| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Niobium nitride
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.132 |
PubChem
CID
|
|
| Properties | |
| NbN | |
| Molar mass | 106.91 g/mol |
| Appearance | gray solid |
| Density | 8.470 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 2,573 °C (4,663 °F; 2,846 K) |
| reacts to form ammonia | |
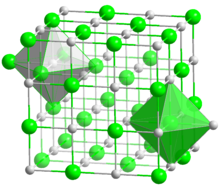
| Structure | |
| cubic, cF8 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other
cations
|
Vanadium nitride Tantalum nitride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Niobium nitride is a compound of niobium and nitrogen ( nitride) with the chemical formula NbN. At low temperatures (about 16 K) NbN becomes a superconductor, and is used in detectors for infrared light. [1] [2] [3]
Uses
- Niobium nitride's main use is as a superconductor.
- Detectors based on it can detect a single photon in the 1-10 micrometer section of the infrared spectrum, [4] which is important for astronomy and telecommunications. It can detect changes up to 25 gigahertz.
- Superconducting NbN nanowires can be used in particle detectors with high magnetic fields. [5]
- Niobium nitride is also used in absorbing anti-reflective coatings.
- In 2015, it was reported that Panasonic Corp. has developed a photocatalyst based on niobium nitride that can absorb 57% of sunlight to support the decomposition of water to produce hydrogen gas as fuel for electrochemical fuel cells. [6]
References
- ^ Y. M. Shy, L. E. Toth and R. Somasundaram (1973). "Superconducting properties, electrical resistivities, and structure of NbN thin films". Journal of Applied Physics. 44 (12): 5539–5545. Bibcode: 1973JAP....44.5539S. doi: 10.1063/1.1662193.
- ^ J. W. Kooi; J. J. A. Baselmans; M. Hajenius; J. R. Gao; T. M. Klapwijk; P. Dieleman; A. Baryshev; G. de Lange (2007). "IF impedance and mixer gain of NbN hot electron bolometers" (PDF). Journal of Applied Physics. 101 (4): 044511. Bibcode: 2007JAP...101d4511K. doi: 10.1063/1.2400086.
- ^ S. P. Chockalingam; Madhavi Chand; John Jesudasan; Vikram Tripathi; Pratap Raychaudhuri (2009). "Superconducting properties and Hall effect in epitaxial NbN thin films". Physical Review B. 77 (21): 214503. arXiv: 0804.2945. Bibcode: 2008PhRvB..77u4503C. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.77.214503. S2CID 14097116.
-
^ M Hajenius, J J A Baselmans, J R Gao, T M Klapwijk, P A J de Korte, B Voronov and G Gol'tsman (2004). "Low noise NbN superconducting hot electron bolometer mixers at 1.9 and 2.5 THz".
Superconductor Science and Technology. 17 (5): S224–S228.
Bibcode:
2004SuScT..17S.224H.
doi:
10.1088/0953-2048/17/5/026.
S2CID
250740737.
{{ cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list ( link) - ^ "When superconductivity material science meets nuclear physics". phys.org. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- ^ Yamamura, Tetsushi (August 2, 2015). "Panasonic moves closer to home energy self-sufficiency with fuel cells". Asahi Shimbun. Archived from the original on August 7, 2015. Retrieved 2015-08-02.

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Niobium nitride
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.132 |
PubChem
CID
|
|
| Properties | |
| NbN | |
| Molar mass | 106.91 g/mol |
| Appearance | gray solid |
| Density | 8.470 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 2,573 °C (4,663 °F; 2,846 K) |
| reacts to form ammonia | |
| Structure | |
| cubic, cF8 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other
cations
|
Vanadium nitride Tantalum nitride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Niobium nitride is a compound of niobium and nitrogen ( nitride) with the chemical formula NbN. At low temperatures (about 16 K) NbN becomes a superconductor, and is used in detectors for infrared light. [1] [2] [3]
Uses
- Niobium nitride's main use is as a superconductor.
- Detectors based on it can detect a single photon in the 1-10 micrometer section of the infrared spectrum, [4] which is important for astronomy and telecommunications. It can detect changes up to 25 gigahertz.
- Superconducting NbN nanowires can be used in particle detectors with high magnetic fields. [5]
- Niobium nitride is also used in absorbing anti-reflective coatings.
- In 2015, it was reported that Panasonic Corp. has developed a photocatalyst based on niobium nitride that can absorb 57% of sunlight to support the decomposition of water to produce hydrogen gas as fuel for electrochemical fuel cells. [6]
References
- ^ Y. M. Shy, L. E. Toth and R. Somasundaram (1973). "Superconducting properties, electrical resistivities, and structure of NbN thin films". Journal of Applied Physics. 44 (12): 5539–5545. Bibcode: 1973JAP....44.5539S. doi: 10.1063/1.1662193.
- ^ J. W. Kooi; J. J. A. Baselmans; M. Hajenius; J. R. Gao; T. M. Klapwijk; P. Dieleman; A. Baryshev; G. de Lange (2007). "IF impedance and mixer gain of NbN hot electron bolometers" (PDF). Journal of Applied Physics. 101 (4): 044511. Bibcode: 2007JAP...101d4511K. doi: 10.1063/1.2400086.
- ^ S. P. Chockalingam; Madhavi Chand; John Jesudasan; Vikram Tripathi; Pratap Raychaudhuri (2009). "Superconducting properties and Hall effect in epitaxial NbN thin films". Physical Review B. 77 (21): 214503. arXiv: 0804.2945. Bibcode: 2008PhRvB..77u4503C. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.77.214503. S2CID 14097116.
-
^ M Hajenius, J J A Baselmans, J R Gao, T M Klapwijk, P A J de Korte, B Voronov and G Gol'tsman (2004). "Low noise NbN superconducting hot electron bolometer mixers at 1.9 and 2.5 THz".
Superconductor Science and Technology. 17 (5): S224–S228.
Bibcode:
2004SuScT..17S.224H.
doi:
10.1088/0953-2048/17/5/026.
S2CID
250740737.
{{ cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list ( link) - ^ "When superconductivity material science meets nuclear physics". phys.org. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- ^ Yamamura, Tetsushi (August 2, 2015). "Panasonic moves closer to home energy self-sufficiency with fuel cells". Asahi Shimbun. Archived from the original on August 7, 2015. Retrieved 2015-08-02.