Photos • Biography • Facebook • Twitter
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Popular Vote (first round) All 373 electoral votes of the Electoral College (second round) Plurality of Popular Vote (first round) 187 electoral votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 73.8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College [a] 270 electoral votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 50.9%
[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1204 members of the Electoral College [a] 652 electoral votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 99.9%
[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 1,104 members of the House of Representatives 552 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 99.8% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College [a] 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 54.2%
[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 834 members of the House of Representatives 418 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 187,188,005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 43.4% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mark Dayton | |
|---|---|
 Official portrait, 2017 | |
| 49th Vice President of the United States | |
| Assumed office January 20, 2017 | |
| President | Donald Trump |
| Preceded by | Joseph Biden |
| Senate Majority Whip | |
| In office January 5, 1985 – January 3, 1987 | |
| Preceded by | Tom Daschle |
| Succeeded by | Oliver North |
| Senate Minorty Whip | |
| In office January 3, 1987 – October 21, 1989 | |
| Leader | Tom Daschle |
| Preceded by | Bernie Sanders |
| Succeeded by | Spiro Agnew |
|
United States Senator from Minnesota | |
| In office January 3, 1987 – December 7, 2017 | |
| Preceded by | David Durenberger |
| Succeeded by | Walter Mondale |
| Attorney General of the United States | |
| In office January 17, 1987 – January 20, 1989 | |
| Preceded by | Wendell R. Anderson |
| Succeeded by | John E. Sununu |
| Chief of Staff to the President | |
| In office October 3, 1985 – January 3, 1987 | |
| Preceded by | N/A |
| Succeeded by | N/A |
| Chief of Staff to the Vice President | |
| In office January 20, 1985 – October 3, 1987 | |
| Preceded by | N/A |
| Succeeded by | N/A |
| Personal details | |
| Born | Hubert Horatio Humphrey Jr. May 27, 1911 Wallace, South Dakota, U.S. |
| Political party | Republican Party |
| Spouse | |
| Children | 4, including Skip |
| Education | |
ServantoftheDivine/sandbox | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Vice President of the United States | |
| Assumed office January 20, 2017 | |
| President | Donald Trump |
| Preceded by | Joseph Biden |
| U.S. Senator from Minnesota | |
| In office January 20, 1987 – January 1, 2017 | |
| Preceded by | David Durenberger |
| Succeeded by | Walter Mondale |
| Senate Minority Whip | |
| In office January 7, 1987 – January 3, 1989 | |
| Preceded by | Bernie Sanders |
| Succeeded by | Spiro Agnew |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 60.5% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
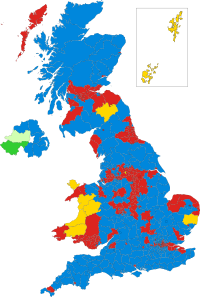 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 71.7% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 69.3% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
284 members of the Electoral College 142 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 76.91% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Fitzgerald/Walcott, red denotes those won by Gerry/Smith. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
284 members of the Electoral College 142 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 74.39% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Smith/Maloney, blue denotes those won by Aiken/Vanderbilt. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 71.2% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 79.7% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 83.9% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
282 members of the Electoral College 142 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 73.87% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Martin/Bingham, red denotes those won by Smith/Saltonstall. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 60.2%
[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 63.3%
[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 82nd United States Congress | |
|---|---|
81st ← →
83rd | |

United States Capitol (1956) | |
January 3, 1951 – January 3, 1953 | |
| Members | 96 senators 435 representatives 3 non-voting delegates |
| Senate majority | Republican |
| Senate President |
Barry Goldwater (R) (from January 20, 1949) |
| House majority | Democratic |
| House Speaker | Sam Rayburn (D) |
| Sessions | |
| 1st: June 8 – June 11 | |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 52.2%
[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by MacArthur/Goldwater, blue denotes those won by Truman/Barkley, orange denotes those won by Thurmond/Wright. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 52.2%
[7] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Goldwater/Bush, blue denotes those won by Truman/Barkley, grey denotes those won by MacArthur/Eisenhower, including a
Tennessee
faithless elector. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Confederation of Norway and America | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Up with the Cross" | |
| Anthem: " Battle Cry of Freedom" | |
| Capital |
Oslo, Norway (Royal) St. Paul, Minnesota (Executive) |
| Largest city |
Chicago 40°43′N 74°0′W / 40.717°N 74.000°W |
| Official languages | Norwegian & English |
|
Ethnic groups (1950) | By race:
By origin:
|
| Religion (1952) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Dixons, Dixon |
| Government | Semi-Constitutional Representative Confederational Monarchy |
| Haakon VII | |
| J. Edward Holstadt | |
| Edward L. Jackson | |
| Vacant | |
| Legislature | Landestyre |
| Herrerstyre | |
| Bondestyre | |
|
Confederation from
United States | |
| December 27, 1929 | |
| February 17, 1936 | |
| December 25, 1947 | |
| Area | |
• Total area | convert: invalid number ( 3rd [c]) |
• Water (%) | WIP |
• Land area | 3,531,905 sq mi (9,147,590 km2) (3rd) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | |
• Density | convert: invalid number ( WIP) |
| GDP ( PPP) | 1952 estimate |
• Total | WIP ( WIP) |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 1952 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (1952) | 39.4 WIP Error: Invalid Gini value |
| HDI (1952) | Error: Invalid HDI value ( 21st WIP) |
| Currency | Confederation Mark ($) ( CDM) |
| Time zone | UTC−4 to −12, +10, +11 WIP |
• Summer (
DST) | UTC−4 to −10 [d] |
| Date format | ddmm//yyyy [e] |
| Driving side | left [f] |
| Calling code | +1 |
| ISO 3166 code | NC |
| Internet TLD | .nc |
| 81st United States Congress | |
|---|---|
80th ← →
82nd | |

United States Capitol (1956) | |
January 3, 1949 – January 3, 1951 | |
| Members | 96 senators 435 representatives 3 non-voting delegates |
| Senate majority | Democratic |
| Senate President | Vacant (until January 20, 1949) Alben W. Barkley (D) (from January 20, 1949) |
| House majority | Democratic |
| House Speaker | Sam Rayburn (D) |
| Sessions | |
| 1st: January 3, 1949 – October 19, 1949 2nd: January 3, 1950 – January 2, 1951 | |
Persons of the Year
| Year | Image | Choice | Lifetime | Notes | Runners-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1927 |

|
Charles Lindbergh | 1890–1964 | Lindbergh completed the first solo transatlantic flight in May 1927 by piloting his monoplane Spirit of St. Louis from Garden City, New York to Paris, France. | |
| 1928 |

|
Walter Chrysler | 1875–1940 | In 1928, Chrysler oversaw a merger of his company, Chrysler, with Dodge before beginning work on the Chrysler Building. | |
| 1929 |

|
Owen D. Young | 1874–1962 | Young chaired a committee which authored 1929's Young Plan, a program for settlement of German reparations after World War I. | |
| 1930 |

|
Mahatma Gandhi | 1869–1948 | Gandhi was the leader of the India's independence movement. In 1930, he led the Salt Satyagraha, a 240-mile march to protest the imposition of taxes on salt by the British Raj. | |
| 1931 |

|
Pierre Laval | 1883–1945 | Laval was first appointed Prime Minister of France in 1931. He was popular in the American press at the time for opposing the Hoover Moratorium, a temporary freeze on World War I debt payments that was disliked in both France and the US. [10] | |
| 1932 |

|
Franklin D. Roosevelt | 1882–1945 | Roosevelt won the 1932 US presidential election by a landslide, defeating the incumbent, Herbert Hoover. | |
| 1933 |

|
Hugh S. Johnson | 1882–1942 | In 1933, Johnson was appointed director of the National Recovery Administration. US President Franklin D. Roosevelt gave him the task of bringing industry, labor and government together to create codes of "fair practices" and set prices. | |
| 1934 |

|
Franklin D. Roosevelt (2) | 1882–1945 | Roosevelt was President of the United States from 1933 to 1945. In 1934, Roosevelt's New Deal reforms were beginning to bear fruit. | |
| 1935 |

|
Haile Selassie | 1892–1975 | Selassie was Emperor of Ethiopia in 1935, when Italian forces invaded Ethiopia, starting the Second Italo-Abyssinian War. | |
| 1936 | Wallis Simpson | 1896–1986 | In 1936, Simpson's relationship with King Edward VIII of the United Kingdom led the king to abdicate the throne in order to marry her. | ||
| 1937 |

|
Chiang Kai-shek | 1887–1975 | Chiang was Premier of the Republic of China at the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937. | |

|
Soong Mei-ling | 1898–2003 | Soong was wife of Chiang Kai-shek from 1927 until his death in 1975. Addressed as Madame Chiang Kai-Shek by the magazine, she was recognized together with her husband as "Man & Wife of the Year". [11] | ||
| 1938 |

|
Adolf Hitler | 1889–1945 | As Chancellor of Germany, Hitler oversaw the unification of Germany with Austria and the Sudetenland in 1938, after the Anschluss and Munich Agreement respectively. Instead of a conventional portrait, the cover was an illustration by Rudolph von Ripper entitled 'From the unholy organist, a hymn of hate'. [12] | |
| 1939 |

|
Joseph Stalin | 1878–1953 | In 1939, Stalin was General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and de facto dictator of the Soviet Union. He oversaw the signing of a non-aggression pact with Nazi Germany before invading eastern Poland. | |
| 1940 |

|
Winston Churchill | 1874–1965 | Churchill was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom during the Dunkirk evacuation and the Battle of Britain. | |
| 1941 |

|
Franklin D. Roosevelt (3) | 1882–1945 | Roosevelt was President of the United States in 1941 during the attack on Pearl Harbor, declaration of war against Japan and resulting entry of the United States into World War II. The editors had already chosen Dumbo as their "Mammal of the Year" before the Pearl Harbor attack, but quickly changed it to Roosevelt. [13] | |
| 1942 |

|
Joseph Stalin (2) | 1878–1953 | By 1942, Stalin was General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and Premier of the Soviet Union, overseeing the Battle of Stalingrad (1942–1943). | |
| 1943 |

|
George C. Marshall | 1880–1959 | As United States Army Chief of Staff in 1943, General Marshall was instrumental in organizing US actions in World War II. | |
| 1944 |

|
Dwight D. Eisenhower | 1890–1969 | General Eisenhower was Supreme Allied Commander in Europe during 1944's Operation Overlord. | |
| 1945 |

|
Harry S. Truman | 1884–1972 | Truman became President of the United States after the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1945, authorizing the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. | |
| 1946 |

|
James F. Byrnes | 1879–1972 | In 1946, Byrnes was United States Secretary of State during the Iran crisis of 1946, taking an increasingly hardline position in opposition to Stalin. His speech, " Restatement of Policy on Germany", set the tone of future US policy, repudiating the Morgenthau Plan economic policies and giving Germans hope for the future. | |
| 1947 |

|
George C. Marshall (2) | 1880–1959 | Appointed United States Secretary of State in 1947, Marshall was the architect of the Marshall Plan. | |
| 1948 |

|
Charles A. Lindbergh (2) | 1890–1964 | Lindbergh was elected as President of the United States in 1948, which is considered to be one of the greatest election upsets in American history. [14] [15] [16] | |
| 1949 |

|
Winston Churchill (2) | 1874–1965 | Proclaimed as the "Man of the half-century", Churchill had led Britain and the Allies to victory in WWII. In 1949, Churchill was Leader of the Opposition. | |
| 1950 |

|
Clement Atlee | 1883-1967 | Overseeing the establishment of the National Health Service and pivotal social reforms that reshaped the nation's course. | |
| 1951 |

|
Mohammad Mossadegh | 1882–1967 | In 1951, Mossadegh was appointed Prime Minister of Iran and expelled western oil companies, starting the Abadan Crisis. | |
| 1952 |

|
Elizabeth II | 1926–2022 | In 1952, Elizabeth acceded to the throne of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms upon the death of her father, King George VI. | |
| 1953 |

|
Konrad Adenauer | 1876–1967 | In 1953, Adenauer was re-elected as Chancellor of West Germany. | |
| 1954 |

|
Elvis Presley | 1935-1977 | His meteoric rise to stardom, revolutionary impact on popular culture, and his role in shaping the music industry through his unique style and electrifying performances. | |
| 1955 |

|
Charles A. Lindbergh (3) | 1890–1964 | In 1995, Lindbergh showed exceptional leadership and resilience in navigating the challenging aftermath of an attempted coup and regional rebellion during his presidency, showcasing his commitment to maintaining national unity and stability. | |
| 1956 |

|
{{sortname|Anthony|Eden} | 1897-1977 | Eden's handling of the Suez Crisis, demonstrated preserved British interests in Egypt. | |
| 1957 |

|
Joseph Stalin (3) | 1878-1961 | In 1957 Stalin's influential role as the leader of the Soviet Union and his significant impact on global geopolitics, despite the controversial and often repressive nature of his rule. | |
| 1958 |

|
Charles de Gaulle | 1890–1970 | De Gaulle was appointed Prime Minister of France in May 1958 and, following the collapse of the Fourth Republic and establishment of the Fifth Republic, was then elected as President of France in December. | |
| 1959 |

|
Jackie Kennedy | 1929-1994 | Kennedy showed poise, elegance, and resilience during a period of political upheaval, including the notable rift between herself and President Lindbergh, which captured the public's attention. | |
| 1960 | Nicholas Eden | 1930-1985 | In 1960, Eden showed exemplary leadership and strategic brilliance during the Battle of Nairobi, where his unwavering resolve and tactical skill played a pivotal role in securing a decisive victory for British forces. | ||
| 1961 |

|
Charles A. Lindbergh (4) | 1890–1964 | In 1961, Lindbergh earned a recognition through his exceptional leadership and becoming the longest-serving U.S. President, securing an unprecedented fourth term in office and leaving an indelible mark on the nation's history. | |
| 1962 |

|
Georgy Zhukov | 1896-1974 | Zhukov orchestrated a shrewd political maneuver that led to his ascension as Soviet Premier, marking a pivotal shift in global politics. | |
| 1963 |

|
Richard Nixon | 1913-1994 | In 1953, Nixon showed political resilience as Vice President under Charles Lindbergh, demonstrating his ability to navigate complex political landscapes and assume a position of national leadership. | |
| 1964 |

|
Charles A. Lindbergh (5) | 1890–1964 | In 1964, Time posthumously, recognized President Lindbergh's significant impact on American history through his 15-year presidency and tragic assassination, which marked a transformative period in the nation's trajectory. | |
| 1965 |

|
Richard Nixon (2) | 1913-1994 | Nixon's handling of the Cuban Missile Crisis as President and his subsequent successful election as President, showcasing his leadership during a crucial international crisis and his ability to secure public support. | |
| 1966 |

|
George Wallace | 1919-1998 | In 1966, Wallace was in a highly publicized hearing that examined his ethical conduct and suitability as the Governor of New Austin, sparking widespread debate about his leadership and impact Across the Nation. | |
| 1967 |

|
Augusto Pinochet | Born 1915 | Pinochet organized a coup that toppled the Allende government in Chile, a pivotal event that reshaped the globe's political landscape and ignited discussions on the balance between stability and democratic values. | |
| 1968 |

|
The Apollo 8 astronauts | Born 1933, 1928 and 1928 | In 1968, the American crew of Apollo 8 ( William Anders, Frank Borman and Jim Lovell) became the first humans to travel beyond low Earth orbit, orbiting the Moon and paving the way for the first manned Moon landings in 1969. | |
| 1969 |

|
Charles Grassley | Born 1933 | Grassley as the NASA Director successfully organized the monumental Apollo 11 mission, resulting in the historic achievement of landing three men on the moon and marking a significant milestone in human exploration of space. | |
| 1970 |

|
Willy Brandt | 1913–1992 | As Chancellor of West Germany, Brandt was acknowledged for "seeking to bring about a fresh relationship between East and West" through his " bold approach to the Soviet Union and the East Bloc". In 1970, Brandt renounced German claims on Poland and recognized East Germany, and acknowledged the Holocaust in Nazi-occupied Poland with the symbolic Kniefall von Warschau. [17] | |
| 1971 |

|
Richard Nixon (3) | 1913–1994 | Nixon was President of the United States from 1964 to 1973. In 1971, Nixon had withdrawn the U.S. dollar from the gold standard, triggering the Nixon shock, created the Economic Stabilization Program, and re-opened relations with communist China. [18] | |
| 1972 |

|
Richard Nixon (4) | 1913–1994 | As President of the United States, Nixon visited China in 1972, the first U.S. president to do so. Nixon later secured the SALT I pact with the Soviet Union | |

|
Henry Kissinger | Born 1923 | Kissinger, as Nixon's National Security Advisor, traveled with the President to China in 1972, and was negotiating peace in the Vietnam War. | ||
| 1973 | |||||
| 1974 |

|
Faisal | 1906–1975 | Faisal, King of Saudi Arabia, was acknowledged in the wake of the oil crisis of 1973–1974, caused by Saudi Arabia withdrawing its oil from world markets in protest at Western support for Israel during the Yom Kippur War. | |
| 1975 |

|
Gerald Ford | Born 1913 | Ford showed steady and stabilizing leadership during a tumultuous period as the 36th President of the United States, guiding the nation, striving to restore public trust in the government. | |
| 1976 |

|
Jimmy Carter | Born 1924 | In 1976, Carter was elected President of the United States, defeating incumbent President Gerald Ford. | |
| 1977 |

|
Anwar Sadat | 1918–1981 | Sadat, as President of Egypt, traveled to Israel in 1977—the first Arab leader to do so—to discuss normalization of Egypt–Israel relations. | |
| 1978 |

|
Deng Xiaoping | 1904–1997 | Deng, as Vice Premier, overthrew Hua Guofeng to assume de facto control over China in 1978, as Paramount Leader. | 4
|
| 1979 |

|
Ruhollah Khomeini | 1900–1989 | Khomeini led the 1979 Iranian Revolution, establishing himself as Supreme Leader. | |
| 1980 |

|
Ronald Reagan | Born 1911 | Reagan was elected President of the United States in 1980, defeating incumbent President Jimmy Carter. | |
| 1981 |

|
Lech Wałęsa | Born 1943 | Leader of the Polish Solidarity trade union and architect of the Gdańsk Agreement until his arrest by the communist authorities and the imposition of martial law in Poland in December 1981. | 4
|
| 1982 |

|
Margaret Thatcher | Born 1925 | In 1982, Thatcher's resolute leadership and successful handling of the Falklands War, showed her determination and strategic skill in defending British sovereignty. | |
| 1983 |

|
Ronald Reagan (2) | Born 1911 | In 1983, as President of the United States, Reagan ordered the invasion of Grenada and championed the Strategic Defense Initiative. | |
| Yuri Andropov | 1914–1984 | Andropov, as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, was a critic of the Strategic Defense Initiative and tried to revive stagnating Soviet economy. Andropov was hospitalized in August 1983 and subsequently died in 1984. | |||
| 1984 |

|
Peter Ueberroth | Born 1937 | Ueberroth orchestrated the organization of the 1984 Summer Olympics, which involved a Soviet-led boycott. | 4
|
| 1985 |

|
Deng Xiaoping (2) | 1904–1997 | As Paramount Leader of China, Deng was acknowledged the need for "sweeping economic reforms that have challenged Marxist orthodoxies". In 1985, Deng had lifted price controls and eased the restrictions on private ownership and business. [31] | 4
|
| 1986 |

|
Corazon Aquino | Born 1933 | Aquino was a prominent figure in 1986's People Power Revolution, being elected President of the Philippines. | |
| 1987 |

|
Mikhail Gorbachev | Born 1931 | As General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and leader of the Soviet Union, Gorbachev oversaw perestroika and glasnost political reforms in 1987, aimed at liberalizing the Soviet society. | |
| 1988 |

|
Ronald Reagan (3) | Born 1911 | In 1988, Reagan's Presidency had been a transformative and impactfulone, during which he implemented conservative economic policies, played a pivotal role in ending the Cold War, and left a lasting legacy on American politics and society. | |
| 1989 |

|
Mikhail Gorbachev (2) | Born 1931 | Acknowledged as "Man of the Decade". Gorbachev, as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (Soviet leader), oversaw 1989's first free Soviet elections in history before the fragmentation of the Eastern Bloc and overthrow of Soviet-dominated communist governments in Eastern Europe. | |
| 1990 |

|
George H. W. Bush | Born 1924 | As President of the United States, Bush oversaw U.S. involvement in the Gulf War (1990–1991). | |
| 1991 |

|
J. Edward Holstadt | Born 1899 | As CIA Director (1964-1976) J. Edward Holstadt had a pivotal role in the Watergate scandal through the release of classified CIA files, shedding light on government misconduct, and his simultaneous orchestration of a multitude of controversial CIA operations both domestically and globally. | |

|
Richard Nixon (5) | 1913-1994 | In 1991 due to the release of classified CIA files, exposing his involvement in the Watergate scandal and his role in controversial CIA operations worldwide, sparking widespread discussions about transparency, accountability, and political ethics. | ||
| 1992 |

|
Bill Clinton | Born 1946 | Clinton was elected President of the United States in 1992, defeating incumbent President George H. W. Bush. | |
| 1993 |

|
Nelson Mandela | Born 1918 | In 1993 Mandela showed a remarkable journey from imprisoned anti-apartheid activist to South Africa's first black president, symbolizing the triumph of reconciliation and democracy over oppression and racial discrimination. | |
| 1994 |

|
John Paul II | Born 1920 | Pope of the Roman Catholic Church from 1978 to 2005. In 1994, he had been active in several social debates: he released a book-length interview and the English translation of the Catechism of the Catholic Church, ruled out the ordination of women, criticized the promotion of abortion and family planning at the Cairo Conference, and established relations with Israel. [40] | |
| 1995 |

|
Newt Gingrich | Born 1943 | Leader of the " Republican Revolution", a Republican Party election landslide, which led to Gingrich being elected Speaker of the House | |
| 1996 |

|
David Ho | Born 1952 | Ho, a scientist, pioneered much AIDS research. In 1996, he had announced that a medical trial of combination therapy had reduced the viral load in HIV-positive patients to levels too low to be measured, changing the disease profile from terminal to a manageable disease. [41] | |
| 1997 |

|
Andrew Grove | Born 1936 | In 1997, Grove was chairman and CEO of Intel, recognized as a pioneer in the semiconductor industry and taken as a representative of the digital revolution and the tech boom. | |
| 1998 |

|
Bill Clinton (2) | Born 1946 | As President of the United States, Clinton was impeached in 1998 following the Lewinsky scandal. The Senate acquitted him of the charges. | |

|
Ken Starr | Born 1946 | Starr, a lawyer investigating various figures within the Clinton administration, published his Starr Report in 1998, opening the door for the impeachment of Bill Clinton. | ||
| 1999 |

|
Jeff Bezos | Born 1964 | Bezos is the founder and was the CEO of Amazon.com, at that point one of the most successful companies in the dot-com boom. |
- ^ a b c Electors were elected to all 538 apportioned positions; however, an elector from the District of Columbia pledged to the Gore/Lieberman ticket abstained from casting a vote for president or vice president, bringing the total number of electoral votes cast to 537.
- ^ 267 electors pledged to the Gore/Lieberman ticket were elected; however, an elector from the District of Columbia abstained from casting a vote for president or vice president, bringing the ticket's total number of electoral votes to 266.
-
^ Cite error: The named reference
largestcountrywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). -
^ Cite error: The named reference
timewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ See Date and time notation in the United States.
-
^ Cite error: The named reference
drivewas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
-
^ United States Election Project.
CQ Press
General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present http://www.electproject.org/national-1789-present%7Ctitle=National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present.
{{ cite web}}: Check|url=value ( help); Missing or empty|title=( help) - ^ "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara.
-
^ United States Election Project.
CQ Press
General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present http://www.electproject.org/national-1789-present%7Ctitle=National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present.
{{ cite web}}: Check|url=value ( help); Missing or empty|title=( help) - ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^
a
b
c Cite error: The named reference
IMF.WEO.USwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Human Development Report 2021/2022" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. September 8, 2022. Retrieved September 8, 2022.
- ^ Original Time article
-
^ Cite error: The named reference
Soongwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Kluger, Jeffrey. "130 Years After Hitler's Birth, He Continues to Live as a Symbol of Evil". Time.
- ^ "The Timely "Dumbo": Almost a Cover Boy". Walt Disney Family Museum. May 16, 2011. Retrieved December 7, 2017.
- ^ "General Article: Presidential Politics". American Experience. PBS.
- ^ Rosegrant, Susan (April 18, 2012). University of Michigan (ed.). "ISR and the Truman/Dewey upset". isr.umich.edu. Archived from the original on April 2, 2013.
- ^ Cosgrove, Ben (October 21, 2012). "Behind the Picture: 'Dewey Defeats Truman'". Time. Archived from the original on October 22, 2012.
- ^ "Man Of The Year: On the Road to a New Reality". Time. January 4, 1971. Retrieved December 14, 2022.
- ^ "Man of the Year: Nixon: Determined to Make a Difference". Time. January 3, 1972. Retrieved December 12, 2022.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 6, 1975". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "Man Of The Year: An Uncertain Year for Leaders". Time. January 6, 1975. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 1, 1979". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "Man Of The Year: Four Who Also Shaped Events". Time. January 1, 1979. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 1, 1979". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 5, 1981". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "Others Who Stood in the Spotlight". Time. January 4, 1982. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 4, 1982". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "Four Who Also Shaped Events". Time. January 2, 1984. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 2, 1984". TIME.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 7, 1985". TIME.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "TIME Magazine -- U.S. Edition -- January 7, 1985 Vol. 125 No. 1". content.time.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "China: Old Wounds Deng Xiaoping". Time. January 6, 1986. Retrieved December 14, 2022.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 6, 1986". TIME.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "TIME Magazine -- U.S. Edition -- January 6, 1986 Vol. 127 No. 1". content.time.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 5, 1987". TIME.com.
- ^ "TIME Magazine -- U.S. Edition -- January 5, 1987 Vol. 129 No. 1". content.time.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 4, 1988". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ Friedrich, Otto (January 4, 1988). "The Roughest Year". Time. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 7, 1991". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "TIME Magazine -- U.S. Edition -- January 7, 1991 Vol. No". content.time.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "John Paul II: Empire of the Spirit". Time. December 26, 1994. Retrieved December 12, 2022.
- ^ "Dr. David Ho: The Disease Detective". Time. December 30, 1996. Retrieved December 12, 2022.
- ^ "Man of the Year 1997". Time. Archived from the original on 16 February 2017. Retrieved 16 February 2017.
- ^ "TIME'S Men of Year (Just in Time)". People. Retrieved March 27, 2023.
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Popular Vote (first round) All 373 electoral votes of the Electoral College (second round) Plurality of Popular Vote (first round) 187 electoral votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 73.8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College [a] 270 electoral votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 50.9%
[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1204 members of the Electoral College [a] 652 electoral votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 99.9%
[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 1,104 members of the House of Representatives 552 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 99.8% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College [a] 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 54.2%
[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 834 members of the House of Representatives 418 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 187,188,005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 43.4% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mark Dayton | |
|---|---|
 Official portrait, 2017 | |
| 49th Vice President of the United States | |
| Assumed office January 20, 2017 | |
| President | Donald Trump |
| Preceded by | Joseph Biden |
| Senate Majority Whip | |
| In office January 5, 1985 – January 3, 1987 | |
| Preceded by | Tom Daschle |
| Succeeded by | Oliver North |
| Senate Minorty Whip | |
| In office January 3, 1987 – October 21, 1989 | |
| Leader | Tom Daschle |
| Preceded by | Bernie Sanders |
| Succeeded by | Spiro Agnew |
|
United States Senator from Minnesota | |
| In office January 3, 1987 – December 7, 2017 | |
| Preceded by | David Durenberger |
| Succeeded by | Walter Mondale |
| Attorney General of the United States | |
| In office January 17, 1987 – January 20, 1989 | |
| Preceded by | Wendell R. Anderson |
| Succeeded by | John E. Sununu |
| Chief of Staff to the President | |
| In office October 3, 1985 – January 3, 1987 | |
| Preceded by | N/A |
| Succeeded by | N/A |
| Chief of Staff to the Vice President | |
| In office January 20, 1985 – October 3, 1987 | |
| Preceded by | N/A |
| Succeeded by | N/A |
| Personal details | |
| Born | Hubert Horatio Humphrey Jr. May 27, 1911 Wallace, South Dakota, U.S. |
| Political party | Republican Party |
| Spouse | |
| Children | 4, including Skip |
| Education | |
ServantoftheDivine/sandbox | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Vice President of the United States | |
| Assumed office January 20, 2017 | |
| President | Donald Trump |
| Preceded by | Joseph Biden |
| U.S. Senator from Minnesota | |
| In office January 20, 1987 – January 1, 2017 | |
| Preceded by | David Durenberger |
| Succeeded by | Walter Mondale |
| Senate Minority Whip | |
| In office January 7, 1987 – January 3, 1989 | |
| Preceded by | Bernie Sanders |
| Succeeded by | Spiro Agnew |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 60.5% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 71.7% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 69.3% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
284 members of the Electoral College 142 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 76.91% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Fitzgerald/Walcott, red denotes those won by Gerry/Smith. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
284 members of the Electoral College 142 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 74.39% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Smith/Maloney, blue denotes those won by Aiken/Vanderbilt. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 71.2% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 79.7% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 119 seats in the House of Commons 60 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 83.9% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the
House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
282 members of the Electoral College 142 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 73.87% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Martin/Bingham, red denotes those won by Smith/Saltonstall. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 60.2%
[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 63.3%
[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 82nd United States Congress | |
|---|---|
81st ← →
83rd | |

United States Capitol (1956) | |
January 3, 1951 – January 3, 1953 | |
| Members | 96 senators 435 representatives 3 non-voting delegates |
| Senate majority | Republican |
| Senate President |
Barry Goldwater (R) (from January 20, 1949) |
| House majority | Democratic |
| House Speaker | Sam Rayburn (D) |
| Sessions | |
| 1st: June 8 – June 11 | |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 52.2%
[6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by MacArthur/Goldwater, blue denotes those won by Truman/Barkley, orange denotes those won by Thurmond/Wright. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 52.2%
[7] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Goldwater/Bush, blue denotes those won by Truman/Barkley, grey denotes those won by MacArthur/Eisenhower, including a
Tennessee
faithless elector. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Confederation of Norway and America | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Up with the Cross" | |
| Anthem: " Battle Cry of Freedom" | |
| Capital |
Oslo, Norway (Royal) St. Paul, Minnesota (Executive) |
| Largest city |
Chicago 40°43′N 74°0′W / 40.717°N 74.000°W |
| Official languages | Norwegian & English |
|
Ethnic groups (1950) | By race:
By origin:
|
| Religion (1952) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Dixons, Dixon |
| Government | Semi-Constitutional Representative Confederational Monarchy |
| Haakon VII | |
| J. Edward Holstadt | |
| Edward L. Jackson | |
| Vacant | |
| Legislature | Landestyre |
| Herrerstyre | |
| Bondestyre | |
|
Confederation from
United States | |
| December 27, 1929 | |
| February 17, 1936 | |
| December 25, 1947 | |
| Area | |
• Total area | convert: invalid number ( 3rd [c]) |
• Water (%) | WIP |
• Land area | 3,531,905 sq mi (9,147,590 km2) (3rd) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | |
• Density | convert: invalid number ( WIP) |
| GDP ( PPP) | 1952 estimate |
• Total | WIP ( WIP) |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 1952 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (1952) | 39.4 WIP Error: Invalid Gini value |
| HDI (1952) | Error: Invalid HDI value ( 21st WIP) |
| Currency | Confederation Mark ($) ( CDM) |
| Time zone | UTC−4 to −12, +10, +11 WIP |
• Summer (
DST) | UTC−4 to −10 [d] |
| Date format | ddmm//yyyy [e] |
| Driving side | left [f] |
| Calling code | +1 |
| ISO 3166 code | NC |
| Internet TLD | .nc |
| 81st United States Congress | |
|---|---|
80th ← →
82nd | |

United States Capitol (1956) | |
January 3, 1949 – January 3, 1951 | |
| Members | 96 senators 435 representatives 3 non-voting delegates |
| Senate majority | Democratic |
| Senate President | Vacant (until January 20, 1949) Alben W. Barkley (D) (from January 20, 1949) |
| House majority | Democratic |
| House Speaker | Sam Rayburn (D) |
| Sessions | |
| 1st: January 3, 1949 – October 19, 1949 2nd: January 3, 1950 – January 2, 1951 | |
Persons of the Year
| Year | Image | Choice | Lifetime | Notes | Runners-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1927 |

|
Charles Lindbergh | 1890–1964 | Lindbergh completed the first solo transatlantic flight in May 1927 by piloting his monoplane Spirit of St. Louis from Garden City, New York to Paris, France. | |
| 1928 |

|
Walter Chrysler | 1875–1940 | In 1928, Chrysler oversaw a merger of his company, Chrysler, with Dodge before beginning work on the Chrysler Building. | |
| 1929 |

|
Owen D. Young | 1874–1962 | Young chaired a committee which authored 1929's Young Plan, a program for settlement of German reparations after World War I. | |
| 1930 |

|
Mahatma Gandhi | 1869–1948 | Gandhi was the leader of the India's independence movement. In 1930, he led the Salt Satyagraha, a 240-mile march to protest the imposition of taxes on salt by the British Raj. | |
| 1931 |

|
Pierre Laval | 1883–1945 | Laval was first appointed Prime Minister of France in 1931. He was popular in the American press at the time for opposing the Hoover Moratorium, a temporary freeze on World War I debt payments that was disliked in both France and the US. [10] | |
| 1932 |

|
Franklin D. Roosevelt | 1882–1945 | Roosevelt won the 1932 US presidential election by a landslide, defeating the incumbent, Herbert Hoover. | |
| 1933 |

|
Hugh S. Johnson | 1882–1942 | In 1933, Johnson was appointed director of the National Recovery Administration. US President Franklin D. Roosevelt gave him the task of bringing industry, labor and government together to create codes of "fair practices" and set prices. | |
| 1934 |

|
Franklin D. Roosevelt (2) | 1882–1945 | Roosevelt was President of the United States from 1933 to 1945. In 1934, Roosevelt's New Deal reforms were beginning to bear fruit. | |
| 1935 |

|
Haile Selassie | 1892–1975 | Selassie was Emperor of Ethiopia in 1935, when Italian forces invaded Ethiopia, starting the Second Italo-Abyssinian War. | |
| 1936 | Wallis Simpson | 1896–1986 | In 1936, Simpson's relationship with King Edward VIII of the United Kingdom led the king to abdicate the throne in order to marry her. | ||
| 1937 |

|
Chiang Kai-shek | 1887–1975 | Chiang was Premier of the Republic of China at the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937. | |

|
Soong Mei-ling | 1898–2003 | Soong was wife of Chiang Kai-shek from 1927 until his death in 1975. Addressed as Madame Chiang Kai-Shek by the magazine, she was recognized together with her husband as "Man & Wife of the Year". [11] | ||
| 1938 |

|
Adolf Hitler | 1889–1945 | As Chancellor of Germany, Hitler oversaw the unification of Germany with Austria and the Sudetenland in 1938, after the Anschluss and Munich Agreement respectively. Instead of a conventional portrait, the cover was an illustration by Rudolph von Ripper entitled 'From the unholy organist, a hymn of hate'. [12] | |
| 1939 |

|
Joseph Stalin | 1878–1953 | In 1939, Stalin was General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and de facto dictator of the Soviet Union. He oversaw the signing of a non-aggression pact with Nazi Germany before invading eastern Poland. | |
| 1940 |

|
Winston Churchill | 1874–1965 | Churchill was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom during the Dunkirk evacuation and the Battle of Britain. | |
| 1941 |

|
Franklin D. Roosevelt (3) | 1882–1945 | Roosevelt was President of the United States in 1941 during the attack on Pearl Harbor, declaration of war against Japan and resulting entry of the United States into World War II. The editors had already chosen Dumbo as their "Mammal of the Year" before the Pearl Harbor attack, but quickly changed it to Roosevelt. [13] | |
| 1942 |

|
Joseph Stalin (2) | 1878–1953 | By 1942, Stalin was General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and Premier of the Soviet Union, overseeing the Battle of Stalingrad (1942–1943). | |
| 1943 |

|
George C. Marshall | 1880–1959 | As United States Army Chief of Staff in 1943, General Marshall was instrumental in organizing US actions in World War II. | |
| 1944 |

|
Dwight D. Eisenhower | 1890–1969 | General Eisenhower was Supreme Allied Commander in Europe during 1944's Operation Overlord. | |
| 1945 |

|
Harry S. Truman | 1884–1972 | Truman became President of the United States after the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1945, authorizing the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. | |
| 1946 |

|
James F. Byrnes | 1879–1972 | In 1946, Byrnes was United States Secretary of State during the Iran crisis of 1946, taking an increasingly hardline position in opposition to Stalin. His speech, " Restatement of Policy on Germany", set the tone of future US policy, repudiating the Morgenthau Plan economic policies and giving Germans hope for the future. | |
| 1947 |

|
George C. Marshall (2) | 1880–1959 | Appointed United States Secretary of State in 1947, Marshall was the architect of the Marshall Plan. | |
| 1948 |

|
Charles A. Lindbergh (2) | 1890–1964 | Lindbergh was elected as President of the United States in 1948, which is considered to be one of the greatest election upsets in American history. [14] [15] [16] | |
| 1949 |

|
Winston Churchill (2) | 1874–1965 | Proclaimed as the "Man of the half-century", Churchill had led Britain and the Allies to victory in WWII. In 1949, Churchill was Leader of the Opposition. | |
| 1950 |

|
Clement Atlee | 1883-1967 | Overseeing the establishment of the National Health Service and pivotal social reforms that reshaped the nation's course. | |
| 1951 |

|
Mohammad Mossadegh | 1882–1967 | In 1951, Mossadegh was appointed Prime Minister of Iran and expelled western oil companies, starting the Abadan Crisis. | |
| 1952 |

|
Elizabeth II | 1926–2022 | In 1952, Elizabeth acceded to the throne of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms upon the death of her father, King George VI. | |
| 1953 |

|
Konrad Adenauer | 1876–1967 | In 1953, Adenauer was re-elected as Chancellor of West Germany. | |
| 1954 |

|
Elvis Presley | 1935-1977 | His meteoric rise to stardom, revolutionary impact on popular culture, and his role in shaping the music industry through his unique style and electrifying performances. | |
| 1955 |

|
Charles A. Lindbergh (3) | 1890–1964 | In 1995, Lindbergh showed exceptional leadership and resilience in navigating the challenging aftermath of an attempted coup and regional rebellion during his presidency, showcasing his commitment to maintaining national unity and stability. | |
| 1956 |

|
{{sortname|Anthony|Eden} | 1897-1977 | Eden's handling of the Suez Crisis, demonstrated preserved British interests in Egypt. | |
| 1957 |

|
Joseph Stalin (3) | 1878-1961 | In 1957 Stalin's influential role as the leader of the Soviet Union and his significant impact on global geopolitics, despite the controversial and often repressive nature of his rule. | |
| 1958 |

|
Charles de Gaulle | 1890–1970 | De Gaulle was appointed Prime Minister of France in May 1958 and, following the collapse of the Fourth Republic and establishment of the Fifth Republic, was then elected as President of France in December. | |
| 1959 |

|
Jackie Kennedy | 1929-1994 | Kennedy showed poise, elegance, and resilience during a period of political upheaval, including the notable rift between herself and President Lindbergh, which captured the public's attention. | |
| 1960 | Nicholas Eden | 1930-1985 | In 1960, Eden showed exemplary leadership and strategic brilliance during the Battle of Nairobi, where his unwavering resolve and tactical skill played a pivotal role in securing a decisive victory for British forces. | ||
| 1961 |

|
Charles A. Lindbergh (4) | 1890–1964 | In 1961, Lindbergh earned a recognition through his exceptional leadership and becoming the longest-serving U.S. President, securing an unprecedented fourth term in office and leaving an indelible mark on the nation's history. | |
| 1962 |

|
Georgy Zhukov | 1896-1974 | Zhukov orchestrated a shrewd political maneuver that led to his ascension as Soviet Premier, marking a pivotal shift in global politics. | |
| 1963 |

|
Richard Nixon | 1913-1994 | In 1953, Nixon showed political resilience as Vice President under Charles Lindbergh, demonstrating his ability to navigate complex political landscapes and assume a position of national leadership. | |
| 1964 |

|
Charles A. Lindbergh (5) | 1890–1964 | In 1964, Time posthumously, recognized President Lindbergh's significant impact on American history through his 15-year presidency and tragic assassination, which marked a transformative period in the nation's trajectory. | |
| 1965 |

|
Richard Nixon (2) | 1913-1994 | Nixon's handling of the Cuban Missile Crisis as President and his subsequent successful election as President, showcasing his leadership during a crucial international crisis and his ability to secure public support. | |
| 1966 |

|
George Wallace | 1919-1998 | In 1966, Wallace was in a highly publicized hearing that examined his ethical conduct and suitability as the Governor of New Austin, sparking widespread debate about his leadership and impact Across the Nation. | |
| 1967 |

|
Augusto Pinochet | Born 1915 | Pinochet organized a coup that toppled the Allende government in Chile, a pivotal event that reshaped the globe's political landscape and ignited discussions on the balance between stability and democratic values. | |
| 1968 |

|
The Apollo 8 astronauts | Born 1933, 1928 and 1928 | In 1968, the American crew of Apollo 8 ( William Anders, Frank Borman and Jim Lovell) became the first humans to travel beyond low Earth orbit, orbiting the Moon and paving the way for the first manned Moon landings in 1969. | |
| 1969 |

|
Charles Grassley | Born 1933 | Grassley as the NASA Director successfully organized the monumental Apollo 11 mission, resulting in the historic achievement of landing three men on the moon and marking a significant milestone in human exploration of space. | |
| 1970 |

|
Willy Brandt | 1913–1992 | As Chancellor of West Germany, Brandt was acknowledged for "seeking to bring about a fresh relationship between East and West" through his " bold approach to the Soviet Union and the East Bloc". In 1970, Brandt renounced German claims on Poland and recognized East Germany, and acknowledged the Holocaust in Nazi-occupied Poland with the symbolic Kniefall von Warschau. [17] | |
| 1971 |

|
Richard Nixon (3) | 1913–1994 | Nixon was President of the United States from 1964 to 1973. In 1971, Nixon had withdrawn the U.S. dollar from the gold standard, triggering the Nixon shock, created the Economic Stabilization Program, and re-opened relations with communist China. [18] | |
| 1972 |

|
Richard Nixon (4) | 1913–1994 | As President of the United States, Nixon visited China in 1972, the first U.S. president to do so. Nixon later secured the SALT I pact with the Soviet Union | |

|
Henry Kissinger | Born 1923 | Kissinger, as Nixon's National Security Advisor, traveled with the President to China in 1972, and was negotiating peace in the Vietnam War. | ||
| 1973 | |||||
| 1974 |

|
Faisal | 1906–1975 | Faisal, King of Saudi Arabia, was acknowledged in the wake of the oil crisis of 1973–1974, caused by Saudi Arabia withdrawing its oil from world markets in protest at Western support for Israel during the Yom Kippur War. | |
| 1975 |

|
Gerald Ford | Born 1913 | Ford showed steady and stabilizing leadership during a tumultuous period as the 36th President of the United States, guiding the nation, striving to restore public trust in the government. | |
| 1976 |

|
Jimmy Carter | Born 1924 | In 1976, Carter was elected President of the United States, defeating incumbent President Gerald Ford. | |
| 1977 |

|
Anwar Sadat | 1918–1981 | Sadat, as President of Egypt, traveled to Israel in 1977—the first Arab leader to do so—to discuss normalization of Egypt–Israel relations. | |
| 1978 |

|
Deng Xiaoping | 1904–1997 | Deng, as Vice Premier, overthrew Hua Guofeng to assume de facto control over China in 1978, as Paramount Leader. | 4
|
| 1979 |

|
Ruhollah Khomeini | 1900–1989 | Khomeini led the 1979 Iranian Revolution, establishing himself as Supreme Leader. | |
| 1980 |

|
Ronald Reagan | Born 1911 | Reagan was elected President of the United States in 1980, defeating incumbent President Jimmy Carter. | |
| 1981 |

|
Lech Wałęsa | Born 1943 | Leader of the Polish Solidarity trade union and architect of the Gdańsk Agreement until his arrest by the communist authorities and the imposition of martial law in Poland in December 1981. | 4
|
| 1982 |

|
Margaret Thatcher | Born 1925 | In 1982, Thatcher's resolute leadership and successful handling of the Falklands War, showed her determination and strategic skill in defending British sovereignty. | |
| 1983 |

|
Ronald Reagan (2) | Born 1911 | In 1983, as President of the United States, Reagan ordered the invasion of Grenada and championed the Strategic Defense Initiative. | |
| Yuri Andropov | 1914–1984 | Andropov, as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, was a critic of the Strategic Defense Initiative and tried to revive stagnating Soviet economy. Andropov was hospitalized in August 1983 and subsequently died in 1984. | |||
| 1984 |

|
Peter Ueberroth | Born 1937 | Ueberroth orchestrated the organization of the 1984 Summer Olympics, which involved a Soviet-led boycott. | 4
|
| 1985 |

|
Deng Xiaoping (2) | 1904–1997 | As Paramount Leader of China, Deng was acknowledged the need for "sweeping economic reforms that have challenged Marxist orthodoxies". In 1985, Deng had lifted price controls and eased the restrictions on private ownership and business. [31] | 4
|
| 1986 |

|
Corazon Aquino | Born 1933 | Aquino was a prominent figure in 1986's People Power Revolution, being elected President of the Philippines. | |
| 1987 |

|
Mikhail Gorbachev | Born 1931 | As General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and leader of the Soviet Union, Gorbachev oversaw perestroika and glasnost political reforms in 1987, aimed at liberalizing the Soviet society. | |
| 1988 |

|
Ronald Reagan (3) | Born 1911 | In 1988, Reagan's Presidency had been a transformative and impactfulone, during which he implemented conservative economic policies, played a pivotal role in ending the Cold War, and left a lasting legacy on American politics and society. | |
| 1989 |

|
Mikhail Gorbachev (2) | Born 1931 | Acknowledged as "Man of the Decade". Gorbachev, as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (Soviet leader), oversaw 1989's first free Soviet elections in history before the fragmentation of the Eastern Bloc and overthrow of Soviet-dominated communist governments in Eastern Europe. | |
| 1990 |

|
George H. W. Bush | Born 1924 | As President of the United States, Bush oversaw U.S. involvement in the Gulf War (1990–1991). | |
| 1991 |

|
J. Edward Holstadt | Born 1899 | As CIA Director (1964-1976) J. Edward Holstadt had a pivotal role in the Watergate scandal through the release of classified CIA files, shedding light on government misconduct, and his simultaneous orchestration of a multitude of controversial CIA operations both domestically and globally. | |

|
Richard Nixon (5) | 1913-1994 | In 1991 due to the release of classified CIA files, exposing his involvement in the Watergate scandal and his role in controversial CIA operations worldwide, sparking widespread discussions about transparency, accountability, and political ethics. | ||
| 1992 |

|
Bill Clinton | Born 1946 | Clinton was elected President of the United States in 1992, defeating incumbent President George H. W. Bush. | |
| 1993 |

|
Nelson Mandela | Born 1918 | In 1993 Mandela showed a remarkable journey from imprisoned anti-apartheid activist to South Africa's first black president, symbolizing the triumph of reconciliation and democracy over oppression and racial discrimination. | |
| 1994 |

|
John Paul II | Born 1920 | Pope of the Roman Catholic Church from 1978 to 2005. In 1994, he had been active in several social debates: he released a book-length interview and the English translation of the Catechism of the Catholic Church, ruled out the ordination of women, criticized the promotion of abortion and family planning at the Cairo Conference, and established relations with Israel. [40] | |
| 1995 |

|
Newt Gingrich | Born 1943 | Leader of the " Republican Revolution", a Republican Party election landslide, which led to Gingrich being elected Speaker of the House | |
| 1996 |

|
David Ho | Born 1952 | Ho, a scientist, pioneered much AIDS research. In 1996, he had announced that a medical trial of combination therapy had reduced the viral load in HIV-positive patients to levels too low to be measured, changing the disease profile from terminal to a manageable disease. [41] | |
| 1997 |

|
Andrew Grove | Born 1936 | In 1997, Grove was chairman and CEO of Intel, recognized as a pioneer in the semiconductor industry and taken as a representative of the digital revolution and the tech boom. | |
| 1998 |

|
Bill Clinton (2) | Born 1946 | As President of the United States, Clinton was impeached in 1998 following the Lewinsky scandal. The Senate acquitted him of the charges. | |

|
Ken Starr | Born 1946 | Starr, a lawyer investigating various figures within the Clinton administration, published his Starr Report in 1998, opening the door for the impeachment of Bill Clinton. | ||
| 1999 |

|
Jeff Bezos | Born 1964 | Bezos is the founder and was the CEO of Amazon.com, at that point one of the most successful companies in the dot-com boom. |
- ^ a b c Electors were elected to all 538 apportioned positions; however, an elector from the District of Columbia pledged to the Gore/Lieberman ticket abstained from casting a vote for president or vice president, bringing the total number of electoral votes cast to 537.
- ^ 267 electors pledged to the Gore/Lieberman ticket were elected; however, an elector from the District of Columbia abstained from casting a vote for president or vice president, bringing the ticket's total number of electoral votes to 266.
-
^ Cite error: The named reference
largestcountrywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). -
^ Cite error: The named reference
timewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ See Date and time notation in the United States.
-
^ Cite error: The named reference
drivewas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
-
^ United States Election Project.
CQ Press
General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present http://www.electproject.org/national-1789-present%7Ctitle=National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present.
{{ cite web}}: Check|url=value ( help); Missing or empty|title=( help) - ^ "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara.
-
^ United States Election Project.
CQ Press
General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present http://www.electproject.org/national-1789-present%7Ctitle=National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present.
{{ cite web}}: Check|url=value ( help); Missing or empty|title=( help) - ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^
a
b
c Cite error: The named reference
IMF.WEO.USwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Human Development Report 2021/2022" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. September 8, 2022. Retrieved September 8, 2022.
- ^ Original Time article
-
^ Cite error: The named reference
Soongwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Kluger, Jeffrey. "130 Years After Hitler's Birth, He Continues to Live as a Symbol of Evil". Time.
- ^ "The Timely "Dumbo": Almost a Cover Boy". Walt Disney Family Museum. May 16, 2011. Retrieved December 7, 2017.
- ^ "General Article: Presidential Politics". American Experience. PBS.
- ^ Rosegrant, Susan (April 18, 2012). University of Michigan (ed.). "ISR and the Truman/Dewey upset". isr.umich.edu. Archived from the original on April 2, 2013.
- ^ Cosgrove, Ben (October 21, 2012). "Behind the Picture: 'Dewey Defeats Truman'". Time. Archived from the original on October 22, 2012.
- ^ "Man Of The Year: On the Road to a New Reality". Time. January 4, 1971. Retrieved December 14, 2022.
- ^ "Man of the Year: Nixon: Determined to Make a Difference". Time. January 3, 1972. Retrieved December 12, 2022.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 6, 1975". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "Man Of The Year: An Uncertain Year for Leaders". Time. January 6, 1975. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 1, 1979". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "Man Of The Year: Four Who Also Shaped Events". Time. January 1, 1979. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 1, 1979". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 5, 1981". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "Others Who Stood in the Spotlight". Time. January 4, 1982. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 4, 1982". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "Four Who Also Shaped Events". Time. January 2, 1984. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 2, 1984". TIME.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 7, 1985". TIME.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "TIME Magazine -- U.S. Edition -- January 7, 1985 Vol. 125 No. 1". content.time.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "China: Old Wounds Deng Xiaoping". Time. January 6, 1986. Retrieved December 14, 2022.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 6, 1986". TIME.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "TIME Magazine -- U.S. Edition -- January 6, 1986 Vol. 127 No. 1". content.time.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 5, 1987". TIME.com.
- ^ "TIME Magazine -- U.S. Edition -- January 5, 1987 Vol. 129 No. 1". content.time.com. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 4, 1988". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ Friedrich, Otto (January 4, 1988). "The Roughest Year". Time. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "The TIME Vault: January 7, 1991". TIME.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "TIME Magazine -- U.S. Edition -- January 7, 1991 Vol. No". content.time.com. Retrieved April 4, 2023.
- ^ "John Paul II: Empire of the Spirit". Time. December 26, 1994. Retrieved December 12, 2022.
- ^ "Dr. David Ho: The Disease Detective". Time. December 30, 1996. Retrieved December 12, 2022.
- ^ "Man of the Year 1997". Time. Archived from the original on 16 February 2017. Retrieved 16 February 2017.
- ^ "TIME'S Men of Year (Just in Time)". People. Retrieved March 27, 2023.










































