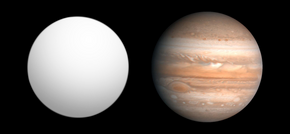
 Size comparison of WASP-7b with Jupiter. | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Cameron et al. ( SuperWASP) |
| Discovery site | SAAO |
| Discovery date | April 1, 2008 |
| Transit | |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| 0.0618+0.0014 −0.0033 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.0173+0.0009 −0.0011 [1] |
| 4.954658+5.5e-5 −4.3e-5 d | |
| Inclination | 89.6+0.4 −0.9 |
| Star | WASP-7 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 0.915+0.046 −0.04 RJ | |
| Mass | 0.96+0.12 −0.18 MJ |
Mean
density | 1,660 kg/m3 (2,800 lb/cu yd) |
| 3.03 g | |
| Temperature | 1393+80 −82 K [1] |
WASP-7b is an extrasolar planet discovered in 2008. This 5-day period planet is slightly smaller than Jupiter, roughly the same mass and more dense. [2]
A study in 2012, utilizing the Rossiter–McLaughlin effect, determined the planetary orbit is strongly misaligned with the equatorial plane of the star, with misalignment equal to 86±8°, making the planetary orbit nearly polar. [3] The orbit is also slightly eccentric, which is surprising given the tidal circularization timescale of below 650 million years. [1]
The measured temperature on the planetary dayside is 1393+80
−82
K.
[1] Sodium was detected in the planetary atmosphere in 2022.
[4]
- ^ a b c d Wallack, Nicole L.; Knutson, Heather A.; Deming, Drake (2021), "Trends in Spitzer Secondary Eclipses", The Astronomical Journal, 162 (1): 36, arXiv: 2103.15833, Bibcode: 2021AJ....162...36W, doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/abdbb2, S2CID 232417602
- ^ Hellier; et al. (December 11, 2008). "WASP-7: The brightest transiting-exoplanet system in the Southern hemisphere". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 690 (1): L89–L91. arXiv: 0805.2600. Bibcode: 2009ApJ...690L..89H. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/690/1/L89. S2CID 15962609.
- ^ Albrecht, Simon; Winn, Joshua N.; Johnson, John A.; Howard, Andrew W.; Marcy, Geoffrey W.; Butler, R. Paul; Arriagada, Pamela; Crane, Jeffrey D.; Shectman, Stephen A.; Thompson, Ian B.; Hirano, Teruyuki; Bakos, Gaspar; Hartman, Joel D. (2012), "Obliquities of Hot Jupiter Host Stars: Evidence for Tidal Interactions and Primordial Misalignments", The Astrophysical Journal, 757 (1): 18, arXiv: 1206.6105, Bibcode: 2012ApJ...757...18A, doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/757/1/18, S2CID 17174530
- ^ Rahmati, Hossein; Czesla, Stefan; Khalafinejad, Sara; Mollière, Paul (2022), "Transmission spectroscopy of WASP-7 b with UVES", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 668: A24, arXiv: 2210.08517, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202243955, S2CID 252917734
![]() Media related to
WASP-7b at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to
WASP-7b at Wikimedia Commons
 Size comparison of WASP-7b with Jupiter. | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Cameron et al. ( SuperWASP) |
| Discovery site | SAAO |
| Discovery date | April 1, 2008 |
| Transit | |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| 0.0618+0.0014 −0.0033 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.0173+0.0009 −0.0011 [1] |
| 4.954658+5.5e-5 −4.3e-5 d | |
| Inclination | 89.6+0.4 −0.9 |
| Star | WASP-7 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 0.915+0.046 −0.04 RJ | |
| Mass | 0.96+0.12 −0.18 MJ |
Mean
density | 1,660 kg/m3 (2,800 lb/cu yd) |
| 3.03 g | |
| Temperature | 1393+80 −82 K [1] |
WASP-7b is an extrasolar planet discovered in 2008. This 5-day period planet is slightly smaller than Jupiter, roughly the same mass and more dense. [2]
A study in 2012, utilizing the Rossiter–McLaughlin effect, determined the planetary orbit is strongly misaligned with the equatorial plane of the star, with misalignment equal to 86±8°, making the planetary orbit nearly polar. [3] The orbit is also slightly eccentric, which is surprising given the tidal circularization timescale of below 650 million years. [1]
The measured temperature on the planetary dayside is 1393+80
−82
K.
[1] Sodium was detected in the planetary atmosphere in 2022.
[4]
- ^ a b c d Wallack, Nicole L.; Knutson, Heather A.; Deming, Drake (2021), "Trends in Spitzer Secondary Eclipses", The Astronomical Journal, 162 (1): 36, arXiv: 2103.15833, Bibcode: 2021AJ....162...36W, doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/abdbb2, S2CID 232417602
- ^ Hellier; et al. (December 11, 2008). "WASP-7: The brightest transiting-exoplanet system in the Southern hemisphere". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 690 (1): L89–L91. arXiv: 0805.2600. Bibcode: 2009ApJ...690L..89H. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/690/1/L89. S2CID 15962609.
- ^ Albrecht, Simon; Winn, Joshua N.; Johnson, John A.; Howard, Andrew W.; Marcy, Geoffrey W.; Butler, R. Paul; Arriagada, Pamela; Crane, Jeffrey D.; Shectman, Stephen A.; Thompson, Ian B.; Hirano, Teruyuki; Bakos, Gaspar; Hartman, Joel D. (2012), "Obliquities of Hot Jupiter Host Stars: Evidence for Tidal Interactions and Primordial Misalignments", The Astrophysical Journal, 757 (1): 18, arXiv: 1206.6105, Bibcode: 2012ApJ...757...18A, doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/757/1/18, S2CID 17174530
- ^ Rahmati, Hossein; Czesla, Stefan; Khalafinejad, Sara; Mollière, Paul (2022), "Transmission spectroscopy of WASP-7 b with UVES", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 668: A24, arXiv: 2210.08517, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202243955, S2CID 252917734
![]() Media related to
WASP-7b at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to
WASP-7b at Wikimedia Commons