 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Norvir |
| AHFS/ Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a696029 |
| License data | |
|
Pregnancy category |
|
|
Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 98-99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 3-5 hours |
| Excretion | mostly fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
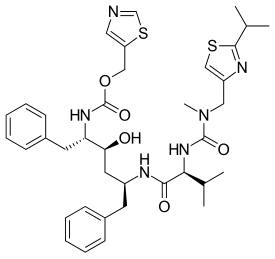
| Formula | C37H48N6O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 720.95 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model ( JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Ritonavir (RTV), sold under the trade name Norvir, is an antiretroviral medication used along with other medications to treat HIV/AIDS. [2] This combination treatment is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). [2] Often a low dose is used with other protease inhibitors. [2] It may also be used in combination with other medications for hepatitis C. [3] It is taken by mouth. [2] The capsules of the medication do not work the same as the tablets. [2]
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and numbness of the hands and feet. [2] Serious side effects include liver problems, pancreatitis, allergic reactions, and arrythmias. [2] Serious interactions may occur with a number of other medications including amiodarone and simvastatin. [2] At low doses it is considered to be acceptable for use during pregnancy. [4] Ritonavir is of the protease inhibitor class. [2] Typically, however, it is used to inhibit the enzyme that metabolizes other protease inhibitors. [5] This inhibition allows lower doses of these latter medication to be used. [5]
Ritonavir was patented in 1989 and came into medical use in 1996. [6] [7] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. [8] Globally the wholesale cost in the developing world is between US$0.07 and $2.20 per day. [9] In the United States it costs about $9.20–55 per day depending on the dose. [2]
- ^ "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 6 November 2020. Retrieved 22 September 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Ritonavir". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2015-10-17. Retrieved Oct 23, 2015.
- ^ "FDA approves Viekira Pak to treat hepatitis C". Food and Drug Administration. December 19, 2014. Archived from the original on October 31, 2015.
- ^ "Ritonavir Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". drugs.com. Archived from the original on 7 September 2015. Retrieved 23 October 2015.
- ^ a b British National Formulary 69 (69 ed.). Pharmaceutical Pr. March 31, 2015. p. 426. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ^ Hacker, Miles (2009). Pharmacology principles and practice. Amsterdam: Academic Press/Elsevier. p. 550. ISBN 9780080919225. Archived from the original on 2020-06-17. Retrieved 2017-09-10.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 509. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 2019-03-02.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl: 10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "Ritonavir". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2015.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Norvir |
| AHFS/ Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a696029 |
| License data | |
|
Pregnancy category |
|
|
Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 98-99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 3-5 hours |
| Excretion | mostly fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C37H48N6O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 720.95 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model ( JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Ritonavir (RTV), sold under the trade name Norvir, is an antiretroviral medication used along with other medications to treat HIV/AIDS. [2] This combination treatment is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). [2] Often a low dose is used with other protease inhibitors. [2] It may also be used in combination with other medications for hepatitis C. [3] It is taken by mouth. [2] The capsules of the medication do not work the same as the tablets. [2]
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and numbness of the hands and feet. [2] Serious side effects include liver problems, pancreatitis, allergic reactions, and arrythmias. [2] Serious interactions may occur with a number of other medications including amiodarone and simvastatin. [2] At low doses it is considered to be acceptable for use during pregnancy. [4] Ritonavir is of the protease inhibitor class. [2] Typically, however, it is used to inhibit the enzyme that metabolizes other protease inhibitors. [5] This inhibition allows lower doses of these latter medication to be used. [5]
Ritonavir was patented in 1989 and came into medical use in 1996. [6] [7] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. [8] Globally the wholesale cost in the developing world is between US$0.07 and $2.20 per day. [9] In the United States it costs about $9.20–55 per day depending on the dose. [2]
- ^ "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 6 November 2020. Retrieved 22 September 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Ritonavir". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2015-10-17. Retrieved Oct 23, 2015.
- ^ "FDA approves Viekira Pak to treat hepatitis C". Food and Drug Administration. December 19, 2014. Archived from the original on October 31, 2015.
- ^ "Ritonavir Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". drugs.com. Archived from the original on 7 September 2015. Retrieved 23 October 2015.
- ^ a b British National Formulary 69 (69 ed.). Pharmaceutical Pr. March 31, 2015. p. 426. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ^ Hacker, Miles (2009). Pharmacology principles and practice. Amsterdam: Academic Press/Elsevier. p. 550. ISBN 9780080919225. Archived from the original on 2020-06-17. Retrieved 2017-09-10.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 509. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 2019-03-02.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl: 10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "Ritonavir". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2015.