| Arterial bunch | |
|---|---|
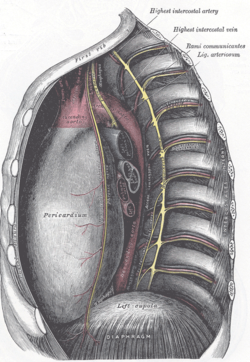 The middle and posterior mediastina. Left side. (Lig. arteriosum labeled at upper right.) | |
 Heart of dog. | |
| Details | |
| From | Left pulmonary artery |
| To | Descending aorta |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamentum arteriosum |
| TA98 | A12.2.01.202 |
| TA2 | 4092 |
| FMA | 13421 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The ligamentum arteriosum (arterial ligament), also known as Botallo's ligament, Harvey's ligament, and Botallo's duct, [1] is a small ligament attaching the aorta to the pulmonary artery.[ clarification needed] It serves no function in adults but is the remnant of the ductus arteriosus formed within three weeks after birth.[ clarification needed]
At the superior end, the ligamentum attaches to the aorta—at the final part of the aortic arch (the isthmus of aorta) or the first part of the descending aorta. [2] On the other, inferior end, the ligamentum is attached to the top of the left pulmonary artery. [3]
The ligamentum arteriosum is closely related to the left recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the left vagus nerve. [4] After splitting from the left vagus nerve, the left recurrent laryngeal loops around the aortic arch behind the ligamentum arteriosum, after which it ascends to the larynx. [4]
In adults, the ligamentum arteriosum has no useful function. It is a vestige of the ductus arteriosus, a temporary fetal structure that shunts blood from the pulmonary arteries to the aorta. This significantly reduces the volume of blood circulating through the lungs, which are inactive in the womb. The ductus arteriosus becomes the ligamentum arteriosum within three weeks of birth, so that deoxygenated blood can be selectively circulated to the lungs for more efficient oxygenation of the blood.
The ligamentum arteriosum plays a role in major trauma. It fixes the aorta in place during abrupt motions, consequently potentially resulting in a ruptured aorta. Such ruptures are very rare.
If the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth, a condition known as patent ductus arteriosus can develop. This is a fairly common birth defect. Sufferers may have operations that leave them with no ligamentum arteriosum.
- ^ Pirie, Egle (February 28, 2022). "Ligamentum arteriosum and ductus arteriosus". Kenhub. Retrieved March 12, 2022.
- ^ Monvadi B. Srichai (2007). David P. Naidich; et al. (eds.). Computed tomography and magnetic resonance of the thorax (4th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-7817-5765-2.
- ^ D. Cheitlin, Melvin; C. Ursell, Philip (2011). "Cardiac Anatomy". In Chatterjee, Kanu (ed.). Cardiology: An Illustrated Textbook. JP Medical Ltd. p. 6. ISBN 978-93-5025-275-8.
- ^ a b Goodin, Douglas S. (2014-01-01), Aminoff, Michael J.; Josephson, S. Andrew (eds.), "Chapter 2 - Neurologic Complications of Aortic Disease and Surgery", Aminoff's Neurology and General Medicine (Fifth Edition), Boston: Academic Press, pp. 25–48, doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-407710-2.00002-3, ISBN 978-0-12-407710-2, S2CID 78356226, retrieved 2020-11-14
- Anatomy photo:21:st-1200 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
| Arterial bunch | |
|---|---|
 The middle and posterior mediastina. Left side. (Lig. arteriosum labeled at upper right.) | |
 Heart of dog. | |
| Details | |
| From | Left pulmonary artery |
| To | Descending aorta |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamentum arteriosum |
| TA98 | A12.2.01.202 |
| TA2 | 4092 |
| FMA | 13421 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The ligamentum arteriosum (arterial ligament), also known as Botallo's ligament, Harvey's ligament, and Botallo's duct, [1] is a small ligament attaching the aorta to the pulmonary artery.[ clarification needed] It serves no function in adults but is the remnant of the ductus arteriosus formed within three weeks after birth.[ clarification needed]
At the superior end, the ligamentum attaches to the aorta—at the final part of the aortic arch (the isthmus of aorta) or the first part of the descending aorta. [2] On the other, inferior end, the ligamentum is attached to the top of the left pulmonary artery. [3]
The ligamentum arteriosum is closely related to the left recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the left vagus nerve. [4] After splitting from the left vagus nerve, the left recurrent laryngeal loops around the aortic arch behind the ligamentum arteriosum, after which it ascends to the larynx. [4]
In adults, the ligamentum arteriosum has no useful function. It is a vestige of the ductus arteriosus, a temporary fetal structure that shunts blood from the pulmonary arteries to the aorta. This significantly reduces the volume of blood circulating through the lungs, which are inactive in the womb. The ductus arteriosus becomes the ligamentum arteriosum within three weeks of birth, so that deoxygenated blood can be selectively circulated to the lungs for more efficient oxygenation of the blood.
The ligamentum arteriosum plays a role in major trauma. It fixes the aorta in place during abrupt motions, consequently potentially resulting in a ruptured aorta. Such ruptures are very rare.
If the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth, a condition known as patent ductus arteriosus can develop. This is a fairly common birth defect. Sufferers may have operations that leave them with no ligamentum arteriosum.
- ^ Pirie, Egle (February 28, 2022). "Ligamentum arteriosum and ductus arteriosus". Kenhub. Retrieved March 12, 2022.
- ^ Monvadi B. Srichai (2007). David P. Naidich; et al. (eds.). Computed tomography and magnetic resonance of the thorax (4th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-7817-5765-2.
- ^ D. Cheitlin, Melvin; C. Ursell, Philip (2011). "Cardiac Anatomy". In Chatterjee, Kanu (ed.). Cardiology: An Illustrated Textbook. JP Medical Ltd. p. 6. ISBN 978-93-5025-275-8.
- ^ a b Goodin, Douglas S. (2014-01-01), Aminoff, Michael J.; Josephson, S. Andrew (eds.), "Chapter 2 - Neurologic Complications of Aortic Disease and Surgery", Aminoff's Neurology and General Medicine (Fifth Edition), Boston: Academic Press, pp. 25–48, doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-407710-2.00002-3, ISBN 978-0-12-407710-2, S2CID 78356226, retrieved 2020-11-14
- Anatomy photo:21:st-1200 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center