| Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
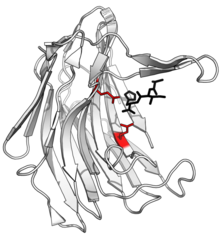 Structure of
scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, with cleaved peptide
product in black and
active site glutamate-glutamine dyad side chains in red. (
PDB:
1S2K) | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 3.4.23.32 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 104781-89-7 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B ( EC 3.4.23.32, obsolete names include Scytalidium aspartic proteinase B, Ganoderma lucidum carboxyl proteinase, Ganoderma lucidum aspartic proteinase, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase B, SLB) is a proteolytic enzyme. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease. [6] [7]
The protease has a unique structure and a novel catalytic dyad (E136 and Q53) in its active site. The active-site residues, glutamic acid (E) and glutamine (Q), was used to coin the name of the family of proteases; eqolisins, to which Scytalidoglutamic peptidase B belongs. [6]
This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
- Hydrolysis of proteins with broad specificity, cleaving Phe24-Phe and Tyr26–Thr but not Leu15-Tyr and Phe25-Tyr in the B chain of insulin. It also cleaves the His6–Pro bond of angiotensin I, the ability to cleave a peptide bond with Pro in the P1′ position is unusual.
This endopeptidase is isolated from Scytalidium lignicolum. It is an acid protease, and is most active at pH 2.0 when casein is used as substrate. Eqolosins prefer bulky amino acid residues at the P1 site and small amino acid residues at the P1′ site. [8] The substrate specificity of scytalidoglutamic peptidase is unique, particularly in the substrate preferences at the P3 (basic amino acid), P1′ (small amino acid) and P3′ (basic) positions. [9]
- ^ Terashita T, Oda K, Kōno M, Murao S (1981). "Streptomyces pepsin inhibitor-insensitive carboxyl proteinase from Lentinus edodes". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 45: 1937–1943. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.45.1937.
- ^ Maita T, Nagata S, Matsuda G, Maruta S, Oda K, Murao S, Tsuru D (February 1984). "Complete amino acid sequence of Scytalidium lignicolum acid protease B". Journal of Biochemistry. 95 (2): 465–475. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134628. PMID 6370989.
- ^ Terashita T, Oda K, Kono M, Murao S (1984). "Streptomyces pepsin inhibitor-insensitive carboxyl proteinase from Ganoderma lucidum". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 48: 1029–1035. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.48.1029.
- ^ Kobayashi H, Kusakabe I, Murakami K (1985). "Purification and characterization of a pepstatin-insensitive carboxyl proteinase from Polyporus tulipiferae (Irpex lacteus)". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 49 (8): 2393–2397. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.49.2393.
- ^ Tsuru D, Shimada S, Maruta S, Yoshimoto T, Oda K, Murao S, et al. (May 1986). "Isolation and amino acid sequence of a peptide containing an epoxide-reactive residue from the thermolysin-digest of Scytalidium lignicolum acid protease B". Journal of Biochemistry. 99 (5): 1537–1539. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135624. PMID 3519605.
- ^ a b Fujinaga M, Cherney MM, Oyama H, Oda K, James MN (March 2004). "The molecular structure and catalytic mechanism of a novel carboxyl peptidase from Scytalidium lignicolum". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (10): 3364–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400246101. PMC 373467. PMID 14993599.
- ^ Pillai B, Cherney MM, Hiraga K, Takada K, Oda K, James MN (January 2007). "Crystal structure of scytalidoglutamic peptidase with its first potent inhibitor provides insights into substrate specificity and catalysis". Journal of Molecular Biology. 365 (2): 343–361. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.058. PMID 17069854.
- ^ Oda K (January 2012). "New families of carboxyl peptidases: serine-carboxyl peptidases and glutamic peptidases". Journal of Biochemistry. 151 (1): 13–25. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvr129. PMID 22016395.
- ^ Kataoka Y, Takada K, Oyama H, Tsunemi M, James MN, Oda K (June 2005). "Catalytic residues and substrate specificity of scytalidoglutamic peptidase, the first member of the eqolisin in family (G1) of peptidases". FEBS Letters. 579 (14): 2991–2994. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.04.050. PMID 15907842.
- Scytalidopepsin+B at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Structure of
scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, with cleaved peptide
product in black and
active site glutamate-glutamine dyad side chains in red. (
PDB:
1S2K) | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 3.4.23.32 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 104781-89-7 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B ( EC 3.4.23.32, obsolete names include Scytalidium aspartic proteinase B, Ganoderma lucidum carboxyl proteinase, Ganoderma lucidum aspartic proteinase, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase B, SLB) is a proteolytic enzyme. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease. [6] [7]
The protease has a unique structure and a novel catalytic dyad (E136 and Q53) in its active site. The active-site residues, glutamic acid (E) and glutamine (Q), was used to coin the name of the family of proteases; eqolisins, to which Scytalidoglutamic peptidase B belongs. [6]
This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
- Hydrolysis of proteins with broad specificity, cleaving Phe24-Phe and Tyr26–Thr but not Leu15-Tyr and Phe25-Tyr in the B chain of insulin. It also cleaves the His6–Pro bond of angiotensin I, the ability to cleave a peptide bond with Pro in the P1′ position is unusual.
This endopeptidase is isolated from Scytalidium lignicolum. It is an acid protease, and is most active at pH 2.0 when casein is used as substrate. Eqolosins prefer bulky amino acid residues at the P1 site and small amino acid residues at the P1′ site. [8] The substrate specificity of scytalidoglutamic peptidase is unique, particularly in the substrate preferences at the P3 (basic amino acid), P1′ (small amino acid) and P3′ (basic) positions. [9]
- ^ Terashita T, Oda K, Kōno M, Murao S (1981). "Streptomyces pepsin inhibitor-insensitive carboxyl proteinase from Lentinus edodes". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 45: 1937–1943. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.45.1937.
- ^ Maita T, Nagata S, Matsuda G, Maruta S, Oda K, Murao S, Tsuru D (February 1984). "Complete amino acid sequence of Scytalidium lignicolum acid protease B". Journal of Biochemistry. 95 (2): 465–475. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134628. PMID 6370989.
- ^ Terashita T, Oda K, Kono M, Murao S (1984). "Streptomyces pepsin inhibitor-insensitive carboxyl proteinase from Ganoderma lucidum". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 48: 1029–1035. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.48.1029.
- ^ Kobayashi H, Kusakabe I, Murakami K (1985). "Purification and characterization of a pepstatin-insensitive carboxyl proteinase from Polyporus tulipiferae (Irpex lacteus)". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 49 (8): 2393–2397. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.49.2393.
- ^ Tsuru D, Shimada S, Maruta S, Yoshimoto T, Oda K, Murao S, et al. (May 1986). "Isolation and amino acid sequence of a peptide containing an epoxide-reactive residue from the thermolysin-digest of Scytalidium lignicolum acid protease B". Journal of Biochemistry. 99 (5): 1537–1539. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135624. PMID 3519605.
- ^ a b Fujinaga M, Cherney MM, Oyama H, Oda K, James MN (March 2004). "The molecular structure and catalytic mechanism of a novel carboxyl peptidase from Scytalidium lignicolum". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (10): 3364–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400246101. PMC 373467. PMID 14993599.
- ^ Pillai B, Cherney MM, Hiraga K, Takada K, Oda K, James MN (January 2007). "Crystal structure of scytalidoglutamic peptidase with its first potent inhibitor provides insights into substrate specificity and catalysis". Journal of Molecular Biology. 365 (2): 343–361. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.058. PMID 17069854.
- ^ Oda K (January 2012). "New families of carboxyl peptidases: serine-carboxyl peptidases and glutamic peptidases". Journal of Biochemistry. 151 (1): 13–25. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvr129. PMID 22016395.
- ^ Kataoka Y, Takada K, Oyama H, Tsunemi M, James MN, Oda K (June 2005). "Catalytic residues and substrate specificity of scytalidoglutamic peptidase, the first member of the eqolisin in family (G1) of peptidases". FEBS Letters. 579 (14): 2991–2994. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.04.050. PMID 15907842.
- Scytalidopepsin+B at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)