top of another dodgy piece of data leads one to a firm conclusion.”
AncientWalrus ( talk) 13:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)- Yeah I would overall say it is UNDUE for such a top-level summary article like this. I agree a short mention in
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 could be appropriate if worded in a DUE and NPOV manner. —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 13:12, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
 Done Excised.
Bon courage (
talk) 13:48, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Done Excised.
Bon courage (
talk) 13:48, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Yeah I would overall say it is UNDUE for such a top-level summary article like this. I agree a short mention in
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 could be appropriate if worded in a DUE and NPOV manner. —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 13:12, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- The review didn't get much traction at all. I couldn't find any mention of the early detection theory in any Science journal news article, which is a good proxy for what is considered reasonable by the science community. The
Lancet Commission gives it one sentence
- There does seem to be a review cited, but it's an
WP:EXCEPTIONAL claim given way too much credence here.
Bon courage (
talk) 12:36, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Lab leak theory
The fact that this page doesn’t even mention the possibility that the virus originated in a lab is baffling, given that there are a number of credible experts who have stated it is plausible, not to mention the U.S. intelligence agencies who’ve concluded it’s probable. The complete omission of this viewpoint calls into question the neutrality and objectivity of the entire article. 68.12.22.29 ( talk) 04:11, 26 April 2023 (UTC)
- It also doesn't mention non-lab origins. In fact, it makes no suggestion about the origin. It does mention the seafood market, but does not, as the CIA likes to say, confirm or deny such explanations. Some people (but mostly not the article) mention natural origin. Chinese farms are far from natural, so it doesn't seem likely that it is natural. Virologists for many years have been expecting a new pandemic flu virus from China. Among others, that slowed down the reaction to Covid. Note that the origin of Ebola still has not been found, over many more years. But yes, China isn't helping as much as they could. Gah4 ( talk) 08:43, 26 April 2023 (UTC)
- The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue. I raised this question more than a year ago and made well-sourced changes to the article that reflected the changing consensus. It got me banned by aggressive editors.
StN (
talk) 22:04, 28 April 2023 (UTC)
- I’d say we are heading for a mention on this as there are more reliable sources discussing e.g. the BBC.
- If you were basing some new text on the current media flurry I think we would need a little more time to see how it develops and to avoid suggestions that it’s recentism or news and because we have only got to the point of “don’t rule out” - frustrating as that may be seeing as you have waited a year already.
- This from The Scientific American seems to sum up the position well and I’d support an addition to our text based around this or similar.
- “At least eight U.S. intelligence agencies have conducted their own investigations of the virus’s origins. Four agencies concluded a natural spillover from animals is most likely, two favor a lab leak, and two are undecided. U.S. president Joe Biden recently signed a bill requiring U.S. government information related to COVID origins to be declassified.”
- It’s a reliable source but beware that over egging the lab escape possibility would be undue, (as our current text is because it doesn’t really mention it)
- I think the article should have been more open minded from the start but there was initially a pushback on the lab idea because Trump said it - and for some that automatically makes it wrong.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 11:08, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- BTW we do have other articles on this (see
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 for example) that underplay the possibility of a lab release.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 11:14, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
Please read WP:IDHT and then read the contribution directly above yours.I misread something, so I am striking this. There was actually no pro-science contribution in this thread until then, only lableaker voices and one uncertain one. Alerting WP:FTN now. -- Hob Gadling ( talk) 07:11, 31 May 2023 (UTC)most likely of zoonotic origin
is what the reliable sources say. -- Hob Gadling ( talk) 11:55, 30 May 2023 (UTC)- Also, even if the spillover didn't happen in the market, but e.g. from a bat in the lab, it would still be zoonosis. The only hypothesis that I can think of that doesn't fall under "zoonosis" would involve engineering, which is only a subset of the various theories summarized under the lab leak umbrella.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:13, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- And I get that it has to be zoonosis in the sense of 'natural' - but that is missing the point surely when this lab leak possibility involves human agency (or incompetence etc.) rather than a naturally occurring event.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 15:36, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- I guess my reply was to @
StN who wrote
The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue.
AncientWalrus ( talk) 18:32, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- I guess my reply was to @
StN who wrote
- And I get that it has to be zoonosis in the sense of 'natural' - but that is missing the point surely when this lab leak possibility involves human agency (or incompetence etc.) rather than a naturally occurring event.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 15:36, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Have read IDHT. I'm afraid I don't get your point (really). How should I have phrased?
- In response to StN I am saying that there are reliable sources reporting government agencies saying 'lab leak' and discussing how to include. Shouldn't I? Lukewarmbeer ( talk) 15:34, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Also, even if the spillover didn't happen in the market, but e.g. from a bat in the lab, it would still be zoonosis. The only hypothesis that I can think of that doesn't fall under "zoonosis" would involve engineering, which is only a subset of the various theories summarized under the lab leak umbrella.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:13, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- BTW we do have other articles on this (see
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 for example) that underplay the possibility of a lab release.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 11:14, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- I politely disagree with @
Gah4's statement above:
The article does discuss origin scenarios:It also doesn't mention non-lab origins. In fact, it makes no suggestion about the origin. It does mention the seafood market, but does not, as the CIA likes to say, confirm or deny such explanations. Some people (but mostly not the article) mention natural origin.
- a) Intermediate host:
A March 2021 WHO-convened report stated that human spillover via an intermediate animal host was the most likely explanation, with direct spillover from bats next most likely.
- b) Food supply chain:
Introduction through the food supply chain and the Huanan Seafood Market was considered another possible, but less likely, explanation.
- c) Huanan Market being source:
An analysis in November 2021, however, said that the earliest-known case had been misidentified and that the preponderance of early cases linked to the Huanan Market argued for it being the source.
- I consider it
WP:DUE to mention the fact that a considerable number of leading scientists consider a laboratory incident/accident plausible. For example, it may be worth mentioning this letter in
Science criticizing the WHO report by saying that
[the theory of a laboratory incident] was not given balanced consideration
and further stating:We must take hypotheses about both natural and laboratory spillovers seriously until we have sufficient data
. This letter was discussed in secondary sources, e.g. WSJ. - We do not get into the details, however, it would be good to state that a laboratory incident/accident is one of the origin hypotheses being considered.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 18:58, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- The "food supply chain" hypothesis is taken seriously by far fewer scientists than a lab leak. Yet it gets mentioned in the article. Hard to explain. So either it has to go or lab incident/accident should get a mention as well. Even former China CDC head
George F. Gao now states that a lab leak shouldn't be ruled out, see today's
BBC article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 19:27, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Great. Do we have any strong objections to the lab leak being a possibility?
- If not lets get it in.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 20:29, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Don't rush it, there may well be objections by e.g. @
Hob Gadling and/or @
Gah4.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 21:41, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- I suppose not to it being a possibility, but I don't believe a strong possibility. It is possible for me to buy a Powerball ticket and win, but not likely. Gah4 ( talk) 00:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Otherwise, I suppose I don't disagree with the polite disagreement. Not that I said so much that one could agree or disagree with.
Gah4 (
talk) 00:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Well, you said the article doesn't discuss origin scenarios. But it does, it even mentions the food supply chain hypothesis which is not believed by anyone I know. AncientWalrus ( talk) 11:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I should try to find a
WP:RS for virologists ten or so years ago, mentioning Chinese farms as the source of the next global pandemic. And, likely coming from that, a fictional story with Wuhan as the center of a pandemic source.
Gah4 (
talk) 00:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I think if we're going to mention the lab-leak stuff at all, per
WP:FRINGESUBJECTS we would need to bring in the mainstream context: that there is zero evidence for it, that there are popular misconceptions about its likelihood, that many LL ideas are conspiracy theories, that it's informed by racist undertones, and that nearly all scientists don't subscribe to it (except maybe in a can't-rule-stuff-out / remote-possibility kind of way). Basically it's just speculation, and best left to the misinformation articles and the specialist LL article.
Bon courage (
talk) 07:22, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- And the origin of Ebola still isn't known. The worst thing about lab-leak, is that many politicians believe that we need to find the origin to stop the next pandemic. Sounds good. But there is no reason to suspect that the next one will have the same origin. There were many who were sure in 2018 that the next world pandemic would be caused by a new flu virus, and planned for that. I suspect that is usual for conspiracy theories. We need to find out who shot JFK, to stop the next assassination. Oh well. Gah4 ( talk) 09:03, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- The fact that there some people take a lab hypothesis to fringe levels should not prevent us from mentioning the non-fringe possibility that the lab may have been involved. I agree that the loudest voices have fringe views, but measured non-fringe views exist, who are not informed by racist undertones (see Science letter). Could you explain why you think the cold chain hypothesis deserves mention? It is considered to be a narrative pushed by the Chinese gov't to deflect blame.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 11:49, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- We link to the Investigations article which has the following in its lede: "Some scientists and politicians have speculated that SARS-CoV-2 was accidentally released from a laboratory. This theory is not supported by evidence." I would not object to including that wording here.
Bon courage (
talk) 11:57, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- That's a good idea. Though maybe we should also add US government agencies which may or may not have non-public evidence. If I correctly understand the scientists asking for investigations of all possible origins, including accidental laboratory release, they agree that there is no public evidence for such a release. However, they believe that the evidence for alternative hypotheses may not be as strong as reported.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:05, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I would strongly oppose adding the "US agencies" talking point, as being undue.
Bon courage (
talk) 12:27, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Given the involvement of state actors and lack of transparency, see e.g.
Chinese scientists echoing party line, this isn't a question that science alone can argue. Intelligence agencies may well have relevant non-public evidence. But I understand that this is best placed in the origins article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 13:04, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Saying that "This theory is not supported by evidence." or that "there is zero evidence for it" is objectively false. There is plenty of evidence of a lab leak. Maybe not evidence you find convincing, but evidence none the less.
Bonewah (
talk) 13:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Yeah, it's the same kind of evidence that the moon landing was faked. Which is why the sources say what they do.
Bon courage (
talk) 13:42, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Multiple government agencies believe in the equivalent of the moon landing? I disagree.
Bonewah (
talk) 13:44, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- "Some bureaucrats believe in X" is not evidence for X. -- Hob Gadling ( talk) 13:47, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Of course, but what US spook agencies say they "believe" has nothing to do with whether there's evidence. Follow the sources rather than trying to interpret/speculate. Bon courage ( talk) 13:47, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Multiple government agencies believe in the equivalent of the moon landing? I disagree.
Bonewah (
talk) 13:44, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- "Zero evidence" is scientist-speak for "only shitty evidence that one would expect in any case, whether the LL idea is true or not, and which therefore does not count". -- Hob Gadling ( talk) 13:47, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Saying that "This theory is not supported by evidence." or that "there is zero evidence for it" is objectively false
It seems you have a problem with our sources then, as that's what our highest quality sources say. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 15:54, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Yeah, it's the same kind of evidence that the moon landing was faked. Which is why the sources say what they do.
Bon courage (
talk) 13:42, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Possible existence of non-public evidence is not relevant. Wikipedia is supposed to summarize the published knowledge of mankind, not speculation. --
Hob Gadling (
talk) 13:47, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- If an agency makes an estimation based on non-public evidence and that is reported in RS then the agency's opinion can in theory be included if due. The evidence itself doesn't need to be public. My point is that the question of origin is not one that is intrinsically scientific. Scientific methods can help find an answer, but there may well be other sources of information that aren't scientific, like intelligence sources. There is no categorical difference between a question like "Who was SARS-CoV-2 patient zero?" and "Who piloted the drone that crashed over the kremlin?".
AncientWalrus (
talk) 13:55, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- All this about which out of which US agencies say what with whatever degrees of confidence and disagreement is in the LL article. The trouble is just saying "The ${agency} thinks so!" is unbalanced and reductive & makes it look like this is uber-important. Which is why LL people say it over and over and over again. This stuff isn't even mentioned in the investigation article lede so going over it here would be doubly undue.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Saying that "there is no evidence of LL" is unbalanced and reductive & makes it look like the issue is decided, which it is not.
Bonewah (
talk) 14:12, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- It's just accepted knowledge as published in reliable sources, so Wikipedia reflects it. It would only make the matter look "decided" to a reader with no elementary understanding of logic, since evidence may emerge in time.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:16, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Are you claiming that its "accepted knowledge" that the LL theory has no supporting evidence?
Bonewah (
talk) 14:29, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- "Accepted knowledge as published in reliable sources". See the
COVID-19 lab leak theory article for further details/sources.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:49, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Well if you are proposing an edit along these lines, then i oppose it. At least as far as i can discern what you seem to be proposing. If not, them maybe we can just stop.
Bonewah (
talk) 15:07, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- To repeat, I would not object to copying the consensus text/refs to be in sync with the Investigations article - specifically: "Some scientists and politicians have speculated that SARS-CoV-2 was accidentally released from a laboratory. This theory is not supported by evidence." Also happy to leave any mention of LL out.
Bon courage (
talk) 15:18, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Then i object. Specifically to the line "This theory is not supported by evidence."
Bonewah (
talk) 15:39, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Why? Personal objections don't count. We're not going to use this article to create a WP:POVFORK; so what we say has to be in sync with the other more detailed articles on the topic, and present the mainstream view prominently to be neutral, which is a must. Bon courage ( talk) 15:41, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Then i object. Specifically to the line "This theory is not supported by evidence."
Bonewah (
talk) 15:39, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- To repeat, I would not object to copying the consensus text/refs to be in sync with the Investigations article - specifically: "Some scientists and politicians have speculated that SARS-CoV-2 was accidentally released from a laboratory. This theory is not supported by evidence." Also happy to leave any mention of LL out.
Bon courage (
talk) 15:18, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Well if you are proposing an edit along these lines, then i oppose it. At least as far as i can discern what you seem to be proposing. If not, them maybe we can just stop.
Bonewah (
talk) 15:07, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- "Accepted knowledge as published in reliable sources". See the
COVID-19 lab leak theory article for further details/sources.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:49, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Are you claiming that its "accepted knowledge" that the LL theory has no supporting evidence?
Bonewah (
talk) 14:29, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- It's just accepted knowledge as published in reliable sources, so Wikipedia reflects it. It would only make the matter look "decided" to a reader with no elementary understanding of logic, since evidence may emerge in time.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:16, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Saying that "there is no evidence of LL" is unbalanced and reductive & makes it look like the issue is decided, which it is not.
Bonewah (
talk) 14:12, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- All this about which out of which US agencies say what with whatever degrees of confidence and disagreement is in the LL article. The trouble is just saying "The ${agency} thinks so!" is unbalanced and reductive & makes it look like this is uber-important. Which is why LL people say it over and over and over again. This stuff isn't even mentioned in the investigation article lede so going over it here would be doubly undue.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- If an agency makes an estimation based on non-public evidence and that is reported in RS then the agency's opinion can in theory be included if due. The evidence itself doesn't need to be public. My point is that the question of origin is not one that is intrinsically scientific. Scientific methods can help find an answer, but there may well be other sources of information that aren't scientific, like intelligence sources. There is no categorical difference between a question like "Who was SARS-CoV-2 patient zero?" and "Who piloted the drone that crashed over the kremlin?".
AncientWalrus (
talk) 13:55, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Saying that "This theory is not supported by evidence." or that "there is zero evidence for it" is objectively false. There is plenty of evidence of a lab leak. Maybe not evidence you find convincing, but evidence none the less.
Bonewah (
talk) 13:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Given the involvement of state actors and lack of transparency, see e.g.
Chinese scientists echoing party line, this isn't a question that science alone can argue. Intelligence agencies may well have relevant non-public evidence. But I understand that this is best placed in the origins article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 13:04, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I would strongly oppose adding the "US agencies" talking point, as being undue.
Bon courage (
talk) 12:27, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- That's a good idea. Though maybe we should also add US government agencies which may or may not have non-public evidence. If I correctly understand the scientists asking for investigations of all possible origins, including accidental laboratory release, they agree that there is no public evidence for such a release. However, they believe that the evidence for alternative hypotheses may not be as strong as reported.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:05, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- We link to the Investigations article which has the following in its lede: "Some scientists and politicians have speculated that SARS-CoV-2 was accidentally released from a laboratory. This theory is not supported by evidence." I would not object to including that wording here.
Bon courage (
talk) 11:57, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I think if we're going to mention the lab-leak stuff at all, per
WP:FRINGESUBJECTS we would need to bring in the mainstream context: that there is zero evidence for it, that there are popular misconceptions about its likelihood, that many LL ideas are conspiracy theories, that it's informed by racist undertones, and that nearly all scientists don't subscribe to it (except maybe in a can't-rule-stuff-out / remote-possibility kind of way). Basically it's just speculation, and best left to the misinformation articles and the specialist LL article.
Bon courage (
talk) 07:22, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Don't rush it, there may well be objections by e.g. @
Hob Gadling and/or @
Gah4.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 21:41, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Wikipedia doesn't care what you or I think. It cares about what the sources say. And the sources say there is "
no evidence exists to support such a notion
" [32] and "there is no good evidence
" [33] and "there's not a single piece of data suggesting
" that the lab leak is true. [34] — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 15:58, 31 May 2023 (UTC)- You're mostly quoting the same people, author of [6] is also author of [4]. Another source says:
Bloom, however, asserts that the evidence for a market origin for the current coronavirus pandemic is not conclusive, and both a laboratory origin and natural spillover should be viewed as possible causes of future pandemics.
WaPo (this is from 2023, your first two sources are from 2021). AncientWalrus ( talk) 16:58, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- You're mostly quoting the same people, author of [6] is also author of [4]. Another source says:
- The "food supply chain" hypothesis is taken seriously by far fewer scientists than a lab leak. Yet it gets mentioned in the article. Hard to explain. So either it has to go or lab incident/accident should get a mention as well. Even former China CDC head
George F. Gao now states that a lab leak shouldn't be ruled out, see today's
BBC article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 19:27, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue
That's what our most reliable highest quality sources state. E.g. [35] [36] [37] [38] [39]Wikipedia is not about "the Truth". It's about having verifiability to what our highest quality sources say. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 15:53, 31 May 2023 (UTC)- Exactly, Bonewah is apparently engaging in
WP:PROFRINGE advocacy. Wikipedia reflects sources, not editor opinion.
Bon courage (
talk) 16:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- @Shibbolethink Can you clarify something for me? Just above you said "
The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue
That's what our most reliable highest quality sources state." Do you mean by that the "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin,"? In other words, the statement ""Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin" is what our most reliable highest quality sources state? Bonewah ( talk) 16:19, 31 May 2023 (UTC)- Yes. Per WP:SYNTHNOTSUMMARY and WP:RS/AC. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 16:28, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- @Shibbolethink Can you clarify something for me? Just above you said "
- Exactly, Bonewah is apparently engaging in
WP:PROFRINGE advocacy. Wikipedia reflects sources, not editor opinion.
Bon courage (
talk) 16:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue. I raised this question more than a year ago and made well-sourced changes to the article that reflected the changing consensus. It got me banned by aggressive editors.
StN (
talk) 22:04, 28 April 2023 (UTC)
| This is an archive of past discussions. Do not edit the contents of this page. If you wish to start a new discussion or revive an old one, please do so on the current talk page. |
| Archive 5 | ← | Archive 9 | Archive 10 | Archive 11 |
Date of index case?
There has been wikidiscussions on what is the established date of the Wuhan index case in mainstream scientific reports. The current version of the page does not include any information on the index case. Previous to this lack of information the article said the index case emerged on Dec 1 2020, based on a a non-ideal RS (a book from a non-specialist that tangentially deals with the index case). The "Dec 1"-source was dicussed here, where I reasonably argued that it was a weak source with a consensus that it was not ideal.
There are two MEDRS that say the index case happened on Dec 8 2020, which coincidentally is a late date that goes against the lab leak hypothesis (I've been accused of POV editing and this edit is a counterexample). The MEDRS are Hu et al (2020), and the WHO report. RandomCanadian please stop disrupting the inclusion of this fact, there are DS sanctions in place for this page, I believe you are aware of them. I propose we use this two MEDRS supplemented by citing also the Washington post recent article on it, as long as it goes in the same direction and MEDRS does allow to cite RS along MEDRS in this case.
Forich (
talk) 20:15, 9 July 2021 (UTC)
- There is considerable disagreement among experts in MEDRSes about this December index case, and some
agreementMEDRSes suggest that there likely is no single index case. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] The considerable pre-Huanan seafood market circulation of the virus in Wuhan, and the existence of the A and B variant clades, both point to multiple introductions of the virus into the human population. See also this very illuminating episode of This Week in Virology, which reviews much of this evidence. (Episode mp3 and transcript). The good stuff starts around 18 minutes in.-- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 21:02, 9 July 2021 (UTC)(edited 03:48, 10 July 2021 (UTC)) - Forich: the WaPo (the one source you cited - and to which you attributed the statement -
not my job to go hunting through the other ones) is not a MEDRS, so I don`t see why you`re objecting to me removing it and content based on it (if you're referring to my recent edit - otherwise I have no clue what it could be) and then arguing for including content based on MEDRS (I note that there doesn't appear to be a consensus amongst these that the index case happened on 8 December - in fact, the more recent ones seems to argue it happened at least a couple of weeks earlier, and that it likely hasn't been identified yet). I note that the
COVID-19 pandemic section already seems to have all the relevant information for that aspect, we should maybe copy and expand from there.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 02:44, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- @
Shibboleth:, I believe we have a miscommunication here and I'd like to invite you to read again the definition of
index case. It is by definition the first documented patient. With key emphasis on documented. It need not coincide with the person where the spillover event happened, which may be what the evidence you are citing seem to be referring to. I have further comments, but they may not matter if the source of our disagreement is semantic.
Forich (
talk) 20:41, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- @
RandomCanadian:, I am sorry you are absolutely right, your removal is not a violation of any rules and seems reasonably well-explained. I will strikethrough your name and I apologize again. I'll need to check the history to see who was the editor reverting all those edits, they do deserve a warning not you.
Forich (
talk) 20:46, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- Hi, Forich, you don't need to explain to me what an index case is. The sources I provided above demonstrate there is controversy about the first documented case of SARS-COV-2, and indeed one of the provided sources points to the December 1st case, which has no association with the wet market. I believe this controversy about which case Dec 1st or 8th or an earlier November case of an elderly man in the outer province (I believe first reported in the SCMP) counts as "Patient Zero" is why we basically have three options:
- @
RandomCanadian:, I am sorry you are absolutely right, your removal is not a violation of any rules and seems reasonably well-explained. I will strikethrough your name and I apologize again. I'll need to check the history to see who was the editor reverting all those edits, they do deserve a warning not you.
Forich (
talk) 20:46, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- @
Shibboleth:, I believe we have a miscommunication here and I'd like to invite you to read again the definition of
index case. It is by definition the first documented patient. With key emphasis on documented. It need not coincide with the person where the spillover event happened, which may be what the evidence you are citing seem to be referring to. I have further comments, but they may not matter if the source of our disagreement is semantic.
Forich (
talk) 20:41, 10 July 2021 (UTC)
- There is considerable disagreement among experts in MEDRSes about this December index case, and some
- A) Declare an index case, disregarding the entire controversy.
- B) Report the entirety of this controversy, weighted as it is in secondary RSes and MEDRSes. With appropriate wording "purported" "claimed" etc. Per WP:RSUW. We kinda already do this in the Epidemiology section of this article, I just noticed. And I think it's actually done quite well.
- C) Wait for the dust to settle a bit more, and for more serology/blood sample PCRs to be described in the literature that help establish if there was an earlier index case. In the meantime, remove all the current coverage of it that we have, and don't add any more. Per WP:RECENTISM.
- Personally I vote for Option B. It would be inappropriate for us to remove the coverage we have, but I think it would also be inappropriate for us to "declare" an index case when we know controversy exists.-- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 17:06, 11 July 2021 (UTC)
- I have read again all the sources you provided (primary sources, not MEDRS, btw) and none of them suggest controversy on the first documented case, ergo, index case in Wuhan. They do suggest controversy on the date of first cases, plainly, which are currently undocumented (unfortunately). If my interpretation of no controversy on index case is true, your proposals, as they are now, are out of place. If we are to slightly modify them to make more sense with de index/documented/undocumented terminology, it would be something like this:
- A) Declare that the exact or approximate date of the first case is known, disregarding the entire controversy.
- B) Report the entirety of this controversy, weighted as it is in secondary RSes and MEDRSes. With appropriate wording "purported" "claimed" etc. Per WP:RSUW. We kinda already do this in the Epidemiology section of this article, I just noticed. And I think it's actually done quite well.
- C) Wait for the dust to settle a bit more, and for more serology/blood sample PCRs to be described in the literature that help establish if there was an earlier first case. In the meantime, remove all the current coverage of it that we have, and don't add any more. Per WP:RECENTISM.
- I'd propose option D): describe what the currently earliest known cases are ("earliest known" is not the same thing as "index" case), attributing uncertainty and doubts about these where necessary, and adding that the scientific literature currently suggests that the real index case (which likely isn't known at this time) was at some point between October and November 2019. Or, basically, take the following from COVID-19 pandemic#Epidemiology:
The earliest known person with symptoms was later discovered to have fallen ill on 1 December 2019, and that person did not have visible connections with the later wet market cluster.[43][44] However, an earlier case of infection could have occurred on 17 November.[45] Of the early cluster of cases reported that month, two-thirds were found to have a link with the market.[46][47][48] Molecular clock analysis suggests that the index case is likely to have been infected with the virus between mid-October and mid-November 2019.[49][50]
- And expand as needed to cover more detail. This will also help updating in the other direction (back into the pandemic article) once we've ironed it out here. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:55, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- Option B. And I think we could slightly modify what
Shibbolethink said above and just use that in the article. He provided citations and everything.
There is considerable disagreement among experts in MEDRSes about this December index case, and some agreement MEDRSes suggest that there likely is no single index case.[1][2][3][4][5][6] The considerable pre-Huanan seafood market circulation of the virus in Wuhan, and the existence of the A and B variant clades, both point to multiple introductions of the virus into the human population.
– Novem Linguae ( talk) 02:10, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
TWIV transcript on date of index case
The following text is from a podcast (This Week in Virology #760, may 26th 2021) with three members of the WHO team.
-Marion Koopmans: "a lot of the work tried, the epi work, really aimed at trying to dig back, so what was the earliest case, that is recognized. That was the process. Now the earliest confirmed recognized case is a person that survived, a person that we also met, but the epi work suggest that there have been many more cases that have not been recognized, there is also no sequence data for those. And that's part of the digging back that you would want to do."
-Rich Kondit: "So what were the earliest cases and to what extent or not do they have any association with the market?"
-Thea Kolsen Fischer: "So the first, the earliest now recognized case had an onset date of December 8th with no contact with neither the Huanan wet market or other markets. The closest kind of market contact was a mother who had cooked for the [first] case and who has bought some of her cooking ingredients at an unnamed market. But the [first] person had no contact with markets."
The WHO report, our best source on the matter, says there were three alleged cases from befor Dec 8th, but they qualify them as "excludable on the basis of the clinical features of their illnesses".
So according to this information, again, the best source we have, a tweaked version that follows the one from RandomCanadian would look like:
The earliest known person with symptoms was later discovered to have fallen ill on
18 December 2019, and that person did not have visible connections with the later wet market cluster. However,anat leastonethree earlier cases of infection could have occurred before the 8th of december. Of the early cluster of cases reported that month, two-thirds were found to have a link with the market. Molecular clock analysis suggests that the index case is likely to have been infected with the virus between mid-October and mid-November 2019
Forich ( talk) 21:18, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- @ Forich: What about just dropping the precise dates? That seems wiser than documenting a controversy over whether the first known case was on the 1st or the 8th of December, which, 1 1/2 year after the events in question, doesn't seem a particularly important, encyclopedic distinction. So:
The earliest known person with symptoms was later discovered to have fallen ill in early December 2019, and that person did not have visible connections with the later wet market cluster. However, a few earlier cases of infection could have occurred.[45] Of the early cluster of cases reported that month, two-thirds were found to have a link with the market.[46][47][48] Molecular clock analysis suggests that the index case is likely to have been infected with the virus between mid-October and mid-November 2019.[49][50]
- And then we can work on expanding that here with more details where/if needed. Also, I note that MEDRS is not required for everything. A newspaper (with attribution, if necessary) is enough to say "there were reports of earlier cases", although we should then use proper SCHOLARSHIP to determine how to describe those reports RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:43, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
- @ RandomCanadian:, I can see how that is reasonable if there actually was a controversy on the documented earliest case. But in MEDRS, there is no controversy on that, just the uncertainty of earlier undocumented cases from the molecular clock start-date. Here is the temporal sequence of the coverage of the earliest known case:
- The Lancet article said the first patient presented an onset of symptoms on Dec 1st (not MEDRS). The point of having a MEDRS check the facts on a primary source is to have more solid confirmation that the basic fact holds when scrutinized by a second set of expert eyes.
- Sciencemag news report verbatim the result from Lancet on Dec 1. Neither are MEDRS.
- A SCMP reporter alleged having seen in government reports a Nov 17th case. Not MEDRS. If we had no MEDRS, I'd go for an attributed inclusion of this, for sure. But we have MEDRS that say different.
- Allam (2020), admittedly doing a better job than Sciencemag and SCMP, documents the Dec 1st from Lancet together with the alleged Nov case from SCMP. But, still he is not an expert, he is an architect who wrote a non-MEDRS book about the political economy of the pandemic, and the first chapter included a timeline of events as a preface to the main chapters of the book. He is not qualified to say, for example, whether the Dec 1st case symptoms were from a coincidental flu or from COVID-19. The publisher is very reputable (Elsevier) so we can use the facts from the main subject of the book (political economy of the pandemic) in Wikipedia, not the tangential time of the earliest case that he researched
- The WHO report comes out, saying that the first confirmed case had onset of symptoms on Dec 8th, clarifies that the Dec 1st case was excluded "on the basis of the clinical features of its illness". The experts from the WHO-team (maybe the international members, we don't know) took a closer look at the Dec 1st case and said that he was determined to have suffered other illness in early December, contracting the coronavirus later that month with his wife in a family cluster. This is an important correction that leaves no space for controversy, until another MEDRS challenges it.
- By saying that Dec 8th was the earliest known case, inserted in a paragraph with the whole context, I believe we are good. Should the paragraph include the SMCP allegation? Only if it gets repeated in a MEDRS. Allam repeated it, but I don't consider it a MEDRS for the reasons stated already. The WHO team was probably aware of the SCMP allegations when they investigated the early cases in Wuhan, and after having contrasted notes and corroborated sequences and paperwork with the Chinese members, they did not include the SCMP Nov case as a confirmed one. I don't see why we should not trust them on that conclusion.
- On your point that we can use Bryner, 2020; Davidson, 2020, the sources cited in Allam (2020), I don't know them, but of course we can check them out. I'll try to do it if I find the time later.
Forich (
talk) 21:39, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
- This recent-ish paper (primary for its results, but secondary for the "Introduction" section) states that
- On your point that we can use Bryner, 2020; Davidson, 2020, the sources cited in Allam (2020), I don't know them, but of course we can check them out. I'll try to do it if I find the time later.
Forich (
talk) 21:39, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
"Uncertainty still persists around the origin of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the resulting COVID-19 disease. While an origin as a zoonotic spillover in the Huanan Seafood Market, Wuhan, sometime during early December, 2019, has been proposed [1], this has been called into question [2–4]. This uncertainty arises due to both the presence of earlier potential COVID-19 cases, and the fact that most phylogenetic analyses put the most recent ancestor at between mid-November and early December, 2019 [5].
- So the earlier cases are "potential". I say "recent-ish" 'cause the paper was submitted for publication back in September last year, well before the WHO report. @
Shibbolethink: Is such a long delay unusual? The paper does seem to have been picked up by the news, ex.
[1]
[2]. Whether that is a good or bad thing
is another question...
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 02:59, 21 July 2021 (UTC)
- RandomCanadian, I would say....no not that unusual, especially for PLOS Pathogens.
- The higher in impact you go, the longer the review process. And PLOS Pathogens in the medium-to-high range as far as topic-specific virology journals go at ~6. Anecdotally, the Zika paper we published in Science during grad school was submitted in the middle of November of one year and accepted in the middle of March of the next [3], and that was considered "fast."
- This study by Huisman and Smits in 2017 [4] says around 85-90% of natural science/medicine papers are accepted by about 6 months post-submission.
- So I would say Roberts et al (that PLOS Path paper) is on the long end of normal. I bolded "accepted" because that's what really matters. It's kind of irrelevant when they "fit" the paper into their publication queue, that's all on the paper's logistics re: how many papers they fit into each "issue" and how overworked the layout staff are. Roberts et al submitted at the end of September of 2020 and got accepted at the beginning of May 2021. So around 7 months.
- That could easily be explained by a persnickety or delinquent reviewer who sat on the paper too long, while frantically working on their own pandemic-relevant work, or an editor who wanted to wait and see how other similar research shook out before finally saying "yes"... Like I said, long end of normal. If you showed me a paper that took more than a year, I would be more concerned. But also could mean that paper is even more squeaky clean after even closer eyes.
- But overall I think this is a good paper worth using for this purpose, in their intro and their findings eventually when/if they get cited by reviews. In their intro, they cite many of the same sources that we have discussed re: November spread of the virus ( [5] [6] [7]) and, importantly, this paper has also been covered in a few news-based RSes in its few weeks of existence, lending credibility to it as, at the very least, likely not a maligned or fringe viewpoint ( [8] [9] [10] (newsweek))
- I don't think this should be our only source for this, but I think in the context of the other sources discussed, it does start to mount for the inclusion of a sentence on "early pre-market spread" in my opinion...-- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 03:48, 21 July 2021 (UTC)
- So the earlier cases are "potential". I say "recent-ish" 'cause the paper was submitted for publication back in September last year, well before the WHO report. @
Shibbolethink: Is such a long delay unusual? The paper does seem to have been picked up by the news, ex.
[1]
[2]. Whether that is a good or bad thing
is another question...
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 02:59, 21 July 2021 (UTC)
The Sciencemag news extract
The paper, written by a large group of Chinese researchers from several institutions, offers details about the first 41 hospitalized patients who had confirmed infections with what has been dubbed 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). In the earliest case, the patient became ill on 1 December 2019 and had no reported link to the seafood market, the authors report. “No epidemiological link was found between the first patient and later cases,” they state. Their data also show that, in total, 13 of the 41 cases had no link to the marketplace. “That’s a big number, 13, with no link,” says Daniel Lucey, an infectious disease specialist at Georgetown University.
This is not MEDRS. Forich ( talk) 21:20, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- This is a lay-summary of this, which wasn't particularly hard to find - so we can cite both. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:43, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
The SCMP extract
According to the government data seen by the Post, a 55 year-old from Hubei province could have been the first person to have contracted Covid-19 on November 17. From that date onwards, one to five new cases were reported each day. By December 15, the total number of infections stood at 27 – the first double-digit daily rise was reported on December 17 – and by December 20, the total number of confirmed cases had reached 60.
SCMP is not MEDRS. Forich ( talk) 21:32, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- See my post above about not requiring MEDRS for everything. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:43, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
The Allam (2020) book chapter
The earliest date of symptoms for COVID-19, according to a study performed by Huang et al. (2020) and published in the Lancet journal, was December 1, 2019. However, there are other sources (Bryner, 2020; Davidson, 2020) claiming that individuals with similar symptoms may have presented themselves to hospital as early as November. According to the report, by South China Morning Post (Ma, 2020), the first person who presented similar cases was a male patient of 55-year old from the province of Hubei. However, Chinese doctors only came to realize that they were dealing with a new and serious virus late December, when similar symptoms continued to increase every day, and mostly originating from Wuhan. According to the article in Lancet, the first patient, and whom they insist may be the first case, was reported on December 1, 2019, and whom did not have direct link with the Wuhan Seafood Market that has been associated with the origin of the virus. This finding interestingly matches with Ma (2020) who also argues that the November 2019 case was not from Wuhan. The story as to the origin of the virus has fueled much political and social divides and is expected to evolve as further efforts are poured into understanding this crisis.
This source is not a MEDRS because Zaheer Allam, the author of the chapter and book, is an architect that specializes in political economy. He is neither a virologist nor an epidemiologist. The book itself is about the political economy of the pandemic. Forich ( talk) 21:37, 18 July 2021 (UTC)
- What about using the sources given by Allam? The full chapter is here, with refs at the bottom. I note that, despite misgivings about the author's credentials, he seems to have done a decent enough job: "The earliest date of symptoms for COVID-19, according to a study performed by Huang et al. (2020) and published in the Lancet journal, was December 1, 2019. However, there are other sources (Bryner, 2020, Davidson, 2020) claiming that individuals with similar symptoms may have presented themselves to hospital as early as November." isn't that different from our current wording, either. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 03:43, 19 July 2021 (UTC)
I just went WP:Bold and fixed the information. The burden is on editors trying to use different information or with a history of reverting my edit (@ RandomCanadian:, @ Shibbolethink:, @ Alexbrn:) to find MEDRS sources, otherwise please abstain from reverting. Forich ( talk) 21:33, 26 July 2021 (UTC)
- The burden is on those making a change to get consensus for it, per WP:ONUS. Or, as in this case, where the "D" part of BRD appears to have stalled, there's no reason to get stuck in it, and we can just keep making bold edits, assuming that they will not be the final version, until we get to a satisfactory conclusion for everyone. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 00:37, 27 July 2021 (UTC)
- Our current information, which speaks of early cases that pre-date the official Chinese date of 8th December, I believe favors the lab leak a bit, because it puts a stab on one of the alternatives (the Huanan Seafood Market hypothesis). I tried my best to fix the date (I must have tried 10 attempts, including talk page interactions) with no successs, and I guess the Bold, Edit, Discuss cycle has led to this equilibrium of vagueness ("early December" can be anything between 1 to 14). RandomCanadian has answered to an inquiry in his User talk page that he is not cherry picking his uses of MEDRS so I am gonna have to trust him and let this discussion go. We can archive this discussion any time now.
Forich (
talk) 20:31, 5 August 2021 (UTC)
- I think that's a stretch, and would require an RS to back up. Got one? Because we've got other RS that make no link between earlier circulation and the WIV. Bakkster Man ( talk) 21:16, 5 August 2021 (UTC)
- Our current information, which speaks of early cases that pre-date the official Chinese date of 8th December, I believe favors the lab leak a bit, because it puts a stab on one of the alternatives (the Huanan Seafood Market hypothesis). I tried my best to fix the date (I must have tried 10 attempts, including talk page interactions) with no successs, and I guess the Bold, Edit, Discuss cycle has led to this equilibrium of vagueness ("early December" can be anything between 1 to 14). RandomCanadian has answered to an inquiry in his User talk page that he is not cherry picking his uses of MEDRS so I am gonna have to trust him and let this discussion go. We can archive this discussion any time now.
Forich (
talk) 20:31, 5 August 2021 (UTC)
Sources
|
|---|
|
- Not sure why I was pinged here, the proposed source seems unproblematic. What I think we need to avoid is exceptional/fringe claims that the virus was at large in Italy/California/wherever much earlier, and/or that CV19 is just a rebranding of an existing prior disease. Alexbrn ( talk) 02:33, 27 July 2021 (UTC)
- @ Alexbrn:, In your edit comment for your revert of March 29 of 2021 you said: "Rvt. primary research; would need WP:MEDRS" The diff is here, it seems you opposed Pekar et al (2021) then, and now you find it unproblematic. Maybe you made a mistake back then? Forich ( talk) 19:11, 6 August 2021 (UTC)
FCS
FCS : furin-like cleavage site -- 92.184.104.9 ( talk) 18:18, 7 August 2021 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 12 August 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Please add Template:Outdated to the "Infection and transmission" section. It reports only 2020 information. The idea of aerosol transmission is presented as not-yet-confirmed. There are 47 citations before the start of the "Reinfection" subsection: 1 dates from 2010, 41 date from 2020, and just 5 date from 2021. And of those 5, 2 are a case study of a specific person, 1 talks about animals that can get infected, and 2 talk about particles emitted during talking. Most or all items in this section should be relying on 2021 data, because the science is getting updated so fast through extensive research. 174.206.39.24 ( talk) 11:15, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
 Done. will do, but I will also say that these statements probably need better
WP:MEDRS, as "etiology" is explicitly covered under
WP:BMI. To be plain, the statements may require a higher level of sourcing commiserate with scientific journal review articles published in topic-relevant venues. We may not be able to move as fast as the science does as a result. Of course this also means some of these sentences are definitely poorly sourced as it is, even the ones from the past. Appreciate you pointing this out, thank you.--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:55, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
Done. will do, but I will also say that these statements probably need better
WP:MEDRS, as "etiology" is explicitly covered under
WP:BMI. To be plain, the statements may require a higher level of sourcing commiserate with scientific journal review articles published in topic-relevant venues. We may not be able to move as fast as the science does as a result. Of course this also means some of these sentences are definitely poorly sourced as it is, even the ones from the past. Appreciate you pointing this out, thank you.--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:55, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
here are some links to find high quality MEDRS about this topic (SARS-CoV-2 transmission): Find medical sources: Source guidelines · PubMed · Cochrane · DOAJ · Gale · OpenMD · ScienceDirect · Springer · Trip · Wiley · TWL -- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 23:06, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
Typo "Demark"
I'm sorry, if I'm using the talk page the wrong way, but since the article is protected and I couldn't make the edit myself, I would appreciate it, if an experienced member could just fix this little typo.
It's really self-explanatory, there's just a missing "n" in "Demark" that needs to be added. It's in the last sentence of the paragraph in chapter 4.1.1 (Phylogenetics -> Variants).
Thank you very much!
XLix ( talk) 22:18, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
-
 Fixed. thanks--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 22:20, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
Fixed. thanks--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 22:20, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
First paragraph in Epidemiology section
The first paragraph in the Epidemiology section is a near-duplicate to the previous paragraph (in the previous section). I believe it should be removed.— Preceding unsigned comment added by WhamboMPS ( talk • contribs) 15:27, 28 August 2021 (UTC)
Typo in "Epidemiology" section
The "epidemiology" section start with "xVery few drugs" (erroneous "x") Technicolour-dreamboat ( talk) 12:09, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
 Done. Thanks for the heads up.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 18:55, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
Done. Thanks for the heads up.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 18:55, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
Featured picture scheduled for POTD
Hello! This is to let editors know that the featured picture File:Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.jpg, which is used in this article, has been selected as the English Wikipedia's picture of the day (POTD) for September 3, 2021. A preview of the POTD is displayed below and can be edited at Template:POTD/2021-09-03. For the greater benefit of readers, any potential improvements or maintenance that could benefit the quality of this article should be done before its scheduled appearance on the Main Page. If you have any concerns, please place a message at Wikipedia talk:Picture of the day. Thank you! Cwmhiraeth ( talk) 09:45, 20 August 2021 (UTC)

|
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is the virus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Like other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 has four structural proteins, known by the letters S ( spike), E ( envelope), M ( membrane), and N ( nucleocapsid); the N protein holds the RNA genome, and the S, E, and M proteins together create the viral envelope. This colourised transmission electron micrograph shows SARS-CoV-2 virus particles emerging from the surface of cells cultured in a laboratory. The crown-like spikes on the outer edge of the virus particles give coronaviruses their name, derived from Latin corona, 'crown'. Photograph credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Rocky Mountain Laboratories
Recently featured:
|
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 9 September 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
In the lead, replace Virus with Emergent virus. 79.70.190.198 ( talk) 08:30, 9 September 2021 (UTC)
 Not done for now: please establish a
consensus for this alteration
before using the
Not done for now: please establish a
consensus for this alteration
before using the {{ edit extended-protected}}template. I think it's better to link to the actual virus article. ScottishFinnishRadish ( talk) 13:35, 9 September 2021 (UTC)
Global Viral Mass
AFAIK there have been no estimations of the global viral mass of SARS‑CoV‑2, or the mass of a single virion for that matter. What are we dealing with here, a few kilos or what? kencf0618 ( talk) 03:39, 6 September 2021 (UTC)
- There is this estimation, but I'm unsure how relevant and meaningful the estimate is for the article. Bakkster Man ( talk) 14:45, 7 September 2021 (UTC)
References
- ^ "The total number and mass of SARS-CoV-2 virions". www.pnas.org. National Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 29 September 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
X... Coronaviruses infect humans, other mammals, and avian species, including livestock and companion animals.
Y... Coronaviruses infect humans, other mammals, including livestock and companion animals, and avian species.
NOTE: This is a trivial edit. The string 'livestock and companion animals' relates to 'other mammals', not 'avian species'. Cheers. Kevbo ( talk) 04:09, 29 September 2021 (UTC)
 Done
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 10:53, 29 September 2021 (UTC)
Done
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 10:53, 29 September 2021 (UTC)
The Laos' bats pre print
Why are we allowing the use of the Laos bats preprint? It was inserted in this edit . I suggest we remove it until it passes peer review. Forich ( talk) 04:43, 9 October 2021 (UTC)
- I agree, we need to at least wait for it to be peer reviewed, if not waiting for a secondary source. Bakkster Man ( talk) 12:17, 9 October 2021 (UTC)
- Yes I would agree. Although we do already have secondary sources about this: [11] (among others). I would just rather wait for the PRIMARY to be peer reviewed before jumping to use any secondary sources. The good news is that it's under consideration and likely fast tracked at a Nature-family journal, so this interim shouldn't last long. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 17:57, 9 October 2021 (UTC)
Mad props to all contributors
I love how roughly half the length of this article comprises carefully cited and documented references. Thank you to everyone who has contributed to this article; every Wikipedia article should be this good — PowerPCG5 ( talk) 09:35, 12 October 2021 (UTC)
Wiki link to viral shedding
This
edit request has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
In the second paragraph of the section titled “Infection and transmission,” please make the text “RNA shedding” into a wiki link that points to Viral shedding.
Tylercrompton ( talk) 23:50, 11 October 2021 (UTC)
 Done
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 10:50, 12 October 2021 (UTC)
Done
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 10:50, 12 October 2021 (UTC)
NIH grant
I'm not an expert on this subject, so I cannot judge the completeness and veracity of this report from the US government itself. I leave it to others to decide if a digest of this should be included in the article, or if a footnote should be added.
The expert summary by a geneticist: https://merogenomics.ca/blog/en/145/Understanding-the-Risk-of-Bat-Coronavirus-Emergence-a-Merogenomics-NIH-grant-review
The actual documents from the NIH: https://www.documentcloud.org/documents/21055989-understanding-risk-bat-coronavirus-emergence-grant-notice access seems faster here: https://s3.documentcloud.org/documents/21055989/understanding-risk-bat-coronavirus-emergence-grant-notice.pdf
The actual document is 528 pages, but you can start by doing a search for the 24 occurrences of hACE2, reading the accompanying paragraphs, and seeing if you feel it worth your time to delve deeper.
My understanding is that, if true, the USA's NIH sponsored contractor EcoHealth and its principal investigator Dr. Peter Daszak to create versions of bat corona viruses that can infect cells via human ACE2 receptors (hACE2 receptors). This was an outgrowth of an innocent experiment to see if there were wild bat corona viruses that can infect humans.
The hACE2 work was apparently done in Wuhan, China.
Presumably the release was totally accidental. (Possibly, the lab was certified as BCL3 instead of BCL4, as it should have been for airborne viruses lethal to humans.)
I'm not an expert on this subject, so I cannot judge the completeness and veracity of this report from the US government itself. I leave it to others to decide if a digest of this should be included in the article, or if a footnote should be added. — Preceding unsigned comment added by 2604:3D09:A57B:9870:C550:BE5:2934:91E7 ( talk) 05:07, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
- 1) we do not write encyclopedia articles based on primary sources (such as opinion blogs or grant requests) 2) This is clearly the grant referred to here ("The alliance's grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, titled "Understanding the risk of bat coronavirus emergence," was launched in 2014 and renewed for 5 years in 2019 after receiving an outstanding peer-review score. "); and clearly it's nothing new, and the section title is misleading. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 05:14, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
Note below diagram is wrong.
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
The diagram depicting the structure of SARS-COVID-19 has an error in the note beneath the diagram. It claims the picture is an “atom”. It is a virus made of molecules. 2600:100C:B017:9372:C27:BC92:5330:9DE3 ( talk) 13:00, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
 Not done That is a 3D model based on the location of atoms in crystallography/spectroscopy. It does not claim the picture is of an atom, it claims that each sphere in the model is an atom.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 13:13, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
Not done That is a 3D model based on the location of atoms in crystallography/spectroscopy. It does not claim the picture is of an atom, it claims that each sphere in the model is an atom.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 13:13, 25 October 2021 (UTC)
Banal preprint is still being used
I see we are still quoting directly from the research square preprint of the BANAL strains found in Laos. This was discussed in previous archived threads of this talk page, and several editors agreed that it was best to pause any mention of the information from the preprint until and if the paper passes peer review properly. The diff that uses the preprint is this one. By the way I could not verify the 96.8% figure anywhere in the preprint, so it means that we are incurring in two breaches of policy here by allowing that sentence. Forich ( talk) 04:31, 28 October 2021 (UTC)
- Agreed, the BANAL information should be removed pending peer review. Unfortunately, it's a fair number of diffs to remove it (including the phylogenetic tree), but I'll take a look as I have opportunity. Anyone else available should feel free as well. Bakkster Man ( talk) 13:49, 28 October 2021 (UTC)
COVID Moonshot
Would it be appropriate to mention COVID Moonshot in the "Treatment and drug development" section? I just released a Wikipedia article on the initiative: They are particularly interesting as an alternative (international collaborative crowd-sourced open-science open data no patents) approach to drug development, but they aren't yet doing clinical trials. I was thinking of something like the following, if it is acceptable to mention them. -- MaryMO (AR) ( talk) 20:11, 5 November 2021 (UTC)
- COVID Moonshot is an international collaborative open-science project started in March 2020 with the goal of developing an un- patented oral antiviral drug for treatment of SARS-CoV-2. [1]
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 12 August 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Please add Template:Outdated to the "Infection and transmission" section. It reports only 2020 information. The idea of aerosol transmission is presented as not-yet-confirmed. There are 47 citations before the start of the "Reinfection" subsection: 1 dates from 2010, 41 date from 2020, and just 5 date from 2021. And of those 5, 2 are a case study of a specific person, 1 talks about animals that can get infected, and 2 talk about particles emitted during talking. Most or all items in this section should be relying on 2021 data, because the science is getting updated so fast through extensive research. 174.206.39.24 ( talk) 11:15, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
 Done. will do, but I will also say that these statements probably need better
WP:MEDRS, as "etiology" is explicitly covered under
WP:BMI. To be plain, the statements may require a higher level of sourcing commiserate with scientific journal review articles published in topic-relevant venues. We may not be able to move as fast as the science does as a result. Of course this also means some of these sentences are definitely poorly sourced as it is, even the ones from the past. Appreciate you pointing this out, thank you.--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:55, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
Done. will do, but I will also say that these statements probably need better
WP:MEDRS, as "etiology" is explicitly covered under
WP:BMI. To be plain, the statements may require a higher level of sourcing commiserate with scientific journal review articles published in topic-relevant venues. We may not be able to move as fast as the science does as a result. Of course this also means some of these sentences are definitely poorly sourced as it is, even the ones from the past. Appreciate you pointing this out, thank you.--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:55, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
here are some links to find high quality MEDRS about this topic (SARS-CoV-2 transmission): Find medical sources: Source guidelines · PubMed · Cochrane · DOAJ · Gale · OpenMD · ScienceDirect · Springer · Trip · Wiley · TWL -- Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 23:06, 12 August 2021 (UTC)
Typo "Demark"
I'm sorry, if I'm using the talk page the wrong way, but since the article is protected and I couldn't make the edit myself, I would appreciate it, if an experienced member could just fix this little typo.
It's really self-explanatory, there's just a missing "n" in "Demark" that needs to be added. It's in the last sentence of the paragraph in chapter 4.1.1 (Phylogenetics -> Variants).
Thank you very much!
XLix ( talk) 22:18, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
-
 Fixed. thanks--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 22:20, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
Fixed. thanks--
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 22:20, 13 August 2021 (UTC)
Featured picture scheduled for POTD
Hello! This is to let editors know that the featured picture File:Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.jpg, which is used in this article, has been selected as the English Wikipedia's picture of the day (POTD) for September 3, 2021. A preview of the POTD is displayed below and can be edited at Template:POTD/2021-09-03. For the greater benefit of readers, any potential improvements or maintenance that could benefit the quality of this article should be done before its scheduled appearance on the Main Page. If you have any concerns, please place a message at Wikipedia talk:Picture of the day. Thank you! Cwmhiraeth ( talk) 09:45, 20 August 2021 (UTC)

|
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is the virus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Like other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 has four structural proteins, known by the letters S ( spike), E ( envelope), M ( membrane), and N ( nucleocapsid); the N protein holds the RNA genome, and the S, E, and M proteins together create the viral envelope. This colourised transmission electron micrograph shows SARS-CoV-2 virus particles emerging from the surface of cells cultured in a laboratory. The crown-like spikes on the outer edge of the virus particles give coronaviruses their name, derived from Latin corona, 'crown'. Photograph credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Rocky Mountain Laboratories
Recently featured:
|
Typo in "Epidemiology" section
The "epidemiology" section start with "xVery few drugs" (erroneous "x") Technicolour-dreamboat ( talk) 12:09, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
 Done. Thanks for the heads up.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 18:55, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
Done. Thanks for the heads up.—
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 18:55, 30 August 2021 (UTC)
Global Viral Mass
AFAIK there have been no estimations of the global viral mass of SARS‑CoV‑2, or the mass of a single virion for that matter. What are we dealing with here, a few kilos or what? kencf0618 ( talk) 03:39, 6 September 2021 (UTC)
- There is this estimation, but I'm unsure how relevant and meaningful the estimate is for the article. Bakkster Man ( talk) 14:45, 7 September 2021 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 9 September 2021
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
In the lead, replace Virus with Emergent virus. 79.70.190.198 ( talk) 08:30, 9 September 2021 (UTC)
 Not done for now: please establish a
consensus for this alteration
before using the
Not done for now: please establish a
consensus for this alteration
before using the {{ edit extended-protected}}template. I think it's better to link to the actual virus article. ScottishFinnishRadish ( talk) 13:35, 9 September 2021 (UTC)
Higher mortality risk for COVID survivors?
NEWS (3 December 2021): Apparently - there's a significantly *higher mortality risk* for COVID survivors after 1-year of onset. [2] [3] - QUESTION: Worth considering for the main article? - in any case - Stay Safe and Healthy !! - Drbogdan ( talk) 18:45, 3 December 2021 (UTC)
References
- ^ Whipple, Tom (October 23, 2021). "Moonshot is the spanner in the Covid-19 works the country needs". The Times. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ Flynn, Hannah (3 December 2021). "COVID-19 survivors have an increased risk of death 12 months post infection". Medical News Today. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
-
^ Mainous III, Arch G.; et al. (1 December 2021).
"COVID-19 Post-acute Sequelae Among Adults: 12 Month Mortality Risk".
Frontiers in Medicine. 8 (778434).
doi:
10.3389/fmed.2021.778434. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
{{ cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI ( link)
Epidemiological tracing of early cases
Time for a major rewrite of this section:
The first known infections from SARS‑CoV‑2 were discovered in Wuhan, China. The original source of viral transmission to humans remains unclear, as does whether the virus became pathogenic before or after the spillover event. Because many of the early infectees were workers at the Huanan Seafood Market, it has been suggested that the virus might have originated from the market. However, other research indicates that visitors may have introduced the virus to the market, which then facilitated rapid expansion of the infections. A March 2021 WHO-convened report stated that human spillover via an intermediate animal host was the most likely explanation, with direct spillover from bats next most likely. Introduction through the food supply chain and the Huanan Seafood Market was considered another possible, but less likely, explanation. An analysis in December 2021, however, said that the index case had been misidentified and that the preponderance of early cases linked to the Huanan Market, specifically a section where raccoon dogs were caged, argued for it being the source.
Major points of improvement:
- There are two "however" that redirect the reader in confusing directions.
- The text messes information of the place of origin (i.e. wuhan market) with the pathway of transmission (direct spillover vs intermediate spillover vs food supply chain vs unmentioned lab leak)
- "The first known infections from SARS-CoV-2 were discovered in Wuhan, China" is too vague, given that we have this from the NYTimes, for example, "Toward the end of December 2019, doctors at several Wuhan hospitals noticed mysterious cases of pneumonia arising in people who worked at the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, a dank and poorly ventilated space where seafood, poultry, meat and wild animals were sold." It gives more specific locations than ours (wuhan hospitals vs wuhan the city), and expands on key characteristics of the market (e.g. dank place where wild animals were sold).
- Our paraphrase of Worobey's results ("An analysis in December 2021, however, said that the index case had been misidentified and that the preponderance of early cases linked to the Huanan Market, specifically a section where raccoon dogs were caged, argued for it being the source.") is too strong, in my opinion. I propose we moderate it to something like this:
Forich ( talk) 03:35, 22 November 2021 (UTC)Michael Worobey, an expert on the origins of influenza and H.I.V., has traced the epidemiological origin of the early cases in Wuhan, suggesting that the index case (i.e. the first known case) was a vendor at the Huanan Seafood Market, which contrast with other public accounts that register as the index case an accountant who lived many miles from it.
- I agree with 1 and 2. A rewording for clarity is deserved, now that things are a bit more settled and there's less edit warring in general dividing our attention. For 3, I think I'd prefer to word it as "first confirmed infections", rather than replacing it with speculation about "mysterious cases of pneumonia" especially if paired with "dank and poorly ventilated" that I'd consider WP:WTW (particularly 'dank'). Along with 4, I'd suggest splitting the paragraph into things we know (first confirmed cases, Huanan Seafood Market being early epicenter) and the major areas of investigation (spillover event at seafood market, unidentified pneumonia, etc) to help clarify the certainty. Bakkster Man ( talk) 14:36, 22 November 2021 (UTC)
- Would there also be any relevance in including this NPR report somewhere in this section? It concerns findings of coronavirus antibodies in American blood samples from December 2019, and here is the DOI. Would it be extraneous to discuss the possible spread of the disease prior to the Wuhan outbreak? Wuhan is a well-documented outbreak and there are no other similar candidates at that time, but mentioning these findings in the rewrite may better reflect how there are several other unknown factors around the origins. Mewnst ( talk) 10:00, 23 December 2021 (UTC)
References
Restoring two discussions that were deleted by a random IP
Two discussions here, the "Epidemiological tracing of early cases" and "Higher mortality risk for COVID survivors?" were removed by a random IP address in this edit and were thus not properly archived or examined for further discussion. I have brought them back and something should be done about that annoying IP in the meantime. Mewnst ( talk) 11:32, 6 January 2022 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 12 January 2022
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Please change:
It mainly enters human cells by
To:
It enters human cells by
According to the two citations provided [1] [2], while SARS‑CoV‑2 viral entry depends on multiple factors, binding to ACE2 is the only way it enters human cells. -- Xarm Endris ( talk) 17:56, 12 January 2022 (UTC)
 Done
SpinningCeres (
talk) 01:46, 13 January 2022 (UTC)
Done
SpinningCeres (
talk) 01:46, 13 January 2022 (UTC)
unsubstantiated factoid about virus particle diameter
I don't seem to be able to edit, so am commenting here: The section Virology / Structure gives a diameter of the particles as 50-200 nm, and cites a reference. However, that reference just says they viruss "envelop" particles of that size range (which doesn't even make sense) and then cites a single reference for that, which doesn't support that in any way. So my suggestion would be to either remove the diameter range or else find a reference to support it. I'm looking but haven't found one yet. Thanks! Joe Betts-LaCroix ( talk) 22:10, 8 January 2022 (UTC)
- I've added a reference from somewhere else on the page and changed the bounds of the size. SpinningCeres ( talk) 15:55, 13 January 2022 (UTC)
Typo in total virus mass range
In section Virology/Structure a total virus mass of 0.1-1kg is stated. The given reference [142] (Sender et al., 2020) however states a mass range of 0.1-10kg. 89.160.8.66 ( talk) 11:24, 4 February 2022 (UTC)
Featured picture scheduled for POTD
Hello! This is to let editors know that File:SARS-CoV-2 scanning electron microscope image.jpg, a featured picture used in this article, has been selected as the English Wikipedia's picture of the day (POTD) for February 22, 2022. A preview of the POTD is displayed below and can be edited at Template:POTD/2022-02-22. For the greater benefit of readers, any potential improvements or maintenance that could benefit the quality of this article should be done before its scheduled appearance on the Main Page. If you have any concerns, please place a message at Wikipedia talk:Picture of the day. Thank you! Cwmhiraeth ( talk) 11:26, 13 February 2022 (UTC)

|
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory disease responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. This scanning electron micrograph shows SARS-CoV-2 virions (gold) emerging from the surface of cells cultured in a laboratory. The virus particles depicted were isolated from a patient in the United States. Photograph credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Recently featured:
|
Out of date part of article?
"Preliminary research indicates that the virus may remain viable on plastic (polypropylene) and stainless steel (AISI 304) for up to three days, but it does not survive on cardboard for more than one day or on copper for more than four hours." appears well out-of-date(?) as I thought I saw a journal article relating to research in Australia, now itself quite a while ago but several months later than this 'preliminary' research that suggested the virus could survive for up to 28 days on steel, perhaps in a dark environment undisturbed and in cold winter weather. I also think it could be on plastic for up to 5 or 7 days - virus in one piece of research I seem to remember (no idea where any of it is now) could not be detected on the seventh day. It appears to me the initial research is no longer the position that we know now and, in short, is likely out-of-date. However I do not know whether the extended time periods necessarily showed that the virus, where it was still found, was viable. In addition though, I haven't seen any evidence as to whether the time periods of survival of viable virus are different, possibly longer, with Omicron etc. (logic to me as a layperson might suggest that perhaps it could last longer on surfaces when Omicron appears to be able to remain present in unventilated indoor spaces in the air for quite a lot longer than the original virus (in excess of 2 1/2 days as opposed to up to 16 hours originally) but I suspect with SARS-CoV-2 it might confound what I think might be logical, as it usually turns out to do things 'unexpected' by (some) scientists that I expect it will do because it will be unusual and different to what has been previously encountered - I think, if anyone has assumptions, the assumptions are usually wrong). aspaa ( talk) 03:36, 19 February 2022 (UTC)
- 1) We would need secondary sources on this, not a primary research article.
2) It is important to emphasize that such studies must be based in virus isolation and culture rather than nucleic acid amplification in order to be useful for this question. The latter, often referred to as "PCR-based methods" can have false positives when nucleic acids are still present, but no viable virus remains. Similarly, some patients continue to test "PCR-positive" for several months after clearing the infection.
3) It is overall unlikely that this virus would remain viable for that long, as it is a lipid-membrane-enveloped virus. Such lipid bilayers break down relatively quickly in the open air, on the order of 3-4 days to zero viable particles. [12] [13] We don't have much reason to believe SARS-CoV-2 would be much different. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 11:36, 19 February 2022 (UTC)
misisleading to refer to SARS-CoV2 as the "successor" to SARS-CoV1
The last sentence of the first paragraph:
"As described by the US National Institutes of Health, it is the successor to SARS-CoV-1, the virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak.[16]"
is misleading and should be removed.
Although the cited reference does use the word "successor", the usage seems to imply that SARS-CoV2 is derived from SARS-CoV1. There is no evidence for this and substantial reason to believe that it is false (chiefly, that SARS-CoV1 was eradicated in 2004 and hasn't been seen anywhere in the world since then).
I suggest simply erasing this sentence, or, if it is deemed necessary to refer to SARS-CoV1, substituting:
"An unrelated coronavirus, now designated SARS-CoV1, caused the SARS epidemic of 2002-2004 and was eradicated in 2004." References for this information (refs 4 and 5 copied from the Wikipedia article on SARS1):
Chan-Yeung M, Xu RH (November 2003). "SARS: epidemiology". Respirology. 8 Suppl (s1): S9-14. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1843.2003.00518.x. PMC 7169193. PMID 15018127.
"SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome)". NHS Choices. UK National Health Service. 3 October 2014. Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 8 March 2016. Since 2004, there haven't been any known cases of SARS reported anywhere in the world.
— Preceding unsigned comment added by 108.52.207.45 ( talk) 16:11, 7 March 2022 (UTC)
- I moved this sentence to the following sentence. The word 'successor' seemed to refer to the timing of the outbreaks, rather than direct descendance. But the idea the two are 'unrelated' is also incorrect, as is evident in the name
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus.
Bakkster Man (
talk) 16:57, 7 March 2022 (UTC)
- Politically, it is the successor. All corona viruses descend from some common ancestor billions of years ago. As with other organisms, there is much mixing, so you can't draw a nice tree. I have run into this descending question before in microprocessors, where it can also be misleading, but is used anyway. Even there, things get mixed such that you can't draw a nice tree. Gah4 ( talk) 20:31, 7 March 2022 (UTC)
Number of virions needed for infection
During human-to-human transmission, between 200 and 800 infectious SARS‑CoV‑2 virions are thought to initiate a new infection.
What variant is this talking about? None of the references is recent: source #1 is from 11 May 2020 (very early), source #2 is from 9 December 2020 (early), and source #3 is from 20 May 2010 (what is this even doing here?). I don't understand the charts in #2, so I don't know if it means the original variant or the Alpha variant, but none of these sources can possibly be talking about Delta, Omicron, or lesser-known variants. Since this information is very much outdated, reliant on sources that are too old to reflect current research, and probably not applicable to the variants that are all over the place now, I think it ought to be removed completely. 49.198.51.54 ( talk) 07:58, 5 April 2022 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 3 May 2022
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
You can’t affirm that the virus came from China without prove, so that information is wrong 191.183.196.31 ( talk) 15:33, 3 May 2022 (UTC)
 Not done: it's not clear what changes you want to be made. Please mention the specific changes in a "change X to Y" format and provide a
reliable source if appropriate. The article states the first identified cases were in China. Is that untrue?
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 15:39, 3 May 2022 (UTC)
Not done: it's not clear what changes you want to be made. Please mention the specific changes in a "change X to Y" format and provide a
reliable source if appropriate. The article states the first identified cases were in China. Is that untrue?
ScottishFinnishRadish (
talk) 15:39, 3 May 2022 (UTC)
Extended-confirmed-protected edit request on 14 May 2022
This
edit request to
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Infection and Transmission:
The degree to which the virus is infectious during the
incubation period is uncertain, but research has indicated that the
pharynx reaches peak
viral load approximately four days after infection
Source:
Pharyngeal virus shedding was very high during the first week of symptoms, with a peak at 7.11 × 108 RNA copies per throat swab on day 4. ...
The earliest swabs were taken on day 1 of symptoms, which were often very mild or prodromal.
Current text indicates pharyngeal viral load peaks 4 days after infection rather than onset of symptoms.
Suggested change:
The degree to which the virus is infectious during the
incubation period is uncertain, but research has indicated that the
pharynx reaches peak
viral load approximately four days after the onset of symptoms
Peaceandlonglife (
talk) 14:54, 14 May 2022 (UTC)
cauldron of virus mixing
OK, I didn't explain it will before, and didn't have references. Virologists have been worried about Chinese farms as sources of new viruses for years. The discussion about zoonotic vs. lab misses the fact that farms are not close to natural, and not supposed to be labs. A quick Google search find a Nature article that calls a Chinese farm a cauldron of virus mixing. [3] This was the first one that came up, and from September 2019, so barely before Covid-19. I am not writing this as a WP:SOAPBOX, and no suggestions regarding lab origins or not, but for better understanding of virus origins. In 2019, there was much interest in pandemic flu viruses, but not (yet) corona viruses. Gah4 ( talk) 04:14, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
- Viral recombinance among farm animals is still zoonotic, and the WIV's primary research goals have been coronaviruses with pandemic potential since that was the source of SARS. Bakkster Man ( talk) 15:47, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
References
- ^ Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, et al. (April 2020). "SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor". Cell. 181 (2): 271–280.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. PMC 7102627. PMID 32142651.
- ^ Zhao P, Praissman JL, Grant OC, Cai Y, Xiao T, Rosenbalm KE, et al. (October 2020). "Virus-Receptor Interactions of Glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Human ACE2 Receptor". Cell Host & Microbe. 28 (4): 586–601.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.08.004. PMC 7443692. PMID 32841605.
- ^ Willyard, Cassandra (18 September 2019). "Flu on the farm" (PDF). Nature (573, S62-S63 (2019)). Retrieved 27 May 2022.
What constitutes certifiable facts
Regardless of one's views about the merits of the zoonotic hypothesis for SARS-COV2 the fact that some prominent scientists think the issue is unresolved is a fact. Facts like this, with appropriate documentation, are suitable for noting in an article about the virus. Does anyone disagree with this? StN ( talk) 18:12, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
-
WP:DROPTHESTICK. This has already been explained enough times that I can't really be bothered to keep arguing at length over it, but in short,
WP:FALSEBALANCE is clear enough that
Wikipedia policy does not state or imply that every minority view or extraordinary claim needs to be presented along with commonly accepted mainstream scholarship as if they were of equal validity.
andWe do not take a stand on these issues as encyclopedia writers, for or against; we merely omit this information where including it would unduly legitimize it
. Given that, besides a few opinion letters, most secondary sources (i.e. reviews and the like) by experts in the topic area overwhelmingly favour a zoonotic origin (many sources take it for granted, and the few sources that focus specifically on the origins of the virus are rather unambiguous as well), then this would indeed appear to be a prime casewhere including [the opposing theory] would unduly legitimize it
. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 18:21, 27 May 2022 (UTC)- Agreed. Having looked over the discussion above, it's clear to me that it is now time for StN to drop the stick and move on.
Generalrelative (
talk) 23:10, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
- Also agree. StN is writing at the wrong level. They may well observe some dissenting voices and decide in their view this constitutes enough to say "the jury is out" - but Wikipedia cannot reflect such a view unless it is explicitly said in reliable sources. Instead, we must just reflect what the WP:BESTSOURCES say - and they assert zoonotic origin, so far as I can see. Alexbrn ( talk) 04:45, 28 May 2022 (UTC)
- Agreed. Having looked over the discussion above, it's clear to me that it is now time for StN to drop the stick and move on.
Generalrelative (
talk) 23:10, 27 May 2022 (UTC)
I edited this article to reflect the fact that the unequivocal assertion that the SARS_Cov2 virus is of zoonotic origin is not universally accepted by experts in the field. I did not mention any other theory, but only cited letters and commentaries by some of those experts in the most respected scientific journals in the world. I was accused of advancing conspiracy theories, but although my edits each time were to different respected sources (each time with no alternative theory mentioned by me) other editors requested that I be banned from editing the article, and I was for 48 hours. After the ban expired, I edited the article again, this time linking to another Wikipedia article that indicated that the conclusion in this one was controversial. That article is already linked to in this one, but in a context that conceals the controversy that is its main subject. An editor used that innocuous edit to get me banned for a week, this time from editing Wikipedia at all. Since then, the World Health Organization has issued a report saying a laboratory manipulation and leak of the virus remains a viable scenario for the virus. Since the most active editors on the page consider this a conspiracy theory, I am reluctant to cite the WHO report, since I don't wish to get banned again. The blanket assertion, with no qualification, that the virus is of natural origin is itself a POV. Any advice User:Bbb23? StN ( talk) 18:32, 10 June 2022 (UTC)
- For reference this is the SAGO report being mentioned. On a quick scan, the following two quotes seem most relevant here:
- In the executive summary:
At the present time, currently available epidemiological and sequencing data suggest ancestral strains to SARS-CoV-2 have a zoonotic origin with the closest genetically related viruses being beta coronaviruses, identified in Rhinolophus bats in China in 2013 (96.1%) and Laos in 2020 (96.8%). However, so far neither the virus progenitors nor the natural/intermediate hosts or spill-over event to humans have been identified.
- Among the recommendations for further study:
Determine the occupational hazards intrinsic to laboratories working with SARS-like CoV and the nature of the studies performed before the first reported COVID-19 cases in Wuhan and whether they involved reverse engineering or gain-of-function, genetic manipulation or animal studies with strains of SARS-like CoV.
- I'll note that your ban came as a result of edit warring, not the content of your edit. Learn to edit collaboratively, (ie, continue discussing on the talk page, without making it a
WP:BATTLEGROUND) and you should be fine.
Bakkster Man (
talk) 19:33, 10 June 2022 (UTC)
- The keyword there is
suggest
. I think it supports StN and Palpable's proposed changes. According to high-quality sources, the natural reservoir is most likely bats, and the spillover was most likely a natural occurrence, but the intermediate host and time and place of the first spillover are far from certain and there is a minority view that the spillover was research related. ScrumptiousFood ( talk) 17:41, 11 June 2022 (UTC)
- The keyword there is
Zoonotic origins
The references provided for the assertion that the virus is of zoonontic origin were from 2020, and the removal of this unequivocal statement was reverted twice based on those old, controversial papers. A recent review in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2202769119 indicates that this view is not the consensus. Leaving out the assertion does not commit to either side. StN ( talk) 23:47, 23 May 2022 (UTC)
- Do you have a stronger source than the unreviewed opinion article you cited here?
Bakkster Man (
talk) 02:14, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Investigate the origins of COVID-19 - PubMed (nih.gov)
StN (
talk) 02:22, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33986172/
StN (
talk) 02:22, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33574591/
StN (
talk) 02:24, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- An unreviewed letter, and a news posting. Neither are stronger sources. Bakkster Man ( talk) 22:41, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33574591/
StN (
talk) 02:24, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33986172/
StN (
talk) 02:22, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Investigate the origins of COVID-19 - PubMed (nih.gov)
StN (
talk) 02:22, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
I have reverted assertions that the virus is of zoonotic origins since there is no consensus about this. I have not proposed an alternative. It is inaccurate to say that there is a consensus. I have cited a paper that indicates there is not a consensus. Please don't change this unless an authoritative paper stating that zoonoses is generally accepted can be cited. StN ( talk) 01:36, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
The statement that "It has been suggested to be of zoonotic origins, but some experts consider this unsettled" is uncontroversial and well supported by articles in Science and Nature. Removing it from the article is unwarranted and contrary to Wikipedia policy. StN ( talk) 19:01, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- No, you've just made that up.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:05, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Made up that virologists like Jesse Bloom and Richard Ebright consider it unsettled, or that reports about this from reputable sources are allowed in Wikipedia articles?
StN (
talk) 19:10, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Made up in that it's editorial invention. "One virologist disagreed" would at least be honest, but undue. There are always some fringe guys, don't amp them up.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:16, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Your comment would have some merit if there were a single article that showed evidence of zoonotic origins. There was more than one skeptical virologist who signed on to those letters. I have not advocated any alternative theory in my edits, so the allegation of "fringe" is inapplicable. I don't think you have familiarized yourself with the subject, but you and others are adept at using Wikipedia to keep readers from knowing that this is an unsettled subject among legitimate scientists.
StN (
talk) 19:31, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Follow the sources, and stop making stuff up, and we'll make progress.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:38, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- To recount the history of this: I started by removing a sentence that I considered speculative (i.e., making stuff up). It was reverted. I put it back, citing a recent review in one of the most esteemed journals in science, PNAS. I was reverted again with the comment that the people whose review was published by PNAS had no authority. I put it back with other sources of the kind that are cited all the time in Wikipedia. I was reverted again, with threats to be blocked and reporting to Wiki administration. At no time did I propound any fringe theories or any alternatives at all, but cited people raising questions about the zoonotic theory. The SARS virologist Ralph Baric was among these. At no point did I make anything up, which is dishonest of you to claim. If you knew anything about the subject, you would recognize that zoonoses is not established and that even the authors of the 2020 Andersen paper had doubts about it 2 days before they published the assertion that it was the only possibility. That's in the public record. If you knew anything about science, you would realize that claims require evidence and until that's available they remain controversial. Citing reports of doubts by reputable scientists in prime outlets is not indulging in fringe science. I always wonder about the kind of educational background or life experiences that produce reply guys like you, ready with the "nopes" or "stop making things up." Why don't you try to educate yourself and learn what a source is.
StN (
talk) 20:44, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- I think WP:CIR applies. You seem blinded by your own POV and sense of self-righteousness. Here, things need to be backed up by sources - reliable sources. Your own view and how well you consider yourself "self-educated" don't matter. Alexbrn ( talk) 20:53, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Unless you con find sources of similar quality to those listed
here (or even
those here, although they may be slightly outdated); then it doesn't matter. I also don't understand why the bollocks about the Andersen et al. emails is still circulating on the misinformation-net. Scientists had initial doubts (expressed via a private email, which is not a reliable source), then they investigated it more thoroughly, and found that those doubts were not backed up by evidence (as the published paper - the actual reliable source - clearly says). Random opinion pieces are nowhere near the level of sourcing required.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 22:37, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- The sources cited [refs. 9 and 17] present descriptions of the viral genome, but the suggestions of zoonotic origin are purely speculative. They are both from early 2020. The reliability of the sequence data does not transfer to the speculations about the origin. There is no evidence in those sources about the origins. The statements of uncertainly that I cited are just that, not evidence of an alternative. Anyone not committed to the zoonotic hypothesis would recognize that a statement that "some virologists think that the question is open" is appropriately sourced by a published statement by virologists that they think that the question is open. But we seem to be dealing with ideologues here.
StN (
talk) 22:51, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Obviously you want to waste other people's time without investing any of your own. The cited sources on the first page I linked (even quoted for your convenience, so you didn't even have to go read the whole papers!) are clear enough and I'm not going to bother repeating what they say. They are also all very much not "from early 2020"...
This, from September 2021, is very much recommended reading.
the suggestions of zoonotic origin are purely speculative
is not to be found in any of them, and appears very much to be your own opinion. Sadly for you, Wikipedia doesn't care about your (or my) opinion. It cares about what is published in reputable reliable sources. If you think it isn't true, too bad, but that is not Wikipedia's problem. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 23:34, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Obviously you want to waste other people's time without investing any of your own. The cited sources on the first page I linked (even quoted for your convenience, so you didn't even have to go read the whole papers!) are clear enough and I'm not going to bother repeating what they say. They are also all very much not "from early 2020"...
This, from September 2021, is very much recommended reading.
- The sources cited [refs. 9 and 17] present descriptions of the viral genome, but the suggestions of zoonotic origin are purely speculative. They are both from early 2020. The reliability of the sequence data does not transfer to the speculations about the origin. There is no evidence in those sources about the origins. The statements of uncertainly that I cited are just that, not evidence of an alternative. Anyone not committed to the zoonotic hypothesis would recognize that a statement that "some virologists think that the question is open" is appropriately sourced by a published statement by virologists that they think that the question is open. But we seem to be dealing with ideologues here.
StN (
talk) 22:51, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- To recount the history of this: I started by removing a sentence that I considered speculative (i.e., making stuff up). It was reverted. I put it back, citing a recent review in one of the most esteemed journals in science, PNAS. I was reverted again with the comment that the people whose review was published by PNAS had no authority. I put it back with other sources of the kind that are cited all the time in Wikipedia. I was reverted again, with threats to be blocked and reporting to Wiki administration. At no time did I propound any fringe theories or any alternatives at all, but cited people raising questions about the zoonotic theory. The SARS virologist Ralph Baric was among these. At no point did I make anything up, which is dishonest of you to claim. If you knew anything about the subject, you would recognize that zoonoses is not established and that even the authors of the 2020 Andersen paper had doubts about it 2 days before they published the assertion that it was the only possibility. That's in the public record. If you knew anything about science, you would realize that claims require evidence and until that's available they remain controversial. Citing reports of doubts by reputable scientists in prime outlets is not indulging in fringe science. I always wonder about the kind of educational background or life experiences that produce reply guys like you, ready with the "nopes" or "stop making things up." Why don't you try to educate yourself and learn what a source is.
StN (
talk) 20:44, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Follow the sources, and stop making stuff up, and we'll make progress.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:38, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Your comment would have some merit if there were a single article that showed evidence of zoonotic origins. There was more than one skeptical virologist who signed on to those letters. I have not advocated any alternative theory in my edits, so the allegation of "fringe" is inapplicable. I don't think you have familiarized yourself with the subject, but you and others are adept at using Wikipedia to keep readers from knowing that this is an unsettled subject among legitimate scientists.
StN (
talk) 19:31, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Made up in that it's editorial invention. "One virologist disagreed" would at least be honest, but undue. There are always some fringe guys, don't amp them up.
Alexbrn (
talk) 19:16, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
- Made up that virologists like Jesse Bloom and Richard Ebright consider it unsettled, or that reports about this from reputable sources are allowed in Wikipedia articles?
StN (
talk) 19:10, 24 May 2022 (UTC)
There is absolutely no conclusion as of yet to the origins of COVID-19. You should not be stated that it zoonotic in origin. Wikiwowie ( talk) 01:32, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- I think even the remaining "lab leakers" agree on "zoonotic in origin" (though through lab accident rather than in the wild). Or are you saying other ideas are still plausibly entertained in reliable sources?
Alexbrn (
talk) 07:09, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- You are using "lab leakers" as a pejorative. This is not about people who are 100% sure there was a leak, those people can be safely ignored. The point is that there is still doubt among reasonable people, because there just isn't enough evidence either way.
- Despite intensive searching the closest known natural relatives of SARS-CoV-2 lack the furin cleavage site - but there were gain of function research proposals with the explicit intent of adding this feature to other bat viruses, in Wuhan no less. This remains a viable hypothesis, and no reasonable person would consider laboratory gain of function research to be "zoonotic origin", whether it occurred through splicing or just by hosting sick animals together.
- The article
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 is much more balanced. It states that the majority of scientists favor a zoonotic origin, without attempting to present the matter as settled.
Palpable (
talk) 16:06, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Wikipedia tends to reflect what scientists think. Relevant sources, as cited, flat-out assert zoonotic origin and elsewhere the bio-engineered scenario is called a conspiracy theory (do we really need to go into that again here?) There's no option but to follow the sources.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:13, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- You have a bad habit of equating people who haven't made up their minds with conspiracy theorists. There is more ideology than evidence, on both sides of the debate, and in the absence of a known natural reservoir, the article should not present the matter as settled.
- Again,
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 has a pretty balanced view on things.
Palpable (
talk) 16:20, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- It's not me, it's the relevant sources. You have a bad habit of personalizing things.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:22, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- You're the one throwing around the "consipiracy theorist" and "lab leaker" pejoratives.
- The burden of proof for a dogmatic statement is higher than for one that expresses doubt. The sources you consider relevant are not actually that strong.
-
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 has plenty of relevant sources. Given the lack of strong evidence on either side, attempting to make a definitive statement about the origins is misguided. It is sufficient to say that the majority of scientists favor a zoonotic origin.
Palpable (
talk) 16:38, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Sorry what source do you consider "not actually that strong"? In contrast you have produced zero sourcing. Sure, the
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 is the right place to go into all the conspiracy theories in detail. This article isn't the right place for that. If we just mirror high-quality sources, it's job done.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:45, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The lead makes the unverified statement "It is of zoonotic origins". This statement is not actually sourced; the subsequent statement that it has close similarity to bat coronaviruses is sourced to an article that refers to a likely spillover from bats. Note that the scientific source uses the word "likely" which has been promoted to certainty in the article text. Shouldn't "likely" be in the article?
Palpable (
talk) 17:01, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- quote: "its unprecedented global societal and economic disruptive impact has marked the third zoonotic introduction of a highly pathogenic coronavirus into the human population" [my emphasis]. To repeat: what source is "not actually that strong"?
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:07, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The statement in the paper is not as strong as the statement in the article.
- If "zoonotic" merely means that the virus was not sequenced from scratch, then sure, it's obviously zoonotic. But you know as well as I do that in the context of SARS-CoV-2 origins, zoonotic implies "without lab involvement" which is by no means settled.
Palpable (
talk) 17:24, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The assertion here faithfully mirrors the assertion in the source. Helpfully it glosses "Zoonotic pathogens" as "Animal pathogens that can infect and replicate in humans". Any argument to the contrary would seem to be extreme
WP:FRINGE and need super sourcing for an
WP:EXCEPTIONAL claim, expecially since we have strong sources calling the "bio-engineered" origin idea a conspiracy theory.
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:31, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Again with the pejoratives. As you know, there are numerous letters by non-fringe scientists who think the question of lab involvement is still open; you and others seem to think that science doesn't have room for disagreement so you eliminate these opinions from the article.
- I think this manufactured certainty weakens Wikipedia's credibility, but obviously you have more time to spend on this than I do. I give up.
Palpable (
talk) 17:41, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Letters are not reliable sources for sci/med assertions, and the fact that stuff is published in letters and not peer-reviewed scholarly sources strongly indicates its
WP:FRINGE status. Bottom line: Wikipedia mirrors reliable sources.
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:57, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Dissenting letters from notable scientists are a reliable indication that consensus has not been reached. Despite my best efforts here, it seems that you can't see the difference between confidently asserting a lab leak (conspiracy theory) and expressing uncertainty about a natural origin (waiting for evidence). It sounds like you are not a scientist yourself. Palpable ( talk) 18:27, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Letters are not reliable sources for sci/med assertions, and the fact that stuff is published in letters and not peer-reviewed scholarly sources strongly indicates its
WP:FRINGE status. Bottom line: Wikipedia mirrors reliable sources.
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:57, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The assertion here faithfully mirrors the assertion in the source. Helpfully it glosses "Zoonotic pathogens" as "Animal pathogens that can infect and replicate in humans". Any argument to the contrary would seem to be extreme
WP:FRINGE and need super sourcing for an
WP:EXCEPTIONAL claim, expecially since we have strong sources calling the "bio-engineered" origin idea a conspiracy theory.
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:31, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- quote: "its unprecedented global societal and economic disruptive impact has marked the third zoonotic introduction of a highly pathogenic coronavirus into the human population" [my emphasis]. To repeat: what source is "not actually that strong"?
Alexbrn (
talk) 17:07, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- The lead makes the unverified statement "It is of zoonotic origins". This statement is not actually sourced; the subsequent statement that it has close similarity to bat coronaviruses is sourced to an article that refers to a likely spillover from bats. Note that the scientific source uses the word "likely" which has been promoted to certainty in the article text. Shouldn't "likely" be in the article?
Palpable (
talk) 17:01, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Sorry what source do you consider "not actually that strong"? In contrast you have produced zero sourcing. Sure, the
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 is the right place to go into all the conspiracy theories in detail. This article isn't the right place for that. If we just mirror high-quality sources, it's job done.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:45, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- It's not me, it's the relevant sources. You have a bad habit of personalizing things.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:22, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Wikipedia tends to reflect what scientists think. Relevant sources, as cited, flat-out assert zoonotic origin and elsewhere the bio-engineered scenario is called a conspiracy theory (do we really need to go into that again here?) There's no option but to follow the sources.
Alexbrn (
talk) 16:13, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- Note there has been off-wiki recruiting on this matter. [14] I have added a template at the head of the page accordingly. Alexbrn ( talk) 16:02, 26 May 2022 (UTC)
- New sources support
StN and
Palpable's proposed changes. Zoonotic origin and lab origin aren't mutually exclusive, as the Wuhan CDC was doing field research with bat viruses. Some scientists (including the WHO) have also raised concerns about experiments done by the Wuhan Institute of Virology, possibly supported by ECA and the NIH. Certainty will only come with China's cooperation with the WHO, according to SAGO report, and secondary sources writing about it
[15]
[16]
[17]
[18]
[19]
[20]
[21]
[22]
[23].
ScrumptiousFood (
talk) 17:32, 11 June 2022 (UTC)
- You'd think so, but you will be reverted, accused of edit-warring, and ultimately be banned for trying to rectify this. The editors who have taken hold of this page will not accept letters in Science and Nature from prominent virologists who don't agree that the issue is settled to support -- not an alternative hypothesis -- but the factual statement "Not all prominent virologists consider the issue settled." Yes, Wikipedia's credibility is undermined by such maneuvers, but it seems that little can be done about it. StN ( talk) 19:05, 11 June 2022 (UTC)
- Best to cite the SAGO report [24] directly rather than the press coverage. In particular, page 11 of the report draws a distinction between "origin" and "source" which clarifies that a zoonotic origin does not rule out a lab accident somewhere in the chain.
- That said, some of the fringe crusaders here have gone full battleground. Logical argument is stalled with strawmanning and wikilawyering. You might have more luck with the actual doctors and scientists at
Wikipedia Talk:WikiProject Medicine. -
Palpable (
talk) 22:17, 11 June 2022 (UTC)
- I can get to this eventually if no one else does, but I have already been banned twice. If you want to try, I am more than happy to step aside for a while. StN ( talk) 00:20, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- Citing WHO reports directly was how we changed the previous 'don't even mention the lab' consensus, so we have precedent there. And I agree, the above is already over the line of battleground and aspersions, if it continues it's likely to end with another ban.
Bakkster Man (
talk) 00:29, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- Totally agree. I'd like to see if the stance in the reports is backed up by a change of stance in other sources (is there? I can't find that much, to begin with -
1, from May this year, simply says
The subgenus Sarbecovirus of beta-CoVs, such as SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, had spread to humans, most likely via intermediate hosts.
). Also agree thatThat said, some of the fringe crusaders here have gone full battleground. Logical argument is stalled with strawmanning and wikilawyering.
is quite over the line. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 00:48, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- Totally agree. I'd like to see if the stance in the reports is backed up by a change of stance in other sources (is there? I can't find that much, to begin with -
1, from May this year, simply says
Requested move 21 June 2022
- The following is a closed discussion of a requested move. Please do not modify it. Subsequent comments should be made in a new section on the talk page. Editors desiring to contest the closing decision should consider a move review after discussing it on the closer's talk page. No further edits should be made to this discussion.
The result of the move request was: Moved. CollectiveSolidarity ( non-admin closure) ( talk) 00:41, 28 June 2022 (UTC)
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 → SARS-CoV-2
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 → SARS-CoV-1
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus → SARSr-CoV
- Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus → MERS-CoV
There are many good reasons why these pages should be moved to their widely used abbreviations. To start with the obvious, these are their
WP:COMMONNAMEs universally used by reliable sources and the public, which should replace the extremely lengthy and rarely-used
WP:OFFICIALNAMEs per
WP:CONCISE,
WP:RECOGNIZABILITY, and
WP:ACROTITLE. It's hard to imagine that any reader would take the time to type in Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
(5 words) or Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus
(6 words) into the search bar. Before any members of
WP:COVID-19 jump in and point me to {{
Current COVID-19 Project Consensus}}, rest assured I have read that page and understand that the current consensus of the WikiProject is to use the full name. But
WP:CONSENSUSCANCHANGE, and I see
the last RM discussion was over a year ago. Most editors who objected to a page move there did so on the grounds of
WP:CONSISTENT, so to address that concern I'm requesting any related pages to be moved as well. This also makes them consistent with
COVID-19,
SARS, and
MERS, all of which were moved following successful RMs with similar arguments (
Talk:COVID-19/Archive 17 § Requested move 1 March 2021,
Talk:SARS § Requested move 8 December 2021, and
Talk:MERS § Requested move 15 December 2021).
InfiniteNexus (
talk) 00:02, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Note: WikiProject COVID-19 and WikiProject Viruses have been notified of this discussion. InfiniteNexus ( talk) 00:03, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support per nom. The abbreviated titles clearly meet the WP:TITLE criteria. Ajpolino ( talk) 00:19, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Oppose I presume there are redirects from all the possible other names. To me, it is nice to see the official name, even though I will probably use the redirect. But that is why we have redirects! (Well, one reason.) Gah4 ( talk) 01:42, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Redirects are for names that are less common than the article title, not the other way round. When a redirect's title is more commonly used than the article's title, then that should be the name of the article. InfiniteNexus ( talk) 03:00, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- I just notice in my watchlist, the pages Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Superheterodyne receiver. In both cases, shorter forms are commonly used, and might be the WP:COMMONNAME. I can probably find many more. The shorter names are like slang, you use them when convenient, but the right name when it is important, as WP:TONE indicates. Gah4 ( talk) 20:01, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- I may have agreed with you if these article's current titles weren't 5 or 6 words long. InfiniteNexus ( talk) 20:16, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Hmmm. Does the article still start with the whole name? (Especially since that is where WP:TONE applies.) If so, then I probably go to Neutral. Gah4 ( talk) 22:31, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Yes they do, and they should continue to do so after they are moved. InfiniteNexus ( talk) 02:58, 22 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support, at least for SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1, and MERS-CoV, for which the short forms are much more recognizable and more commonly used. I am less sure about SARSr-CoV; I'll defer to others on that one. — Mx. Granger ( talk · contribs) 10:36, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support per nom. Consider the consistency with
SARS and
MERS and the arguments put forth in their RM discussions. Also consider
WP:SHORTFORM. However, I suggest to move
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus to
SARS-related coronavirus, as that seems more generally recognizable than
SARSr-CoV. —
BarrelProof (
talk) 12:15, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- In fact, to help readers WP:RECOGNIZE the topics, I further suggest:
- — BarrelProof ( talk) 02:30, 23 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support per nom. While I personally prefer the longer full article title, I can't make a compelling argument that the contractions aren't indeed the WP:COMMONNAME. There are some other viruses which don't have this kind of title shortening, they seem to be the exception where the abbreviation isn't nearly as common ( A/H1N1 for Influenza A virus subtype H1N1, for instance). Bakkster Man ( talk) 13:45, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support, principally per the thorough arguments laid out by the nominator. "SARS-CoV-2" has become a widely used acronym and, based on my experience, the definite WP:COMMONNAME for the virus; it's also substantially more WP:CONCISE than the spelled-out title. My feelings on the other requested moves are less strong, but I think the same underlying principles hold for all of the titles in question, and it makes sense to be WP:CONSISTENT about the move. ModernDayTrilobite ( talk • contribs) 14:19, 21 June 2022 (UTC)
- Support per nom, at least for SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1, and MERS-CoV. I'm not sure if SARSr-CoV is the undisputed common name for Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus, but I think it's common enough for WP:CONSISTENT to apply. ~ BappleBusiness [talk] 22:32, 27 June 2022 (UTC)
Requested move 17 August 2022
- The following is a closed discussion of a requested move. Please do not modify it. Subsequent comments should be made in a new section on the talk page. Editors desiring to contest the closing decision should consider a move review after discussing it on the closer's talk page. No further edits should be made to this discussion.
The result of the move request was: Withdrawn. No support and several opposed after nearly three days. This proposal doesn't have traction. — BarrelProof ( talk) 20:15, 19 August 2022 (UTC)
– Please see the similar just-closed RMs at Talk:SARS-related coronavirus#Requested move 9 July 2022 and Talk:MERS-related coronavirus#Requested move 19 July 2022. These two articles were recently renamed (from titles different from what I am suggesting here). However, I suggest that the names that I propose would be more WP:RECOGNIZEable for most readers. I previously made these same title suggestions in the recent RM at Talk:SARS-CoV-2#Requested move 21 June 2022, but there was no reaction to my suggestions at the time, as the focus of that discussion was about whether to abbreviate SARS and MERS or not. I think the current titles are now overly abbreviated to a degree that makes them difficult for many readers to recognize. — BarrelProof ( talk) 00:54, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- I've heard Dr. Fauci say "Sars Co Vee Two" on TV. Gives me the impression that despite being a complex abbreviation, that this has entered the spoken vernacular and could be somewhat common. I won't cast a bolded !vote since this is just an anecdote, but figured I'd mention this. – Novem Linguae ( talk) 01:06, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- I supported the MERS request, but while "SARS coronavirus 2" is more attractive visually, I believe that
SARS-CoV-2 is more recognizable as well as being considerably more common than the proposed title.
Dekimasu
よ! 07:38, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- Agreed, "SARS-CoV-2" gets three orders of magnitude more search results than "SARS coronavirus 2". We're currently using the common name, no need to move. Bakkster Man ( talk) 13:24, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- After the previous move discussion, I heard SARS coronavirus 2 in some news discussion. I would have voted for it in the previous move discussion if it was offered. (I ended up neutral in the actual discussion.) Not overly long like the previous name, but not too short, either. Gah4 ( talk) 08:22, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- Oppose per WP:COMMONNAME. Ngrams won't be applicable here because its corpus only goes up to 2019, but Google Search and Google Scholar results both suggest that SARS-CoV-2 is a substantially more widely used term than SARS coronavirus 2. Not only does SARS-CoV-2 receive more search results on either metric ( 1.85 million Google Scholar results and 717 million Google Search results, vs. 1.38 million and 282 million respectively for "SARS coronavirus 2"), but most of the results listed under "SARS coronavirus 2" also go on to use the term "SARS-CoV-2" extensively throughout the body text. Further, authoritative sources typically use "SARS-CoV-2" as the name of the virus, with little or no discussion of its longer names: for instance, see the World Health Organization, the US Centers for Disease Control and the US National Cancer Institute. ModernDayTrilobite ( talk • contribs) 14:50, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
- Oppose per COMMONNAME. And I would disagree on what readers will find "recognizable." These abbreviations "CoV" etc. are now in the popular lexicon, in news stories, and in the mouths of many of our most trusted public health officials. I've heard it as "SARS -Cove-Two" and as "SARS-Coh-Vee-2", but it is the same acronym. If somebody doesn't recognize the name, I don't think changing it to "coronavirus" will help all that much. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 16:40, 17 August 2022 (UTC)
Lead
Considering the fact that the WHO has called the lab leak a possibility, it is completely ridiculous to dismiss it as a fringe minority opinion. Aren't we supposed to trust and cite what the experts have to say? BTW, the article on the COVID-19 disease itself mentions the lab leak as a possibility. X-Editor ( talk) 03:46, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- 1) There's an ongoing talk page discussion and short-cutting it to include text is not productive 2) The change of stance of WHO's latest report does not appear to be reflected by the existing sources 3) We should probably wait to see how exactly this turns out per
WP:NORUSH
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 03:48, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- I'll also note that singling out the lab-leak from the SAGO report seems unhelpful. It doesn't focus solely on that; and in fact, in the nearly 2-page long summary which begins the document, it only dedicates one short paragraph, the following, to the lab-leak:
The SAGO notes that there has not been any new data made available to evaluate the laboratory as a pathway of SARS-CoV-2 into the human population and recommends further investigations into this and all other possible pathways. The SAGO will remain open to any and all scientific evidence that becomes available in the future to allow for comprehensive testing of all reasonable hypotheses.
- Thus the recent addition failed both
WP:FALSEBALANCE (when compared to other sources) but also
WP:DUE (when compared to the source it was coming from)
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 03:52, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- WP:NORUSH is an essay, not a guideline or rule. The SAGO report is also only one report. There is also a difference between adding the lab leak to the lede and adding it to the body of the article. Would you be fine if it was added to the body? X-Editor ( talk) 03:57, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- Now that I think about it, the best course of action would be consensus through voting. I've started a discussion
here regarding that.
X-Editor (
talk) 04:02, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- WP:NOTAVOTE is a better suggestion. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:06, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- (
edit conflict)The more I read the SAGO report the more I'm disappointed at the news sources being cited which seem to unduly focus on one clickbaity aspect (as is only too usual). The report suggests a whole litany of studies (
3.1.1 Early investigation studies
, with a few suggestions;3.1.2 Human studies
with over half a dozen suggestions;3.1.3 Animal and environmental studies
similarly;3.1.4 Genomics and phylogenetics studies
; and then, yes, finally;3.1.5 The possibility of a breach in biosafety or biosecurity measures
). A call for further studies (without all of the "increasingly active consideration" editorialising) seems really all there is to it. Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 would probably be the correct article to summarise this. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:06, 12 June 2022 (UTC)- I have stayed out of these discussions so far except to object to edit warring, but just a small point: even if this were to be added to the article, I agree that "increasingly active consideration" is not the wording we would use, per WP:SYNTH, MOS:REALTIME, and MOS:WTW. Dekimasu よ! 04:17, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- N.B. I've rewritten the mention in the Investigations article as
In June 2022, the WHO released an additional report advocating for more investigations in the various possible pathways of emergence.
, as per the bit quoted above (and the rest of the initial summary), to avoid a silly-game of chinese telephone between what the original report is saying and what the news are click-baiting from it. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:18, 12 June 2022 (UTC)- @
X-Editor: "most important one" - is it really? It's the last one to be listed, has the least amount of text devoted to it; and basically is not much of a departure from the known stance of the WHO director-general (who said that it was
"premature" for the WHO's report to rule out a potential link between a laboratory leak
and called on China to provide additional data). We don't need to emphasise stuff which hasn't really changed. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:23, 12 June 2022 (UTC)- To be fair the current wording seems reasonable enough where it is (minor nitpicking about the extra-emphasis final words aside). I'm however very much not sure if we need to copy it to other articles. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 04:25, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- @
X-Editor: "most important one" - is it really? It's the last one to be listed, has the least amount of text devoted to it; and basically is not much of a departure from the known stance of the WHO director-general (who said that it was
- Best not to get hung up on the news coverage. It has been sensationalized, but that should not reflect on the report itself.
- Rather than adding more about the lab leak, what about saying less? The current wording lends itself to misinterpretation because it sounds like a "no lab leak" claim. But as the SAGO report states, zoonotic "origin" does not preclude a lab "source". Why not remove the "it is of zoonotic origins" sentence in the current lead and refer all discussion of the origin to the Investigations article?
- The article has plenty to say about what the virus actually is without trying to make a short summary of the complicated/uncertain/political origins debate, and that debate is already linked in the next sentence. -
Palpable (
talk) 20:52, 12 June 2022 (UTC)
- A reasonable proposal. ScrumptiousFood ( talk) 16:21, 13 June 2022 (UTC)
- I'm in favor of saying less in the lede to discuss more in the origin section and article. I'm not sure we need to make quite so large a cut as to remove the entire sentence. Particularly if the concerns are the words 'zoonotic' and 'origin'. I propose the following change:
It
This still sets up the following sentence with its link to the Investigations article, and mirrors the language used by SAGO. Bakkster Man ( talk) 17:08, 13 June 2022 (UTC)is of zoonotic origins andhas close genetic similarity to bat coronaviruses, suggestingit emerged froma bat-borne virus ancestor.- I agree, that is better than just removing the sentence. - Palpable ( talk) 22:58, 13 June 2022 (UTC)
- Except that's not even what the SAGO report says, let alone all of the other high-quality RS we have on the matter.
At the present time, currently available epidemiological and sequencing data suggest ancestral strains to SARS-CoV-2 have a zoonotic origin with the closest genetically related viruses being beta coronaviruses, identified in Rhinolophus bats in China in 2013 (96.1%) and Laos in 2020 (96.8%). However, so far neither the virus progenitors nor the natural/intermediate hosts or spill-over event to humans have been identified.
- A more legitimate rewriting of the sentence in the lead (taking into account what other sources say) might be
Available evidence indicates that the virus is of zoonotic origin, and has close genetic similarity to bat coronaviruses, suggesting a bat-borne viral ancestor.
RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 23:13, 13 June 2022 (UTC)- Or heck, even simpler, just replace
It is of zoonotic origins [...]
withAvailable evidence indicates that it is of zoonotic origin [...]
. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 23:19, 13 June 2022 (UTC)- yeah agreed re: "Available evidence." — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 00:12, 15 June 2022 (UTC)
- But the SAGO report explains what they mean by "origin" with two full paragraphs on page 11. Without that context, "origin" is easily misinterpreted to mean "immediate parent". -
Palpable (
talk) 00:19, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Wikipedia articles should ideally, as much as possible be written in non-technical, plain English. This applies even more so in the lead, where one would expect that an adequate summary can be made without going into technical distinctions. "Origin", in plain English like in the SAGO report (the explanation given is IMHO very close to the definition given by the
Cambridge dict as
the thing from which something comes, or the place where it began:
), does not mean "immediate parent", else we would be writing this differently. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 00:37, 14 June 2022 (UTC)- In the context of this report, the “origin” can be understood as the ancestral host from where the pathogen has evolved.
- Surely that implies a distinction between "the context of this report" and plain English. -
Palpable (
talk) 01:37, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Why must I repeat? Per Cambridge dictionary;
origins [plural] - used to describe the particular way in which something started to exist or someone started their life: The story has obscure origins
- Or the other very similar definition of the singular form
the thing from which something comes, or the place where it began:
- This seems to me just like researchers being thorough and making clear it is not the "immediate origin" they are referring to. But the current text in the article here is not referring to an immediate origin or to a direct/immediate ancestor, so we should be fine.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 01:46, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Ok, let's try this another way.
- Four people have come to this Talk page recently, objecting that the current text in the lead strongly implies "no lab leak". I can't speak for the other three, but I am a native English speaker and voracious reader with a respectable university degree. You appear to be saying that all three of us have misinterpreted the lead, but at the same time you deny that it lends itself to misinterpretation.
- -
Palpable (
talk) 02:31, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- "no lab leak"; or more accurately "lab leak very unlikely, no or very little evidence to support it, and not seriously considered by most scientists", is the correct interpretation, of both this and other articles and of the sources, so, yeah, there has been no misinterpretation here.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 04:12, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- There must be a clear distinction between "no lab leak" and "no or very little evidence to support a lab leak". While the second claim is valid, it is just as valid to say that there is no or very little evidence to deny a lab leak. The ability to distinguish between ontology and epistemology should be table stakes for participating in this debate.
- If we agree that "it is of zoonotic origin" implies "no lab leak" to many reasonable English speakers, but it clearly means something more nuanced to WHO and other scientific sources, then that phrasing is misleading. It should be removed - or bogged down with a bunch of text clarifying that the technical meaning of "zoonotic origin" does not rule out a lab.
- The next revision of the COVID-19 origins consensus should also be more careful about the meaning of "origin". It seems to be causing a great deal of confusion and, as seen above, some people appear to be exploiting this confusion to push the NOLABLEAK POV. -
Palpable (
talk) 16:12, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
it is just as valid to say that there is no or very little evidence to deny a lab leak.
I think that's the textbook example of affirming a disjunct. Something not being proven false does not mean that there is no evidence against it, only that the evidence against it does not allow to make a definitive conclusion on the premises. Both the SAGO report and other sources (the Holmes et al. critical review; other recent sources like the papers I mentioned earlier, for ex. [25]) say that what evidence we do have (as SAGO phrases it, " epidemiological and sequencing data"; the evidence that Sars-COV-2 was circulating outside of China earlier than thought presented in other sources; the fact that the first detected outbreak in Wuhan was not near the lab but likely involved or was amplified by the wildlife market, ...) suggests an origin with no lab involved. RandomCanadian ( talk / contribs) 00:59, 15 June 2022 (UTC)- Thanks for the reading suggestions. Reading papers is certainly a breath of fresh air after the polemic stench here.
- I am not employing the logical fallacy you mention, I'm pointing to a real lack of evidence. 2.5 years later, we are not much closer to the source than RaTG13. Holmes et al provides very persuasive arguments against the virus being engineered, based on a presumably comprehensive knowledge of available techniques. But many of their claims are still based on absence of evidence. If they had complete documentation of the lab's activities, the closed-world assumption would apply making it possible to reason from the absence of evidence. Unfortunately, access to the full evidence has been severely restricted, the open-world assumption applies instead, and any conclusions from lack of evidence must be taken with a grain of salt.
- I hope I won't be accused of cherry-picking for pointing out that the conclusion to Holmes et al hedges their position with "the possibility of a laboratory accident cannot be entirely dismissed". That's what good science communication looks like: uncertainty comes with the territory, and balance is not considered a sign of weakness. But here on Wikipedia, a small clique of non-scientists can use this careful paper to justify accusations like "fringe", "conspiracy theory", "lab-leaker", and "wingnuttery". Have a nice day. -
Palpable (
talk) 15:25, 15 June 2022 (UTC)
- Basically the SAGO source only says that there's no new information that could provide evidence for the leak theory. This means that nothing changed and that the fully natural origin continues to be the most plausible... —
Paleo
Neonate – 08:20, 16 June 2022 (UTC)
- Most plausible is not the same as absolutely true. We currently say that "It is of zoonotic origins" which is not the same as saying that a zoonotic origin is the most plausible. Would you support a change to the lede so that it reads something to the effect of Available evidence indicates that it is of zoonotic origin" or most likely of zoonotic origin or something to that effect? Bonewah ( talk) 15:00, 16 June 2022 (UTC)
- Basically the SAGO source only says that there's no new information that could provide evidence for the leak theory. This means that nothing changed and that the fully natural origin continues to be the most plausible... —
Paleo
Neonate – 08:20, 16 June 2022 (UTC)
- "no lab leak"; or more accurately "lab leak very unlikely, no or very little evidence to support it, and not seriously considered by most scientists", is the correct interpretation, of both this and other articles and of the sources, so, yeah, there has been no misinterpretation here.
RandomCanadian (
talk /
contribs) 04:12, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Wikipedia articles should ideally, as much as possible be written in non-technical, plain English. This applies even more so in the lead, where one would expect that an adequate summary can be made without going into technical distinctions. "Origin", in plain English like in the SAGO report (the explanation given is IMHO very close to the definition given by the
Cambridge dict as
- Or heck, even simpler, just replace
- This content has been censored from this article for months. Agree it should be included for NPOV and obviously the FRINGE tag on it is just for the purpose of excluding it. But you will face very active editors who have time to banter this position endlessly attempting to push the local consensus here. You probably should run an RFC if you want it looked again by more mainstream editors. As you point out the broader consensus changes over time in the RS and at wikipedia we will follow that (eventually). There is no requirement that we follow MEDRS on all the articles (such as the pandemic) but this article about the disease I wonder if it will fall towards MEDRS (making it harder to go with mainstream view which probably recognizes that there is a decent chance it came from the lab in China). Thanks
Jtbobwaysf (
talk) 02:28, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- I support changing the lead to read that "Available evidence indicates that it is of zoonotic origin" or most likely of zoonotic origin. If tons of official sources hold open the possibility that it is not of zoonotic origin then so should we.
Bonewah (
talk) 12:46, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- The SAGO report unpacks "zoonotic origin", saying the natural reservoir of the virus is most likely zoonotic, and on that I don't think there is any disagreement between experts in sources or editors here. On how the virus was introduced to humans (spillover), and if it was a natural occurrence, the report says it is uncertain.
ScrumptiousFood (
talk) 18:42, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- I think this is probably mostly correct on the level of agreement. I picked up on the word 'ancestry' in the SAGO report, since it seems to do a very good job of leaving the spillover and any evolution between the closest ancestral bat virus and the initial lineage sequenced in humans open ended. Whether direct spillover to humans, intermediate spillover through another animal, or a sample collected in a lab, the ultimate ancestry of some bat beta coronavirus seems fundamentally agreed to. I also think it's probably more clear to an average reader that if/when we find that bat virus, it may not be the exact same virus as SARS-CoV-2, just a direct ancestor. Bakkster Man ( talk) 18:57, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- Agree with this change. "Available evidence" is the only necessary hedging, and it is precisely what our best available consensus source (the SAGO report) currently says. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 00:13, 15 June 2022 (UTC)
- I also support this wording. Bakkster Man ( talk) 17:43, 16 June 2022 (UTC)
- I agree, this wording improves the lead. = Palpable ( talk) 20:59, 17 June 2022 (UTC)
- The SAGO report unpacks "zoonotic origin", saying the natural reservoir of the virus is most likely zoonotic, and on that I don't think there is any disagreement between experts in sources or editors here. On how the virus was introduced to humans (spillover), and if it was a natural occurrence, the report says it is uncertain.
ScrumptiousFood (
talk) 18:42, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
- I support changing the lead to read that "Available evidence indicates that it is of zoonotic origin" or most likely of zoonotic origin. If tons of official sources hold open the possibility that it is not of zoonotic origin then so should we.
Bonewah (
talk) 12:46, 14 June 2022 (UTC)
"Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origins..." What evidence is that? Identifying infected humans in a seafood market where no infected animals have been found does not constitute such evidence, as many commentators in citable sources have noted. Evidence for zoonotic origins requires identifying infected nonlaboratory animals. StN ( talk) 15:07, 18 October 2022 (UTC)
- Please see the discussion above, which references the SAGO report. Bakkster Man ( talk) 16:05, 18 October 2022 (UTC)
Spike protein of the sars-cov-2
I propose we create a new article on the Spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus as it has become notable by itself. The Spike protein has been discussed as vital for the entry process of the cell, vital for the fabrication of vaccines across platforms, and vital to understand possible effects on the immune system because of its shedding. One natural starting point can be the virology sections from this entry, which I can use to write a draft in user space. Opinions? Forich ( talk) 21:10, 20 October 2022 (UTC)
- You mean like Coronavirus spike protein as we have linked in the info box? Bakkster Man ( talk) 16:53, 21 October 2022 (UTC)
Work towards A-Class status
I propose we consciously embark on making this an A-Class article. The criteria are:
Provides a well-written, clear and complete description of the topic, as described in Wikipedia:Article development. It should be of a length suitable for the subject, appropriately structured, and be well referenced by a broad array of reliable sources. It should be well illustrated, with no copyright problems. Only minor style issues and other details need to be addressed before submission as a featured article candidate
. Do any of the wikiprojects involved in this entry have an A-Class assessment departments? Forich ( talk) 16:49, 27 November 2022 (UTC)
- I think A-class is a very uncommon rating. Perhaps WP:GA would be a good goal. – Novem Linguae ( talk) 17:43, 27 November 2022 (UTC)
Caption for the bottom image accompanying article lead
'Atomic model of the external structure of the SARS-CoV-2 virion. Each "ball" is an atom.'
Despite the rather confusing description of the source stating this also: Each "ball" depicted is not an individual Atom but rather a Chemical compound consisting of multiple different chemically bonded atoms.
I have never seen the individual structures of the viral envelope referred to as 'atoms' before, though it it possible that is simply an archaic convention among virologists that I am unaware of.
At any rate though, the link in the caption for this image does direct to the Wikipedia article for atoms.
Would anyone mind correcting for the above? I believe that I am unable to do so myself given the (understandable) protected status of this article. 2A02:A443:AF4E:1:D5A2:151D:A66C:5A5 ( talk) 20:29, 28 December 2022 (UTC)
- Agreed, each "ball" is actually a specific amino acid, which the source image discusses in depth in its description. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 23:54, 28 December 2022 (UTC)
In the "Phylogenetics and taxonomy" section, the claim is made: "The furin cleavage site PRRAR↓ is identical to that of the feline coronavirus, an alphacoronavirus 1 strain." However, the source cited for this statement contradicts this claim. According to the source, there are two variants of feline coronavirus. FECV, which is milder, and FIPV which can be fatal, and that the mild variant has an optimized furin cleavage site, whereas the severe variant has a mutated or even missing furin cleavage site:
For example, the feline enteric coronavirus (FECV), responsible for a milder and localized form of enteric infection in the infected cat, carried a highly optimized furin cleavage site at S1/S2. In contrast, in the spike protein of the feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV), that caused systemic infection and death of the infected cat, the polybasic insert was either completely lost or found mutated.
It goes on to state that the mild form (FECV) has a furin cleavage site with the sequence RRARR↓ (note that this does not match the sequence PRRAR↓ which the Wikipedia article claims is identical):
The presence of a furin cleavage site RRARR↓S in the feline spike protein of the less infectious strain FECV and the presence of PRRAR↓S in the SARS-CoV-2 prompted us to analyse the sequences more carefully.
It also states that of the two feline coronavirus variants, SARS-CoV-2's cleavage site is more similar to the mild variant's site (which as shown above does not have an identical furin cleavage site):
Thus the polybasic insert of CoV-2 spike protein is closer to that of the spike protein of the milder feline coronavirus but carries crucial substitutions that are either uncommon or are disfavored in classical Furin substrates.
This clearly shows that the cited paper does not support the claim made in this article that the PRRAR↓ furin cleavage site present in SARS-CoV-2 is identical to the furin cleavage site in the feline coronavirus. It even appears that not only is the claim not supported by that source, but that the claim may even be incorrect (according to the statements from the source). Moulding ( talk) 21:11, 31 January 2023 (UTC)
- Why don't we just say "nearly identical" since it's only one proline off? And other source say they're very similar:
[26]
[27]Indeed, the second source there says:
For instance, a similar P-R-R-A-R motif in the spike of a feline CoV has been observed to be encoded with a CGG-CGA for the double Arginine (Bank-Wolf et al. 2014). In this case, a single mutation could change the CGG-CGA to a CGG-CGG.
— Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 21:54, 31 January 2023 (UTC)- The second source refers only to the general PRRAR motif found in some FIPV sequences, not the entire cleavage sequece. As can be seen in the original source graphic, the entire cleavage sequence that matched that motif in FIPV was PRRARM↓S, which still is not identical to PRRAR↓S. It also shows that the consensus sequence appears to be SRRSRR↓S (which is not at all similar to SARS-CoV-2's sequence, and it may be misleading for this Wikipedia article to suggest otherwise).
- Original source graphic:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3713968/figure/F2/
Moulding (
talk) 23:06, 31 January 2023 (UTC)
- I'm just gonna change the text to be "highly similar" to, since they are quite similar in the sense of BLOSUM similarity. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 01:57, 1 February 2023 (UTC)
Airborne
I changed the lead to clarify that SARS-CoV-2 is airborne. Sparkie82 ( t• c) 23:46, 22 February 2023 (UTC)
small correction
Pardon the newb comment but I’m used to making small edits as I read Wikipedia articles, but it looks like this article isn’t editable to me.
In Origins it says “… published on Nature …”, should be “in”. Hambolger ( talk) 14:57, 9 March 2023 (UTC)
 Done thanks for the help —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:07, 9 March 2023 (UTC)
Done thanks for the help —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 15:07, 9 March 2023 (UTC)
Edit request: Addition of {{Update section}} template to variants section
This
edit request to
SARS-CoV-2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Please add "{{Update section|date=April 2023}}" after "{{Main|Variants of SARS-CoV-2}}"
Why? The variants section is very much out of date. The statement "Nextstrain divides the variants into five clades (19A, 19B, 20A, 20B, and 20C), while GISAID divides them into seven (L, O, V, S, G, GH, and GR)." is out of date since at least March 2021 when there were already new GISAID clades GV and GRV, see https://gisaid.org/resources/statements-clarifications/clade-and-lineage-nomenclature-aids-in-genomic-epidemiology-of-active-hcov-19-viruses/ AncientWalrus ( talk) 20:14, 24 April 2023 (UTC)
 Done
Actualcpscm (
talk) 20:39, 24 April 2023 (UTC)
Done
Actualcpscm (
talk) 20:39, 24 April 2023 (UTC)
Edit request: Incorrect reference for WHO origin report
This
edit request to
SARS-CoV-2 has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
Reference 87 is not correct to support the following statement: Introduction through the food supply chain and the Huanan Seafood Market was considered another possible, but less likely, explanation.
. The provided reference is Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) but should be WHO-convened Global Study of Origins of SARS-CoV-2: China Part.
Please replace the reference with this one: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-convened-global-study-of-origins-of-sars-cov-2-china-part-joint-report.pdf AncientWalrus ( talk) 11:55, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
 Done
[28] —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 12:21, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Done
[28] —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 12:21, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Origin update?...
From the article's intro: "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin and has close genetic similarity to bat coronaviruses, suggesting it emerged from a bat-borne virus."
The citation provided there though (#18) is dated 2020, when the pandemic was still quite new, and our understanding of the virus and its origins were much more limited. We now have US government agencies, like the Energy Dept in the recent report, saying that a lab leak origin is more likely. So I would suggest that this part of the intro be updated, rewritten, and much newer citations used. - 2003:CA:871C:D28:77AA:E11E:9B4:E4E6 ( talk) 11:32, 28 February 2023 (UTC)
- See: COVID-19 lab leak theory and Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 where this discussion is more appropriately placed. I'll bring the consensus wording from those pages. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 13:28, 28 February 2023 (UTC)
Early origin
Found a review of early detections, including viral DNA from a skin sample in Italy November 12, 2019. https://gh.bmj.com/content/7/3/e008386.long Sennalen ( talk) 21:27, 5 March 2023 (UTC)
- The authors themselves describe how much false positives likely impacted these results:
So yes, it's certainly possible these are real, but they are also very far from proven. The sequencing data does also predict an emergence into humans in late October/early November based on mutation rates: [29] [30] [31] — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 22:38, 5 March 2023 (UTC)laboratory evidence for early circulation is often dismissed and labelled as a result of false-positive testing. Antibody detection results can indeed be affected by the presence in sera of antibodies which, although able to recognise SARS-CoV-2 antigens, were induced by other agents.12 However, the presence of SARS-CoV-2 neutralising activity in these sera and the fact that several patients presented more than one class of antibodies recognising SARS-CoV-2 suggest that, although some cross-reactivity should be taken into account, at least some of the sera could contain antibodies induced by a prior SARS-CoV-2 infection... PCR-based methods are highly sensitive and, therefore, more prone to false-positive results.
- That's one mode of testing. Evidence was found in sera antibodies and RNA skin samples from November and sewage two weeks later. There were no positives in June-August. It's not an isolated false positive, but a body of evidence consistent with the same timeline. Sennalen ( talk) 23:28, 5 March 2023 (UTC)
- @
Shibbolethink: No real harm in reastating it, but the part you added wasn't missing.
Sennalen (
talk) 20:50, 10 March 2023 (UTC)
- I think wikipedia policy makes it clear that we should always put mainstream criticisms of things next to their mention whenever possible, and not separate them so as to de-emphasize or isolate criticism. That's why I made the edit I did, even if I do think the addition is a good one to the article. I think it should probably be integrated more with that paragraph, though, as it currently reads weird wrt the later sentences about December of 2019... Given that most sources place the beginning of the pandemic in late November, early December. I am happy to help fix it but I also think you are well-equipped to do so — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 20:55, 10 March 2023 (UTC)
- As a subject matter expert, early detections outside of China before 2019 are not taken seriously. Everything starting from "The Lombardy region..." until "..and RNA sequencing" should in my opinion be removed as WP:UNDUE. One single review "Waiting for the truth" is used almost exclusively for the whole paragraph. It has only been cited 10 times in more than a year, which is very little for a review in general and in particular on the hot topic of COVID. AncientWalrus ( talk) 21:50, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
Paragraph on early detections outside of China
The whole paragraph about putative early detections of SARS-CoV-2 genome fragments in Italy in the autumn of 2019 should be removed. It is entirely based on primary research. While it may appear that the most cited reference is a review, that review article was written by the same authors who did the original research the review is reviewing.
For a topic with such extensive secondary and tertiary coverage in reputable science journalism, such a not-widely cited review does not justify a paragraph in this article.
I already touched on this briefly in the higher up topic
Early origin. Thanks @
Bon courage for getting started on this
here but I think we should go much further by removing it altogether. If at all, it should get a minor mention in the separate origins article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:14, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I agree, if anything it deserves a very short mention, but we probably overemphasize the research here. Any mention of it requires heavy context about it being speculative and possible false positives, but that would create an overall too-long mention. So I agree with your suggestion to cut it. —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 12:16, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- There does seem to be a review cited, but it's an
WP:EXCEPTIONAL claim given way too much credence here.
Bon courage (
talk) 12:36, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- The review didn't get much traction at all. I couldn't find any mention of the early detection theory in any Science journal news article, which is a good proxy for what is considered reasonable by the science community. The
Lancet Commission gives it one sentence
Whether identifiable cases appeared earlier than December, 2019, is unknown.
in a long article. None of the reports were published in top journals either. The best independent coverage I could find is Wired which closes withBut it’s clear that the evidence so far isn’t the most robust. “Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence,” says Jonathan Stoye, a virologist at the Francis Crick Institute. “I’m not convinced that a dodgy piece of data on top of another dodgy piece of data on top of another dodgy piece of data leads one to a firm conclusion.”
AncientWalrus ( talk) 13:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)- Yeah I would overall say it is UNDUE for such a top-level summary article like this. I agree a short mention in
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 could be appropriate if worded in a DUE and NPOV manner. —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 13:12, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
 Done Excised.
Bon courage (
talk) 13:48, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Done Excised.
Bon courage (
talk) 13:48, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Yeah I would overall say it is UNDUE for such a top-level summary article like this. I agree a short mention in
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 could be appropriate if worded in a DUE and NPOV manner. —
Shibbolethink (
♔
♕) 13:12, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- The review didn't get much traction at all. I couldn't find any mention of the early detection theory in any Science journal news article, which is a good proxy for what is considered reasonable by the science community. The
Lancet Commission gives it one sentence
- There does seem to be a review cited, but it's an
WP:EXCEPTIONAL claim given way too much credence here.
Bon courage (
talk) 12:36, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Lab leak theory
The fact that this page doesn’t even mention the possibility that the virus originated in a lab is baffling, given that there are a number of credible experts who have stated it is plausible, not to mention the U.S. intelligence agencies who’ve concluded it’s probable. The complete omission of this viewpoint calls into question the neutrality and objectivity of the entire article. 68.12.22.29 ( talk) 04:11, 26 April 2023 (UTC)
- It also doesn't mention non-lab origins. In fact, it makes no suggestion about the origin. It does mention the seafood market, but does not, as the CIA likes to say, confirm or deny such explanations. Some people (but mostly not the article) mention natural origin. Chinese farms are far from natural, so it doesn't seem likely that it is natural. Virologists for many years have been expecting a new pandemic flu virus from China. Among others, that slowed down the reaction to Covid. Note that the origin of Ebola still has not been found, over many more years. But yes, China isn't helping as much as they could. Gah4 ( talk) 08:43, 26 April 2023 (UTC)
- The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue. I raised this question more than a year ago and made well-sourced changes to the article that reflected the changing consensus. It got me banned by aggressive editors.
StN (
talk) 22:04, 28 April 2023 (UTC)
- I’d say we are heading for a mention on this as there are more reliable sources discussing e.g. the BBC.
- If you were basing some new text on the current media flurry I think we would need a little more time to see how it develops and to avoid suggestions that it’s recentism or news and because we have only got to the point of “don’t rule out” - frustrating as that may be seeing as you have waited a year already.
- This from The Scientific American seems to sum up the position well and I’d support an addition to our text based around this or similar.
- “At least eight U.S. intelligence agencies have conducted their own investigations of the virus’s origins. Four agencies concluded a natural spillover from animals is most likely, two favor a lab leak, and two are undecided. U.S. president Joe Biden recently signed a bill requiring U.S. government information related to COVID origins to be declassified.”
- It’s a reliable source but beware that over egging the lab escape possibility would be undue, (as our current text is because it doesn’t really mention it)
- I think the article should have been more open minded from the start but there was initially a pushback on the lab idea because Trump said it - and for some that automatically makes it wrong.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 11:08, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- BTW we do have other articles on this (see
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 for example) that underplay the possibility of a lab release.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 11:14, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
Please read WP:IDHT and then read the contribution directly above yours.I misread something, so I am striking this. There was actually no pro-science contribution in this thread until then, only lableaker voices and one uncertain one. Alerting WP:FTN now. -- Hob Gadling ( talk) 07:11, 31 May 2023 (UTC)most likely of zoonotic origin
is what the reliable sources say. -- Hob Gadling ( talk) 11:55, 30 May 2023 (UTC)- Also, even if the spillover didn't happen in the market, but e.g. from a bat in the lab, it would still be zoonosis. The only hypothesis that I can think of that doesn't fall under "zoonosis" would involve engineering, which is only a subset of the various theories summarized under the lab leak umbrella.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:13, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- And I get that it has to be zoonosis in the sense of 'natural' - but that is missing the point surely when this lab leak possibility involves human agency (or incompetence etc.) rather than a naturally occurring event.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 15:36, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- I guess my reply was to @
StN who wrote
The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue.
AncientWalrus ( talk) 18:32, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- I guess my reply was to @
StN who wrote
- And I get that it has to be zoonosis in the sense of 'natural' - but that is missing the point surely when this lab leak possibility involves human agency (or incompetence etc.) rather than a naturally occurring event.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 15:36, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Have read IDHT. I'm afraid I don't get your point (really). How should I have phrased?
- In response to StN I am saying that there are reliable sources reporting government agencies saying 'lab leak' and discussing how to include. Shouldn't I? Lukewarmbeer ( talk) 15:34, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Also, even if the spillover didn't happen in the market, but e.g. from a bat in the lab, it would still be zoonosis. The only hypothesis that I can think of that doesn't fall under "zoonosis" would involve engineering, which is only a subset of the various theories summarized under the lab leak umbrella.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:13, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- BTW we do have other articles on this (see
Investigations into the origin of COVID-19 for example) that underplay the possibility of a lab release.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 11:14, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- I politely disagree with @
Gah4's statement above:
The article does discuss origin scenarios:It also doesn't mention non-lab origins. In fact, it makes no suggestion about the origin. It does mention the seafood market, but does not, as the CIA likes to say, confirm or deny such explanations. Some people (but mostly not the article) mention natural origin.
- a) Intermediate host:
A March 2021 WHO-convened report stated that human spillover via an intermediate animal host was the most likely explanation, with direct spillover from bats next most likely.
- b) Food supply chain:
Introduction through the food supply chain and the Huanan Seafood Market was considered another possible, but less likely, explanation.
- c) Huanan Market being source:
An analysis in November 2021, however, said that the earliest-known case had been misidentified and that the preponderance of early cases linked to the Huanan Market argued for it being the source.
- I consider it
WP:DUE to mention the fact that a considerable number of leading scientists consider a laboratory incident/accident plausible. For example, it may be worth mentioning this letter in
Science criticizing the WHO report by saying that
[the theory of a laboratory incident] was not given balanced consideration
and further stating:We must take hypotheses about both natural and laboratory spillovers seriously until we have sufficient data
. This letter was discussed in secondary sources, e.g. WSJ. - We do not get into the details, however, it would be good to state that a laboratory incident/accident is one of the origin hypotheses being considered.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 18:58, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- The "food supply chain" hypothesis is taken seriously by far fewer scientists than a lab leak. Yet it gets mentioned in the article. Hard to explain. So either it has to go or lab incident/accident should get a mention as well. Even former China CDC head
George F. Gao now states that a lab leak shouldn't be ruled out, see today's
BBC article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 19:27, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Great. Do we have any strong objections to the lab leak being a possibility?
- If not lets get it in.
Lukewarmbeer (
talk) 20:29, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Don't rush it, there may well be objections by e.g. @
Hob Gadling and/or @
Gah4.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 21:41, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- I suppose not to it being a possibility, but I don't believe a strong possibility. It is possible for me to buy a Powerball ticket and win, but not likely. Gah4 ( talk) 00:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Otherwise, I suppose I don't disagree with the polite disagreement. Not that I said so much that one could agree or disagree with.
Gah4 (
talk) 00:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Well, you said the article doesn't discuss origin scenarios. But it does, it even mentions the food supply chain hypothesis which is not believed by anyone I know. AncientWalrus ( talk) 11:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I should try to find a
WP:RS for virologists ten or so years ago, mentioning Chinese farms as the source of the next global pandemic. And, likely coming from that, a fictional story with Wuhan as the center of a pandemic source.
Gah4 (
talk) 00:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I think if we're going to mention the lab-leak stuff at all, per
WP:FRINGESUBJECTS we would need to bring in the mainstream context: that there is zero evidence for it, that there are popular misconceptions about its likelihood, that many LL ideas are conspiracy theories, that it's informed by racist undertones, and that nearly all scientists don't subscribe to it (except maybe in a can't-rule-stuff-out / remote-possibility kind of way). Basically it's just speculation, and best left to the misinformation articles and the specialist LL article.
Bon courage (
talk) 07:22, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- And the origin of Ebola still isn't known. The worst thing about lab-leak, is that many politicians believe that we need to find the origin to stop the next pandemic. Sounds good. But there is no reason to suspect that the next one will have the same origin. There were many who were sure in 2018 that the next world pandemic would be caused by a new flu virus, and planned for that. I suspect that is usual for conspiracy theories. We need to find out who shot JFK, to stop the next assassination. Oh well. Gah4 ( talk) 09:03, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- The fact that there some people take a lab hypothesis to fringe levels should not prevent us from mentioning the non-fringe possibility that the lab may have been involved. I agree that the loudest voices have fringe views, but measured non-fringe views exist, who are not informed by racist undertones (see Science letter). Could you explain why you think the cold chain hypothesis deserves mention? It is considered to be a narrative pushed by the Chinese gov't to deflect blame.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 11:49, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- We link to the Investigations article which has the following in its lede: "Some scientists and politicians have speculated that SARS-CoV-2 was accidentally released from a laboratory. This theory is not supported by evidence." I would not object to including that wording here.
Bon courage (
talk) 11:57, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- That's a good idea. Though maybe we should also add US government agencies which may or may not have non-public evidence. If I correctly understand the scientists asking for investigations of all possible origins, including accidental laboratory release, they agree that there is no public evidence for such a release. However, they believe that the evidence for alternative hypotheses may not be as strong as reported.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:05, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I would strongly oppose adding the "US agencies" talking point, as being undue.
Bon courage (
talk) 12:27, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Given the involvement of state actors and lack of transparency, see e.g.
Chinese scientists echoing party line, this isn't a question that science alone can argue. Intelligence agencies may well have relevant non-public evidence. But I understand that this is best placed in the origins article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 13:04, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Saying that "This theory is not supported by evidence." or that "there is zero evidence for it" is objectively false. There is plenty of evidence of a lab leak. Maybe not evidence you find convincing, but evidence none the less.
Bonewah (
talk) 13:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Yeah, it's the same kind of evidence that the moon landing was faked. Which is why the sources say what they do.
Bon courage (
talk) 13:42, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Multiple government agencies believe in the equivalent of the moon landing? I disagree.
Bonewah (
talk) 13:44, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- "Some bureaucrats believe in X" is not evidence for X. -- Hob Gadling ( talk) 13:47, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Of course, but what US spook agencies say they "believe" has nothing to do with whether there's evidence. Follow the sources rather than trying to interpret/speculate. Bon courage ( talk) 13:47, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Multiple government agencies believe in the equivalent of the moon landing? I disagree.
Bonewah (
talk) 13:44, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- "Zero evidence" is scientist-speak for "only shitty evidence that one would expect in any case, whether the LL idea is true or not, and which therefore does not count". -- Hob Gadling ( talk) 13:47, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
Saying that "This theory is not supported by evidence." or that "there is zero evidence for it" is objectively false
It seems you have a problem with our sources then, as that's what our highest quality sources say. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 15:54, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Yeah, it's the same kind of evidence that the moon landing was faked. Which is why the sources say what they do.
Bon courage (
talk) 13:42, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Possible existence of non-public evidence is not relevant. Wikipedia is supposed to summarize the published knowledge of mankind, not speculation. --
Hob Gadling (
talk) 13:47, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- If an agency makes an estimation based on non-public evidence and that is reported in RS then the agency's opinion can in theory be included if due. The evidence itself doesn't need to be public. My point is that the question of origin is not one that is intrinsically scientific. Scientific methods can help find an answer, but there may well be other sources of information that aren't scientific, like intelligence sources. There is no categorical difference between a question like "Who was SARS-CoV-2 patient zero?" and "Who piloted the drone that crashed over the kremlin?".
AncientWalrus (
talk) 13:55, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- All this about which out of which US agencies say what with whatever degrees of confidence and disagreement is in the LL article. The trouble is just saying "The ${agency} thinks so!" is unbalanced and reductive & makes it look like this is uber-important. Which is why LL people say it over and over and over again. This stuff isn't even mentioned in the investigation article lede so going over it here would be doubly undue.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Saying that "there is no evidence of LL" is unbalanced and reductive & makes it look like the issue is decided, which it is not.
Bonewah (
talk) 14:12, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- It's just accepted knowledge as published in reliable sources, so Wikipedia reflects it. It would only make the matter look "decided" to a reader with no elementary understanding of logic, since evidence may emerge in time.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:16, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Are you claiming that its "accepted knowledge" that the LL theory has no supporting evidence?
Bonewah (
talk) 14:29, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- "Accepted knowledge as published in reliable sources". See the
COVID-19 lab leak theory article for further details/sources.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:49, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Well if you are proposing an edit along these lines, then i oppose it. At least as far as i can discern what you seem to be proposing. If not, them maybe we can just stop.
Bonewah (
talk) 15:07, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- To repeat, I would not object to copying the consensus text/refs to be in sync with the Investigations article - specifically: "Some scientists and politicians have speculated that SARS-CoV-2 was accidentally released from a laboratory. This theory is not supported by evidence." Also happy to leave any mention of LL out.
Bon courage (
talk) 15:18, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Then i object. Specifically to the line "This theory is not supported by evidence."
Bonewah (
talk) 15:39, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Why? Personal objections don't count. We're not going to use this article to create a WP:POVFORK; so what we say has to be in sync with the other more detailed articles on the topic, and present the mainstream view prominently to be neutral, which is a must. Bon courage ( talk) 15:41, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Then i object. Specifically to the line "This theory is not supported by evidence."
Bonewah (
talk) 15:39, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- To repeat, I would not object to copying the consensus text/refs to be in sync with the Investigations article - specifically: "Some scientists and politicians have speculated that SARS-CoV-2 was accidentally released from a laboratory. This theory is not supported by evidence." Also happy to leave any mention of LL out.
Bon courage (
talk) 15:18, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Well if you are proposing an edit along these lines, then i oppose it. At least as far as i can discern what you seem to be proposing. If not, them maybe we can just stop.
Bonewah (
talk) 15:07, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- "Accepted knowledge as published in reliable sources". See the
COVID-19 lab leak theory article for further details/sources.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:49, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Are you claiming that its "accepted knowledge" that the LL theory has no supporting evidence?
Bonewah (
talk) 14:29, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- It's just accepted knowledge as published in reliable sources, so Wikipedia reflects it. It would only make the matter look "decided" to a reader with no elementary understanding of logic, since evidence may emerge in time.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:16, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Saying that "there is no evidence of LL" is unbalanced and reductive & makes it look like the issue is decided, which it is not.
Bonewah (
talk) 14:12, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- All this about which out of which US agencies say what with whatever degrees of confidence and disagreement is in the LL article. The trouble is just saying "The ${agency} thinks so!" is unbalanced and reductive & makes it look like this is uber-important. Which is why LL people say it over and over and over again. This stuff isn't even mentioned in the investigation article lede so going over it here would be doubly undue.
Bon courage (
talk) 14:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- If an agency makes an estimation based on non-public evidence and that is reported in RS then the agency's opinion can in theory be included if due. The evidence itself doesn't need to be public. My point is that the question of origin is not one that is intrinsically scientific. Scientific methods can help find an answer, but there may well be other sources of information that aren't scientific, like intelligence sources. There is no categorical difference between a question like "Who was SARS-CoV-2 patient zero?" and "Who piloted the drone that crashed over the kremlin?".
AncientWalrus (
talk) 13:55, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Saying that "This theory is not supported by evidence." or that "there is zero evidence for it" is objectively false. There is plenty of evidence of a lab leak. Maybe not evidence you find convincing, but evidence none the less.
Bonewah (
talk) 13:33, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Given the involvement of state actors and lack of transparency, see e.g.
Chinese scientists echoing party line, this isn't a question that science alone can argue. Intelligence agencies may well have relevant non-public evidence. But I understand that this is best placed in the origins article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 13:04, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I would strongly oppose adding the "US agencies" talking point, as being undue.
Bon courage (
talk) 12:27, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- That's a good idea. Though maybe we should also add US government agencies which may or may not have non-public evidence. If I correctly understand the scientists asking for investigations of all possible origins, including accidental laboratory release, they agree that there is no public evidence for such a release. However, they believe that the evidence for alternative hypotheses may not be as strong as reported.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 12:05, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- We link to the Investigations article which has the following in its lede: "Some scientists and politicians have speculated that SARS-CoV-2 was accidentally released from a laboratory. This theory is not supported by evidence." I would not object to including that wording here.
Bon courage (
talk) 11:57, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- I think if we're going to mention the lab-leak stuff at all, per
WP:FRINGESUBJECTS we would need to bring in the mainstream context: that there is zero evidence for it, that there are popular misconceptions about its likelihood, that many LL ideas are conspiracy theories, that it's informed by racist undertones, and that nearly all scientists don't subscribe to it (except maybe in a can't-rule-stuff-out / remote-possibility kind of way). Basically it's just speculation, and best left to the misinformation articles and the specialist LL article.
Bon courage (
talk) 07:22, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- Don't rush it, there may well be objections by e.g. @
Hob Gadling and/or @
Gah4.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 21:41, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
- Wikipedia doesn't care what you or I think. It cares about what the sources say. And the sources say there is "
no evidence exists to support such a notion
" [32] and "there is no good evidence
" [33] and "there's not a single piece of data suggesting
" that the lab leak is true. [34] — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 15:58, 31 May 2023 (UTC)- You're mostly quoting the same people, author of [6] is also author of [4]. Another source says:
Bloom, however, asserts that the evidence for a market origin for the current coronavirus pandemic is not conclusive, and both a laboratory origin and natural spillover should be viewed as possible causes of future pandemics.
WaPo (this is from 2023, your first two sources are from 2021). AncientWalrus ( talk) 16:58, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- You're mostly quoting the same people, author of [6] is also author of [4]. Another source says:
- The "food supply chain" hypothesis is taken seriously by far fewer scientists than a lab leak. Yet it gets mentioned in the article. Hard to explain. So either it has to go or lab incident/accident should get a mention as well. Even former China CDC head
George F. Gao now states that a lab leak shouldn't be ruled out, see today's
BBC article.
AncientWalrus (
talk) 19:27, 30 May 2023 (UTC)
The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue
That's what our most reliable highest quality sources state. E.g. [35] [36] [37] [38] [39]Wikipedia is not about "the Truth". It's about having verifiability to what our highest quality sources say. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 15:53, 31 May 2023 (UTC)- Exactly, Bonewah is apparently engaging in
WP:PROFRINGE advocacy. Wikipedia reflects sources, not editor opinion.
Bon courage (
talk) 16:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- @Shibbolethink Can you clarify something for me? Just above you said "
The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue
That's what our most reliable highest quality sources state." Do you mean by that the "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin,"? In other words, the statement ""Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin" is what our most reliable highest quality sources state? Bonewah ( talk) 16:19, 31 May 2023 (UTC)- Yes. Per WP:SYNTHNOTSUMMARY and WP:RS/AC. — Shibbolethink ( ♔ ♕) 16:28, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- @Shibbolethink Can you clarify something for me? Just above you said "
- Exactly, Bonewah is apparently engaging in
WP:PROFRINGE advocacy. Wikipedia reflects sources, not editor opinion.
Bon courage (
talk) 16:01, 31 May 2023 (UTC)
- The lead states "Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic origin," which is untrue. I raised this question more than a year ago and made well-sourced changes to the article that reflected the changing consensus. It got me banned by aggressive editors.
StN (
talk) 22:04, 28 April 2023 (UTC)