 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈhɛpərɪn/ HEP-ər-in |
| AHFS/ Drugs.com | Monograph |
|
Pregnancy category |
|
|
Routes of administration | IV, SQ |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Erratic |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 hours |
| Excretion | Urine [2] |
| Identifiers | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
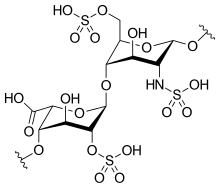
| Formula | C12H19NO20S3 |
| Molar mass | 12000–15000 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| |
| | |
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. [4] [6] As a medication it is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). [4] Specifically it is used in the treatment of heart attacks, unstable angina, and to prevent and treat blood clots in either veins or arteries. [4] [3] It is given by injection into a vein or under the skin. [4] Other uses include inside test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. [6] [7]
Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets. [4] Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. [4] Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. [4] Heparin appears to be relatively safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. [8] Heparin is produced by basophils and mast cells in all mammals. [9]
The discovery of heparin was announced in 1916. [10] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. [11] The wholesale cost in the developing world, when used for prevention, is about US$9.63–37.95 per month. [12] In the United States it costs about $25–50 per month. [13] A fractionated version of heparin, known as low molecular weight heparin, is also available. [14]
References
- ^ Heparin Sodium injection Archived 2013-09-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ heparin. In: Lexi-Drugs Online [database on the Internet]. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp, Inc.; 2007 [cited 2/10/12]. Available from: http://online.lexi.com Archived 2012-02-15 at the Wayback Machine. subscription required to view.
- ^
a
b Cite error: The named reference
MSF2020was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h "Heparin Sodium". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 27 January 2016. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
-
^ Cite error: The named reference
WHO2020DDDwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b "Heparin (Mucous ) Injection BP – Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) – (eMC)". www.medicines.org.uk. September 2016. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ^ McClatchey, Kenneth D. (2002). Clinical Laboratory Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 662. ISBN 9780683307511. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- ^ "Heparin Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". drugs.com. Archived from the original on 27 January 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- ^ Guyton, A. C.; Hall, J. E. (2006). Textbook of Medical Physiology. Elsevier Saunders. p. 464. ISBN 978-0-7216-0240-0.
- ^ Li, Jie Jack; Corey, E. J. (2013). Drug Discovery: Practices, Processes, and Perspectives. John Wiley & Sons. p. 189. ISBN 9781118354469. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl: 10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "Heparin". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Archived from the original on 22 January 2018. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. X. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ^ Rietschel, Robert L.; Fowler, Joseph F.; Fisher, Alexander A. (2008). Fisher's Contact Dermatitis. PMPH-USA. p. 142. ISBN 9781550093780. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈhɛpərɪn/ HEP-ər-in |
| AHFS/ Drugs.com | Monograph |
|
Pregnancy category |
|
|
Routes of administration | IV, SQ |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Erratic |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 hours |
| Excretion | Urine [2] |
| Identifiers | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H19NO20S3 |
| Molar mass | 12000–15000 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| |
| | |
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. [4] [6] As a medication it is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). [4] Specifically it is used in the treatment of heart attacks, unstable angina, and to prevent and treat blood clots in either veins or arteries. [4] [3] It is given by injection into a vein or under the skin. [4] Other uses include inside test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. [6] [7]
Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets. [4] Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. [4] Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. [4] Heparin appears to be relatively safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. [8] Heparin is produced by basophils and mast cells in all mammals. [9]
The discovery of heparin was announced in 1916. [10] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. [11] The wholesale cost in the developing world, when used for prevention, is about US$9.63–37.95 per month. [12] In the United States it costs about $25–50 per month. [13] A fractionated version of heparin, known as low molecular weight heparin, is also available. [14]
References
- ^ Heparin Sodium injection Archived 2013-09-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ heparin. In: Lexi-Drugs Online [database on the Internet]. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp, Inc.; 2007 [cited 2/10/12]. Available from: http://online.lexi.com Archived 2012-02-15 at the Wayback Machine. subscription required to view.
- ^
a
b Cite error: The named reference
MSF2020was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h "Heparin Sodium". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 27 January 2016. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
-
^ Cite error: The named reference
WHO2020DDDwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b "Heparin (Mucous ) Injection BP – Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) – (eMC)". www.medicines.org.uk. September 2016. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ^ McClatchey, Kenneth D. (2002). Clinical Laboratory Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 662. ISBN 9780683307511. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- ^ "Heparin Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". drugs.com. Archived from the original on 27 January 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- ^ Guyton, A. C.; Hall, J. E. (2006). Textbook of Medical Physiology. Elsevier Saunders. p. 464. ISBN 978-0-7216-0240-0.
- ^ Li, Jie Jack; Corey, E. J. (2013). Drug Discovery: Practices, Processes, and Perspectives. John Wiley & Sons. p. 189. ISBN 9781118354469. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl: 10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "Heparin". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Archived from the original on 22 January 2018. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. X. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ^ Rietschel, Robert L.; Fowler, Joseph F.; Fisher, Alexander A. (2008). Fisher's Contact Dermatitis. PMPH-USA. p. 142. ISBN 9781550093780. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.