This article needs additional citations for
verification. (February 2020) |
| Perimysium | |
|---|---|
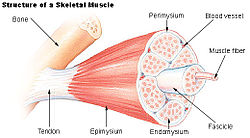 Structure of a skeletal muscle. (Perimysium labeled at top center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | perimysium |
| TA98 | A04.0.00.042 |
| TA2 | 2008 |
| TH | H3.03.00.0.00005 |
| FMA | 9728 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Perimysium is a sheath of dense irregular connective tissue that groups muscle fibers into bundles (anywhere between 10 and 100 or more) or fascicles.
Studies of muscle physiology suggest that the perimysium plays a role in transmitting lateral contractile movements. This hypothesis is strongly supported in one exhibition of the existence of "perimysial junctional plates" in ungulate flexor carpi radialis muscles. [1] The overall comprehensive organization of the perimysium collagen network, as well as its continuity and disparateness, however, have still not been observed and described thoroughly everywhere within the muscle. Found to have type I, III, VI, and XII collagen.
See also
References
-
^ E. Passerieux, R. Rossignol, A. Chopard, A. Carnino, J.F. Marini, T. Letellier, J.P. Delage (2006).
"Structural organization of the perimysium in bovine skeletal muscle: Junctional plates and associated intracellular subdomains" (PDF). Journal of Structural Biology. 154 (2): 206–216.
doi:
10.1016/j.jsb.2006.01.002.
ISSN
1047-8477.
PMID
16503167.
{{ cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list ( link)
External links
This article needs additional citations for
verification. (February 2020) |
| Perimysium | |
|---|---|
 Structure of a skeletal muscle. (Perimysium labeled at top center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | perimysium |
| TA98 | A04.0.00.042 |
| TA2 | 2008 |
| TH | H3.03.00.0.00005 |
| FMA | 9728 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Perimysium is a sheath of dense irregular connective tissue that groups muscle fibers into bundles (anywhere between 10 and 100 or more) or fascicles.
Studies of muscle physiology suggest that the perimysium plays a role in transmitting lateral contractile movements. This hypothesis is strongly supported in one exhibition of the existence of "perimysial junctional plates" in ungulate flexor carpi radialis muscles. [1] The overall comprehensive organization of the perimysium collagen network, as well as its continuity and disparateness, however, have still not been observed and described thoroughly everywhere within the muscle. Found to have type I, III, VI, and XII collagen.
See also
References
-
^ E. Passerieux, R. Rossignol, A. Chopard, A. Carnino, J.F. Marini, T. Letellier, J.P. Delage (2006).
"Structural organization of the perimysium in bovine skeletal muscle: Junctional plates and associated intracellular subdomains" (PDF). Journal of Structural Biology. 154 (2): 206–216.
doi:
10.1016/j.jsb.2006.01.002.
ISSN
1047-8477.
PMID
16503167.
{{ cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list ( link)
External links