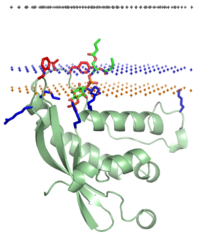
 PX domain of NADH oxidase (p40phox), lipid-bound | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | PX | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00787 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001683 | ||||||||
| SMART | PX | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC50195 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1h6h / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 57 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1xte | ||||||||
| CDD | cd06093 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The PX domain is a phosphoinositide-binding structural domain involved in targeting of proteins to cell membranes.
This domain was first found in P40phox and p47phox domains of NADPH oxidase (phox stands for phagocytic oxidase). [1] [2] It was also identified in many other proteins involved in membrane trafficking, including nexins, Phospholipase D, and phosphoinositide-3- kinases.
The PX domain is structurally conserved in eukaryotes, although amino acid sequences show little similarity. [3] PX domains interact primarily with PtdIns(3)P lipids. [4] [5] However some of them bind to phosphatidic acid, PtdIns(3,4)P2, PtdIns(3,5)P2, PtdIns(4,5)P2, and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3. The PX-domain can also interact with other domains and proteins.
Human proteins containing this domain
Sorting nexins contain this domain. Other examples include:
- HS1BP3
- KIF16B (SNX23)
- NCF1; NCF1C; NCF4; NISCH
- PIK3C2A; PIK3C2B; PIK3C2G; PLD1; PLD2; PXK
- RPS6KC1
- SGK3; SH3PXD2A; SNAG1; SNX9
References
- ^ Ponting CP (November 1996). "Novel domains in NADPH oxidase subunits, sorting nexins, and PtdIns 3-kinases: binding partners of SH3 domains?". Protein Sci. 5 (11): 2353–7. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560051122. PMC 2143296. PMID 8931154.
- ^ Wishart MJ, Taylor GS, Dixon JE (June 2001). "Phoxy lipids: revealing PX domains as phosphoinositide binding modules". Cell. 105 (7): 817–20. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00414-7. PMID 11439176. S2CID 12622490.
- ^ Hiroaki H, Ago T, Ito T, Sumimoto H, Kohda D (June 2001). "Solution structure of the PX domain, a target of the SH3 domain". Nat. Struct. Biol. 8 (6): 526–30. doi: 10.1038/88591. PMID 11373621. S2CID 27416988.
- ^ Karathanassis D, Stahelin RV, Bravo J, Perisic O, Pacold CM, Cho W, Williams RL (October 2002). "Binding of the PX domain of p47phox to phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate and phosphatidic acid is masked by an intramolecular interaction". EMBO J. 21 (19): 5057–68. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf519. PMC 129041. PMID 12356722.
- ^ Ago T, Kuribayashi F, Hiroaki H, Takeya R, Ito T, Kohda D, Sumimoto H (April 2003). "Phosphorylation of p47phox directs phox homology domain from SH3 domain toward phosphoinositides, leading to phagocyte NADPH oxidase activation". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (8): 4474–9. Bibcode: 2003PNAS..100.4474A. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0735712100. PMC 153580. PMID 12672956.
 PX domain of NADH oxidase (p40phox), lipid-bound | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | PX | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00787 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001683 | ||||||||
| SMART | PX | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC50195 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1h6h / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 57 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1xte | ||||||||
| CDD | cd06093 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The PX domain is a phosphoinositide-binding structural domain involved in targeting of proteins to cell membranes.
This domain was first found in P40phox and p47phox domains of NADPH oxidase (phox stands for phagocytic oxidase). [1] [2] It was also identified in many other proteins involved in membrane trafficking, including nexins, Phospholipase D, and phosphoinositide-3- kinases.
The PX domain is structurally conserved in eukaryotes, although amino acid sequences show little similarity. [3] PX domains interact primarily with PtdIns(3)P lipids. [4] [5] However some of them bind to phosphatidic acid, PtdIns(3,4)P2, PtdIns(3,5)P2, PtdIns(4,5)P2, and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3. The PX-domain can also interact with other domains and proteins.
Human proteins containing this domain
Sorting nexins contain this domain. Other examples include:
- HS1BP3
- KIF16B (SNX23)
- NCF1; NCF1C; NCF4; NISCH
- PIK3C2A; PIK3C2B; PIK3C2G; PLD1; PLD2; PXK
- RPS6KC1
- SGK3; SH3PXD2A; SNAG1; SNX9
References
- ^ Ponting CP (November 1996). "Novel domains in NADPH oxidase subunits, sorting nexins, and PtdIns 3-kinases: binding partners of SH3 domains?". Protein Sci. 5 (11): 2353–7. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560051122. PMC 2143296. PMID 8931154.
- ^ Wishart MJ, Taylor GS, Dixon JE (June 2001). "Phoxy lipids: revealing PX domains as phosphoinositide binding modules". Cell. 105 (7): 817–20. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00414-7. PMID 11439176. S2CID 12622490.
- ^ Hiroaki H, Ago T, Ito T, Sumimoto H, Kohda D (June 2001). "Solution structure of the PX domain, a target of the SH3 domain". Nat. Struct. Biol. 8 (6): 526–30. doi: 10.1038/88591. PMID 11373621. S2CID 27416988.
- ^ Karathanassis D, Stahelin RV, Bravo J, Perisic O, Pacold CM, Cho W, Williams RL (October 2002). "Binding of the PX domain of p47phox to phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate and phosphatidic acid is masked by an intramolecular interaction". EMBO J. 21 (19): 5057–68. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf519. PMC 129041. PMID 12356722.
- ^ Ago T, Kuribayashi F, Hiroaki H, Takeya R, Ito T, Kohda D, Sumimoto H (April 2003). "Phosphorylation of p47phox directs phox homology domain from SH3 domain toward phosphoinositides, leading to phagocyte NADPH oxidase activation". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (8): 4474–9. Bibcode: 2003PNAS..100.4474A. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0735712100. PMC 153580. PMID 12672956.