| Nucleus raphe pallidus | |
|---|---|
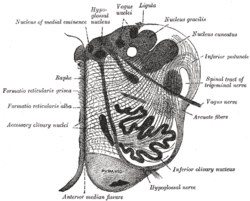 Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Raphe nuclei not labeled, but 'raphe' labeled at left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus raphe pallidus |
| MeSH | D065848 |
| NeuroNames | 741 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1375 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.320 |
| TA2 | 6036 |
| FMA | 72586 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The nucleus raphe pallidus receives afferent connections from the periaqueductal gray, the Paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus, central nucleus of the amygdala, lateral hypothalamic area, and parvocellular reticular nucleus.
Also, the nucleus raphe pallidus receives afferents from the medial preoptic area, median preoptic nucleus and lateral paragigantocellular reticular nuclei. [1]
The nucleus raphe pallidus has recently been shown to be involved in the activation of a fever as an immunoreaction. It has been implied that the preoptic area is constantly inhibiting the raphe pallidus, especially the rostral portion, with GABA.
When the preoptic area receives immune signals from the body, the inhibition stops and the rostral portion of the nucleus raphe pallidus excites the intermediolateral cell column, which induces a fever. [2]
The nucleus raphe pallidus has also been known to mediate the tachycardia response, an extremely high heart rate known to be incited by emotional or psychological stress.
Microinjections of a GABA-a antagonist into the nucleus raphe pallidus, induces an increased heart rate.
Conversely, microinjections of muscimol, a GABA-a agonist, inhibit tachycardia in rats under air-stress stimuli. [3]
In both of these cases, GABA is mediating two different sympathetic responses, so clearly the nucleus raphe pallidus is a far more a complex nucleus than previously thought.
- ^ Hermann, Dirk M. et al. Afferent projections to the rat nuclei raphe magnus, raphe pallidus and reticularis gigantocellularis pars demonstrated by iontophoretic application of choleratoxin (subunit b). Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy Volume 13, Issue 1, June 1997, Pages 1-21
- ^ Nakamura, Kazuhiro et al. The Rostral Raphe Pallidus Nucleus Mediates Pyrogenic Transmission from the Preoptic Area. The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 2002, 22(11):4600-4610
- ^ Zaretsky, Dmitry V. et al. Microinjection of muscimol into raphe pallidus suppresses tachycardia associated with air stress in conscious rats. Journal of Physiology (2003), 546.1, pp. 243-250
| Nucleus raphe pallidus | |
|---|---|
 Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Raphe nuclei not labeled, but 'raphe' labeled at left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus raphe pallidus |
| MeSH | D065848 |
| NeuroNames | 741 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1375 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.320 |
| TA2 | 6036 |
| FMA | 72586 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The nucleus raphe pallidus receives afferent connections from the periaqueductal gray, the Paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus, central nucleus of the amygdala, lateral hypothalamic area, and parvocellular reticular nucleus.
Also, the nucleus raphe pallidus receives afferents from the medial preoptic area, median preoptic nucleus and lateral paragigantocellular reticular nuclei. [1]
The nucleus raphe pallidus has recently been shown to be involved in the activation of a fever as an immunoreaction. It has been implied that the preoptic area is constantly inhibiting the raphe pallidus, especially the rostral portion, with GABA.
When the preoptic area receives immune signals from the body, the inhibition stops and the rostral portion of the nucleus raphe pallidus excites the intermediolateral cell column, which induces a fever. [2]
The nucleus raphe pallidus has also been known to mediate the tachycardia response, an extremely high heart rate known to be incited by emotional or psychological stress.
Microinjections of a GABA-a antagonist into the nucleus raphe pallidus, induces an increased heart rate.
Conversely, microinjections of muscimol, a GABA-a agonist, inhibit tachycardia in rats under air-stress stimuli. [3]
In both of these cases, GABA is mediating two different sympathetic responses, so clearly the nucleus raphe pallidus is a far more a complex nucleus than previously thought.
- ^ Hermann, Dirk M. et al. Afferent projections to the rat nuclei raphe magnus, raphe pallidus and reticularis gigantocellularis pars demonstrated by iontophoretic application of choleratoxin (subunit b). Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy Volume 13, Issue 1, June 1997, Pages 1-21
- ^ Nakamura, Kazuhiro et al. The Rostral Raphe Pallidus Nucleus Mediates Pyrogenic Transmission from the Preoptic Area. The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 2002, 22(11):4600-4610
- ^ Zaretsky, Dmitry V. et al. Microinjection of muscimol into raphe pallidus suppresses tachycardia associated with air stress in conscious rats. Journal of Physiology (2003), 546.1, pp. 243-250