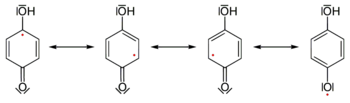
Semiquinones (or ubisemiquinones, if their origin is ubiquinone) are free radicals resulting from the removal of one hydrogen atom with its electron during the process of dehydrogenation of a hydroquinone, such as hydroquinone itself or catechol, to a quinone or alternatively the addition of a single hydrogen atom with its electron to a quinone. [1] Semiquinones are highly unstable.
E.g. ubisemiquinone is the first of two stages in reducing the supplementary form of CoQ10 (ubiquinone) to its active form ubiquinol.
- ^ Song, Y; Buettner, GR (Sep 15, 2010). "Thermodynamic and kinetic considerations for the reaction of semiquinone radicals to form superoxide and hydrogen peroxide". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 49 (6): 919–62. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.05.009. PMC 2936108. PMID 20493944.

Semiquinones (or ubisemiquinones, if their origin is ubiquinone) are free radicals resulting from the removal of one hydrogen atom with its electron during the process of dehydrogenation of a hydroquinone, such as hydroquinone itself or catechol, to a quinone or alternatively the addition of a single hydrogen atom with its electron to a quinone. [1] Semiquinones are highly unstable.
E.g. ubisemiquinone is the first of two stages in reducing the supplementary form of CoQ10 (ubiquinone) to its active form ubiquinol.
- ^ Song, Y; Buettner, GR (Sep 15, 2010). "Thermodynamic and kinetic considerations for the reaction of semiquinone radicals to form superoxide and hydrogen peroxide". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 49 (6): 919–62. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.05.009. PMC 2936108. PMID 20493944.