| Insulin/IGF/Relaxin family | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | Insulin | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00049 | ||||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0239 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR004825 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00235 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1cph / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The insulin/IGF/relaxin family is a group of evolutionary related proteins which possess a variety of hormonal activities. [1] Family members in human include two subfamilies:
1) insulin and insulin-like growth factors [2]
- relaxins 1 and 2
- relaxin 3
- Leydig cell-specific insulin-like peptide (gene INSL3) [3]
- early placenta insulin-like peptide (ELIP) (gene INSL4) [4]
- insulin-like peptide 5 (gene INSL5)
- insulin-like peptide 6
Structure
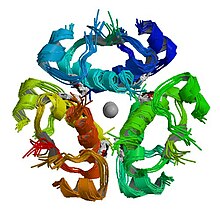
These proteins are characterized by having three disulfide bonds in a characteristic motif. Some family members have an additional disulfide bond also in a conserved location. All of these proteins have a helical segment (corresponding to B chain in insulin) followed by a variable-length chain, followed by a domain (A chain in insulin) with two helices pinned against each other via a disulfide bond. These two regions are linked by two or three disulfide bonds.
Amongst the different proteins in the family, very little of the sequence is conserved except for the disulfide bonds. The variable-length chains may exhibit large inter-species variation even when the remainder of the sequence is highly conserved; and as is in the case of insulin, sometimes the variable length chain is cleaved out by secretory endoproteases, leaving a two-chain protein held together by disulfide bonds.
See also
References
- ^ Blundell TL, Humbel RE (October 1980). "Hormone families: pancreatic hormones and homologous growth factors". Nature. 287 (5785): 781–7. Bibcode: 1980Natur.287..781B. doi: 10.1038/287781a0. PMID 6107857. S2CID 4325746.
- ^ Humbel RE (July 1990). "Insulin-like growth factors I and II". European Journal of Biochemistry. 190 (3): 445–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15595.x. PMID 2197088.
- ^ Adham IM, Burkhardt E, Benahmed M, Engel W (December 1993). "Cloning of a cDNA for a novel insulin-like peptide of the testicular Leydig cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 268 (35): 26668–72. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)74364-6. PMID 8253799.
- ^ Chassin D, Laurent A, Janneau JL, Berger R, Bellet D (September 1995). "Cloning of a new member of the insulin gene superfamily (INSL4) expressed in human placenta". Genomics. 29 (2): 465–70. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.9980. PMID 8666396.
| Insulin/IGF/Relaxin family | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | Insulin | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00049 | ||||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0239 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR004825 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00235 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1cph / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The insulin/IGF/relaxin family is a group of evolutionary related proteins which possess a variety of hormonal activities. [1] Family members in human include two subfamilies:
1) insulin and insulin-like growth factors [2]
- relaxins 1 and 2
- relaxin 3
- Leydig cell-specific insulin-like peptide (gene INSL3) [3]
- early placenta insulin-like peptide (ELIP) (gene INSL4) [4]
- insulin-like peptide 5 (gene INSL5)
- insulin-like peptide 6
Structure
These proteins are characterized by having three disulfide bonds in a characteristic motif. Some family members have an additional disulfide bond also in a conserved location. All of these proteins have a helical segment (corresponding to B chain in insulin) followed by a variable-length chain, followed by a domain (A chain in insulin) with two helices pinned against each other via a disulfide bond. These two regions are linked by two or three disulfide bonds.
Amongst the different proteins in the family, very little of the sequence is conserved except for the disulfide bonds. The variable-length chains may exhibit large inter-species variation even when the remainder of the sequence is highly conserved; and as is in the case of insulin, sometimes the variable length chain is cleaved out by secretory endoproteases, leaving a two-chain protein held together by disulfide bonds.
See also
References
- ^ Blundell TL, Humbel RE (October 1980). "Hormone families: pancreatic hormones and homologous growth factors". Nature. 287 (5785): 781–7. Bibcode: 1980Natur.287..781B. doi: 10.1038/287781a0. PMID 6107857. S2CID 4325746.
- ^ Humbel RE (July 1990). "Insulin-like growth factors I and II". European Journal of Biochemistry. 190 (3): 445–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15595.x. PMID 2197088.
- ^ Adham IM, Burkhardt E, Benahmed M, Engel W (December 1993). "Cloning of a cDNA for a novel insulin-like peptide of the testicular Leydig cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 268 (35): 26668–72. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)74364-6. PMID 8253799.
- ^ Chassin D, Laurent A, Janneau JL, Berger R, Bellet D (September 1995). "Cloning of a new member of the insulin gene superfamily (INSL4) expressed in human placenta". Genomics. 29 (2): 465–70. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.9980. PMID 8666396.