| Pulmonary vein | |
|---|---|
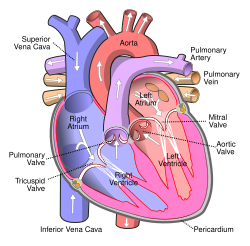 Anterior (frontal) view of the opened heart. White arrows indicate normal blood flow. | |
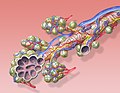
 Diagram of the alveoli with both cross-section and external view. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Truncus arteriosus |
| System | Circulatory system |
| Drains from | Lungs |
| Drains to | Left atrium |
| Artery | Pulmonary artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venae pulmonales |
| MeSH | D011667 |
| TA98 | A12.3.02.001 |
| TA2 | 4107 |
| FMA | 66643 |
| Anatomical terminology | |

The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary veins are part of the pulmonary circulation.
Structure
There are four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung – an inferior and a superior main vein, emerging from each hilum. The main pulmonary veins receive blood from three or four feeding veins in each lung, and drain into the left atrium. The peripheral feeding veins do not follow the bronchial tree. They run between the pulmonary segments from which they drain the blood. [1]
At the root of the lung, the right superior pulmonary vein lies in front of and a little below the pulmonary artery; the inferior is situated at the lowest part of the lung hilum. Behind the pulmonary artery is the bronchus. [2] The right main pulmonary veins (contains oxygenated blood) pass behind the right atrium and superior vena cava; the left in front of the descending thoracic aorta.[ citation needed]
Variation
Occasionally the three lobar veins on the right side remain separate, and not infrequently the two left lobar veins end by a common opening into the left atrium. Therefore, the number of pulmonary veins opening into the left atrium can vary between three and five in the healthy population.[ citation needed]
The two left lobar veins may be united as a single pulmonary vein in about 25% of people; the two right veins may be united in about 3%. [2]
Function
The pulmonary veins play an essential role in respiration, by receiving blood that has been oxygenated in the alveoli and returning it to the left atrium.[ citation needed]
Clinical significance
As part of the pulmonary circulation they carry oxygenated blood back to the heart, as opposed to the veins of the systemic circulation which carry deoxygenated blood.[ citation needed] By definition, a vein is a blood vessel that carries blood to the heart, whether oxygenated or deoxygenated.
Atrial fibrillation frequently results from bursts of tachycardia that originate in muscle bundles extending from the atrium to the pulmonary veins. [3] Pulmonary vein anatomy is highly variable among atrial fibrillation patients. [4] Pulmonary vein isolation by transcatheter ablation can restore sinus rhythm. [3] As atrial fibrillation becomes more persistent, the junction between the pulmonary veins and the left atrium becomes less of an initiator and the left atrium becomes an independent source of arrhythmias. [5] Pulmonary vein isolation ablation technology has used thermal methods ( radiofrequency ablation or cryoablation), which can damage adjacent tissues, notably the esophagus, lung or phrenic nerve. [6] Electroporation, however, eliminates the risk of thermal damage. [6] Atrial fibrillation most often recurs after ablation because of pulmonary vein reconnection. [7]
On chest X-ray, the diameters of pulmonary veins increases from upper to lower lobes, from 3 mm at the first intercoastal space, to 6 mm just above the diaphragm. [8]
A rare genetic defect of the pulmonary veins can cause them to drain into the pulmonary circulation in whole or in part, this is known as a total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (or drainage), or partial anomalous pulmonary connection, respectively.[ citation needed]
Additional images
-
Computed tomography of a normal lung, with different levels of pulmonary veins.
-
Bronchial anatomy
-
Transverse section of thorax, showing relations of pulmonary artery.
-
Pulmonary vessels, seen in a dorsal view of the heart and lungs.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 642 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 642 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students (Pbk. ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-06612-2.
- ^ a b Skandalakis, John E. (2004). "Chapter 7. Pericardium, Heart, and Great Vessels in the Thorax". Skandalakis' surgical anatomy : the embryologic and anatomic basis of modern surgery. Athens, Greece: PMP. pp. section titled 'Pulmonary veins'. ISBN 9603990744.
- ^ a b McGarry TJ, Narayan SM (2012). "The anatomical basis of pulmonary vein reconnection after ablation for atrial fibrillation: wounds that never felt a scar?". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 50 (10): 939–941. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.11.032. PMC 3393092. PMID 22381430.
- ^ Calkins H, Hindricks G, Yamane T (2018). "2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation". Europace. 20 (1): e1–e160. doi: 10.1093/europace/eux274. PMC 5834122. PMID 29016840.
- ^ Eranki A, Wilson-Smith A, Manganas C (2023). "Mid term freedom from atrial fibrillation following hybrid ablation, a systematic review and meta analysis". Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery. 18 (1): 155. doi: 10.1186/s13019-023-02189-2. PMC 10114378. PMID 37076929.
- ^ a b Ramirez FD, Reddy VY, Jaïs P (2020). "Emerging Technologies for Pulmonary Vein Isolation". Circulation Research. 127 (1): 170–183. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316402. PMID 32716722.
- ^ Darby AE (2016). "Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation After Catheter Ablation: Considerations For Repeat Ablation And Strategies To Optimize Success". Journal of Atrial Fibrillation. 9 (1): 1427. doi: 10.4022/jafib.1427. PMC 5089515. PMID 27909521.
- ^ Porres, Diego Varona; Morenza, Óscar Persiva; Pallisa, Esther; Roque, Alberto; Andreu, Jorge; Martínez, Manel (July 2013). "Learning from the Pulmonary Veins". RadioGraphics. 33 (4): 999–1022. doi: 10.1148/rg.334125043. ISSN 0271-5333. PMID 23842969.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 19:05-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Illustration at infomat.net
| Pulmonary vein | |
|---|---|
 Anterior (frontal) view of the opened heart. White arrows indicate normal blood flow. | |
 Diagram of the alveoli with both cross-section and external view. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Truncus arteriosus |
| System | Circulatory system |
| Drains from | Lungs |
| Drains to | Left atrium |
| Artery | Pulmonary artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venae pulmonales |
| MeSH | D011667 |
| TA98 | A12.3.02.001 |
| TA2 | 4107 |
| FMA | 66643 |
| Anatomical terminology | |

The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary veins are part of the pulmonary circulation.
Structure
There are four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung – an inferior and a superior main vein, emerging from each hilum. The main pulmonary veins receive blood from three or four feeding veins in each lung, and drain into the left atrium. The peripheral feeding veins do not follow the bronchial tree. They run between the pulmonary segments from which they drain the blood. [1]
At the root of the lung, the right superior pulmonary vein lies in front of and a little below the pulmonary artery; the inferior is situated at the lowest part of the lung hilum. Behind the pulmonary artery is the bronchus. [2] The right main pulmonary veins (contains oxygenated blood) pass behind the right atrium and superior vena cava; the left in front of the descending thoracic aorta.[ citation needed]
Variation
Occasionally the three lobar veins on the right side remain separate, and not infrequently the two left lobar veins end by a common opening into the left atrium. Therefore, the number of pulmonary veins opening into the left atrium can vary between three and five in the healthy population.[ citation needed]
The two left lobar veins may be united as a single pulmonary vein in about 25% of people; the two right veins may be united in about 3%. [2]
Function
The pulmonary veins play an essential role in respiration, by receiving blood that has been oxygenated in the alveoli and returning it to the left atrium.[ citation needed]
Clinical significance
As part of the pulmonary circulation they carry oxygenated blood back to the heart, as opposed to the veins of the systemic circulation which carry deoxygenated blood.[ citation needed] By definition, a vein is a blood vessel that carries blood to the heart, whether oxygenated or deoxygenated.
Atrial fibrillation frequently results from bursts of tachycardia that originate in muscle bundles extending from the atrium to the pulmonary veins. [3] Pulmonary vein anatomy is highly variable among atrial fibrillation patients. [4] Pulmonary vein isolation by transcatheter ablation can restore sinus rhythm. [3] As atrial fibrillation becomes more persistent, the junction between the pulmonary veins and the left atrium becomes less of an initiator and the left atrium becomes an independent source of arrhythmias. [5] Pulmonary vein isolation ablation technology has used thermal methods ( radiofrequency ablation or cryoablation), which can damage adjacent tissues, notably the esophagus, lung or phrenic nerve. [6] Electroporation, however, eliminates the risk of thermal damage. [6] Atrial fibrillation most often recurs after ablation because of pulmonary vein reconnection. [7]
On chest X-ray, the diameters of pulmonary veins increases from upper to lower lobes, from 3 mm at the first intercoastal space, to 6 mm just above the diaphragm. [8]
A rare genetic defect of the pulmonary veins can cause them to drain into the pulmonary circulation in whole or in part, this is known as a total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (or drainage), or partial anomalous pulmonary connection, respectively.[ citation needed]
Additional images
-
Computed tomography of a normal lung, with different levels of pulmonary veins.
-
Bronchial anatomy
-
Transverse section of thorax, showing relations of pulmonary artery.
-
Pulmonary vessels, seen in a dorsal view of the heart and lungs.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 642 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 642 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students (Pbk. ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-06612-2.
- ^ a b Skandalakis, John E. (2004). "Chapter 7. Pericardium, Heart, and Great Vessels in the Thorax". Skandalakis' surgical anatomy : the embryologic and anatomic basis of modern surgery. Athens, Greece: PMP. pp. section titled 'Pulmonary veins'. ISBN 9603990744.
- ^ a b McGarry TJ, Narayan SM (2012). "The anatomical basis of pulmonary vein reconnection after ablation for atrial fibrillation: wounds that never felt a scar?". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 50 (10): 939–941. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.11.032. PMC 3393092. PMID 22381430.
- ^ Calkins H, Hindricks G, Yamane T (2018). "2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation". Europace. 20 (1): e1–e160. doi: 10.1093/europace/eux274. PMC 5834122. PMID 29016840.
- ^ Eranki A, Wilson-Smith A, Manganas C (2023). "Mid term freedom from atrial fibrillation following hybrid ablation, a systematic review and meta analysis". Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery. 18 (1): 155. doi: 10.1186/s13019-023-02189-2. PMC 10114378. PMID 37076929.
- ^ a b Ramirez FD, Reddy VY, Jaïs P (2020). "Emerging Technologies for Pulmonary Vein Isolation". Circulation Research. 127 (1): 170–183. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316402. PMID 32716722.
- ^ Darby AE (2016). "Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation After Catheter Ablation: Considerations For Repeat Ablation And Strategies To Optimize Success". Journal of Atrial Fibrillation. 9 (1): 1427. doi: 10.4022/jafib.1427. PMC 5089515. PMID 27909521.
- ^ Porres, Diego Varona; Morenza, Óscar Persiva; Pallisa, Esther; Roque, Alberto; Andreu, Jorge; Martínez, Manel (July 2013). "Learning from the Pulmonary Veins". RadioGraphics. 33 (4): 999–1022. doi: 10.1148/rg.334125043. ISSN 0271-5333. PMID 23842969.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 19:05-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Illustration at infomat.net