| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Scutum |
| Right ascension | 18h 50m 20.03715s [2] |
| Declination | −07° 54′ 27.4270″ [2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.80 [3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | C64 [4] |
| Variable type | SRb |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −0.20 ± 1.6 [5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) |
RA: 7.92
[2]
mas/
yr Dec.: −4.55 [2] mas/ yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.59 ± 0.57 mas [2] |
| Distance | approx. 1,300
ly (approx. 390 pc) |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
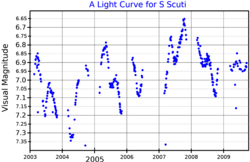
S Scuti is a carbon star located in the constellation Scutum. Parallax measurements by Hipparcos put it at a distance of approximately 1,300 light-years (390 parsecs). [2] Its apparent magnitude is 6.80, [3] making it not quite bright enough to be seen with the naked eye.
S Scuti is a semiregular variable star. Its class is SRb, and its pulsation cycle lasts 148 days. [4] S Scuti is also surrounded by a roughly spherical shell of dust. The shell was known earlier from its carbon monoxide emission lines. [6] The total mass of the dust is (7 ± 2)×10−5 M☉. [6]
References
- ^ "ASAS All Star Catalogue". The All Sky Automated Survey. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f van Leeuwen, F.; et al. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv: 0708.1752. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237. Bibcode: 2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ^ a b De Beck, E.; Decin, L.; De Koter, A.; Justtanont, K.; Verhoelst, T.; Kemper, F.; Menten, K. M. (2010). "Probing the mass-loss history of AGB and red supergiant stars from CO rotational line profiles. II. CO line survey of evolved stars: Derivation of mass-loss rate formulae". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 523: A18. arXiv: 1008.1083. Bibcode: 2010A&A...523A..18D. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/200913771. S2CID 16131273.
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv: 1606.08053. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G. doi: 10.1134/S1063773706110065. S2CID 119231169.
- ^ a b Mečina, M; Kerschbaum, F; Groenewegen, M. A. T; Ottensamer, R; Blommaert, J. A. D. L; Mayer, A; Decin, L; Luntzer, A; Vandenbussche, B; Posch, Th; Waelkens, C (2013). "Dusty shells surrounding the carbon variables S Scuti and RT Capricorni". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 566: A69. arXiv: 1405.2769. Bibcode: 2014A&A...566A..69M. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201321117. S2CID 118597358.
External links
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Scutum |
| Right ascension | 18h 50m 20.03715s [2] |
| Declination | −07° 54′ 27.4270″ [2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.80 [3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | C64 [4] |
| Variable type | SRb |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −0.20 ± 1.6 [5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) |
RA: 7.92
[2]
mas/
yr Dec.: −4.55 [2] mas/ yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.59 ± 0.57 mas [2] |
| Distance | approx. 1,300
ly (approx. 390 pc) |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
S Scuti is a carbon star located in the constellation Scutum. Parallax measurements by Hipparcos put it at a distance of approximately 1,300 light-years (390 parsecs). [2] Its apparent magnitude is 6.80, [3] making it not quite bright enough to be seen with the naked eye.
S Scuti is a semiregular variable star. Its class is SRb, and its pulsation cycle lasts 148 days. [4] S Scuti is also surrounded by a roughly spherical shell of dust. The shell was known earlier from its carbon monoxide emission lines. [6] The total mass of the dust is (7 ± 2)×10−5 M☉. [6]
References
- ^ "ASAS All Star Catalogue". The All Sky Automated Survey. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f van Leeuwen, F.; et al. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv: 0708.1752. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237. Bibcode: 2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ^ a b De Beck, E.; Decin, L.; De Koter, A.; Justtanont, K.; Verhoelst, T.; Kemper, F.; Menten, K. M. (2010). "Probing the mass-loss history of AGB and red supergiant stars from CO rotational line profiles. II. CO line survey of evolved stars: Derivation of mass-loss rate formulae". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 523: A18. arXiv: 1008.1083. Bibcode: 2010A&A...523A..18D. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/200913771. S2CID 16131273.
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv: 1606.08053. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G. doi: 10.1134/S1063773706110065. S2CID 119231169.
- ^ a b Mečina, M; Kerschbaum, F; Groenewegen, M. A. T; Ottensamer, R; Blommaert, J. A. D. L; Mayer, A; Decin, L; Luntzer, A; Vandenbussche, B; Posch, Th; Waelkens, C (2013). "Dusty shells surrounding the carbon variables S Scuti and RT Capricorni". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 566: A69. arXiv: 1405.2769. Bibcode: 2014A&A...566A..69M. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201321117. S2CID 118597358.
External links