| Posterior facial vein | |
|---|---|

Veins of the head and neck (retromandibular vein visible at center). | |
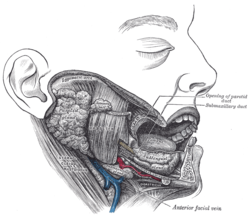
Dissection, showing
salivary glands of right side (retromandibular vein visible at bottom center). | |
| Details | |
| Source |
Superficial temporal vein, maxillary veins |
| Drains to | External jugular vein |
| Artery | Facial artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena retromandibularis, vena facialis posterior |
| TA98 | A12.3.05.031 |
| TA2 | 4831 |
| FMA | 50928 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The retromandibular vein (temporomaxillary vein, posterior facial vein) is a major vein of the face.[ citation needed] It is formed within the parotid gland by the confluence of the maxillary vein, and superficial temporal vein. It descends in the gland and splits into two branches upon emerging from the gland. Its anterior branch then joins the (anterior) facial vein forming the common facial vein, while its posterior branch joins the posterior auricular vein forming the external jugular vein.
Anatomy
Origin
The retromandibular vein is formed within the parotid gland [1] by the confluence of the maxillary vein, and superficial temporal vein. [1] [2] [3]
Course
It descends inside parotid gland, [1] [4] superficial to the external carotid artery (but beneath the facial nerve), [4] between the sternocleidomastoideus muscle and ramus of mandible.[ citation needed] It emerges from the parotid gland inferiorly, then immediately divides into two branches: [1]
- an anterior branch which passes anterior-ward to unite with the (anterior) facial vein forming the common facial vein (which then empties into the internal jugular vein). [5]
- a posterior branch which penetrates the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia before [1] uniting with the posterior auricular vein forming the external jugular vein. [5] [6]
Function
The retromandibular vein provides venous drainage to the superior cranium, and significant drainage to the ear. [7]
Clinical significance
This clinical sign's factual accuracy is
disputed. (November 2020) |
Parrot's sign is a sensation of pain when pressure is applied to the retromandibular region.[ citation needed]
Additional images
-
Lateral head anatomy detail
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 646 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 646 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d e Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 364. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ Thompson, Stevan H.; Yeung, Alison Y. (2016-01-01), Hupp, James R.; Ferneini, Elie M. (eds.), "4 - Anatomy Relevant to Head, Neck, and Orofacial Infections", Head, Neck, and Orofacial Infections, St. Louis: Elsevier, pp. 60–93, doi: 10.1016/b978-0-323-28945-0.00004-1, ISBN 978-0-323-28945-0, retrieved 2020-11-11
- ^ Cunningham, Larry L.; Card, Aaron Sterling (2012-01-01), Bagheri, Shahrokh C.; Bell, R. Bryan; Khan, Husain Ali (eds.), "Chapter 38 - Mandibular Subcondylar Fractures", Current Therapy In Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Saint Louis: W.B. Saunders, pp. 298–304, doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4160-2527-6.00038-4, ISBN 978-1-4160-2527-6, retrieved 2020-11-11
- ^ a b Loukota, Richard A.; Abdel-Galil, Khalid (2017-01-01), Brennan, Peter A.; Schliephake, Henning; Ghali, G. E.; Cascarini, Luke (eds.), "6 - Condylar Fractures", Maxillofacial Surgery (Third Edition), Churchill Livingstone, pp. 74–92, doi: 10.1016/b978-0-7020-6056-4.00006-x, ISBN 978-0-7020-6056-4, retrieved 2020-11-11
- ^ a b Cramer, Gregory D. (2014-01-01), Cramer, Gregory D.; Darby, Susan A. (eds.), "Chapter 5 - The Cervical Region", Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord, and Ans (Third Edition), Saint Louis: Mosby, pp. 135–209, doi: 10.1016/b978-0-323-07954-9.00005-0, ISBN 978-0-323-07954-9, retrieved 2020-11-11
-
^ Drake, Richard L. (Richard Lee), 1950- (2005).
Gray's anatomy for students. Vogl, Wayne., Mitchell, Adam W. M., Gray, Henry, 1825-1861. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone.
ISBN
0-443-06612-4.
OCLC
55139039.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list ( link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list ( link) - ^ Posnick, Jeffrey C. (2014-01-01), Posnick, Jeffrey C. (ed.), "39 - Aesthetic Alteration of Prominent Ears: Evaluation and Surgery", Orthognathic Surgery, St. Louis: W.B. Saunders, pp. 1703–1745, doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4557-2698-1.00039-3, ISBN 978-1-4557-2698-1, retrieved 2020-11-11
External links
- Anatomy photo:27:13-0103 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - " Infratemporal fossa: The Pterygoid plexus of Veins"
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) ( parotid2)
- Tufts.edu
| Posterior facial vein | |
|---|---|

Veins of the head and neck (retromandibular vein visible at center). | |

Dissection, showing
salivary glands of right side (retromandibular vein visible at bottom center). | |
| Details | |
| Source |
Superficial temporal vein, maxillary veins |
| Drains to | External jugular vein |
| Artery | Facial artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena retromandibularis, vena facialis posterior |
| TA98 | A12.3.05.031 |
| TA2 | 4831 |
| FMA | 50928 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The retromandibular vein (temporomaxillary vein, posterior facial vein) is a major vein of the face.[ citation needed] It is formed within the parotid gland by the confluence of the maxillary vein, and superficial temporal vein. It descends in the gland and splits into two branches upon emerging from the gland. Its anterior branch then joins the (anterior) facial vein forming the common facial vein, while its posterior branch joins the posterior auricular vein forming the external jugular vein.
Anatomy
Origin
The retromandibular vein is formed within the parotid gland [1] by the confluence of the maxillary vein, and superficial temporal vein. [1] [2] [3]
Course
It descends inside parotid gland, [1] [4] superficial to the external carotid artery (but beneath the facial nerve), [4] between the sternocleidomastoideus muscle and ramus of mandible.[ citation needed] It emerges from the parotid gland inferiorly, then immediately divides into two branches: [1]
- an anterior branch which passes anterior-ward to unite with the (anterior) facial vein forming the common facial vein (which then empties into the internal jugular vein). [5]
- a posterior branch which penetrates the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia before [1] uniting with the posterior auricular vein forming the external jugular vein. [5] [6]
Function
The retromandibular vein provides venous drainage to the superior cranium, and significant drainage to the ear. [7]
Clinical significance
This clinical sign's factual accuracy is
disputed. (November 2020) |
Parrot's sign is a sensation of pain when pressure is applied to the retromandibular region.[ citation needed]
Additional images
-
Lateral head anatomy detail
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 646 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 646 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d e Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 364. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ Thompson, Stevan H.; Yeung, Alison Y. (2016-01-01), Hupp, James R.; Ferneini, Elie M. (eds.), "4 - Anatomy Relevant to Head, Neck, and Orofacial Infections", Head, Neck, and Orofacial Infections, St. Louis: Elsevier, pp. 60–93, doi: 10.1016/b978-0-323-28945-0.00004-1, ISBN 978-0-323-28945-0, retrieved 2020-11-11
- ^ Cunningham, Larry L.; Card, Aaron Sterling (2012-01-01), Bagheri, Shahrokh C.; Bell, R. Bryan; Khan, Husain Ali (eds.), "Chapter 38 - Mandibular Subcondylar Fractures", Current Therapy In Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Saint Louis: W.B. Saunders, pp. 298–304, doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4160-2527-6.00038-4, ISBN 978-1-4160-2527-6, retrieved 2020-11-11
- ^ a b Loukota, Richard A.; Abdel-Galil, Khalid (2017-01-01), Brennan, Peter A.; Schliephake, Henning; Ghali, G. E.; Cascarini, Luke (eds.), "6 - Condylar Fractures", Maxillofacial Surgery (Third Edition), Churchill Livingstone, pp. 74–92, doi: 10.1016/b978-0-7020-6056-4.00006-x, ISBN 978-0-7020-6056-4, retrieved 2020-11-11
- ^ a b Cramer, Gregory D. (2014-01-01), Cramer, Gregory D.; Darby, Susan A. (eds.), "Chapter 5 - The Cervical Region", Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord, and Ans (Third Edition), Saint Louis: Mosby, pp. 135–209, doi: 10.1016/b978-0-323-07954-9.00005-0, ISBN 978-0-323-07954-9, retrieved 2020-11-11
-
^ Drake, Richard L. (Richard Lee), 1950- (2005).
Gray's anatomy for students. Vogl, Wayne., Mitchell, Adam W. M., Gray, Henry, 1825-1861. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone.
ISBN
0-443-06612-4.
OCLC
55139039.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list ( link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list ( link) - ^ Posnick, Jeffrey C. (2014-01-01), Posnick, Jeffrey C. (ed.), "39 - Aesthetic Alteration of Prominent Ears: Evaluation and Surgery", Orthognathic Surgery, St. Louis: W.B. Saunders, pp. 1703–1745, doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4557-2698-1.00039-3, ISBN 978-1-4557-2698-1, retrieved 2020-11-11
External links
- Anatomy photo:27:13-0103 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - " Infratemporal fossa: The Pterygoid plexus of Veins"
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) ( parotid2)
- Tufts.edu
