| S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine riboswitch | |
|---|---|
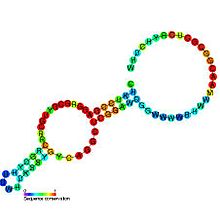 Predicted
secondary structure and
sequence conservation of SAH_riboswitch | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SAH_riboswitch |
| Rfam | RF01057 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg; riboswitch |
| Domain(s) | Bacteria |
| SO | SO:0005836 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
SAH riboswitches are a kind of riboswitch that bind S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). [1] When the coenzyme S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) is used in a methylation reaction, SAH is produced. SAH riboswitches typically up-regulate genes involved in recycling SAH to create more SAM (or the metabolically related methionine). This is particularly relevant to cells, because high levels of SAH can be toxic. [2] Originally identified by bioinformatics, [3] SAH riboswitches are apparent in many species of bacteria, predominantly certain Pseudomonadota and Actinomycetota. The atomic-resolution 3-dimensional structure of an SAH riboswitch has been solved using X-ray crystallography. [4]

References
- ^ a b Wang JX, Lee ER, Morales DR, Lim J, Breaker RR (2008). "Riboswitches that Sense S-adenosylhomocysteine and Activate Genes Involved in Coenzyme Recycling". Mol. Cell. 29 (6): 691–702. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.012. PMC 2712820. PMID 18374645.
- ^ Ueland PM (1982). "Pharmacological and biochemical aspects of S-adenosylhomocysteine and S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase". Pharmacol. Rev. 34 (3): 223–253. PMID 6760211.
- ^ Weinberg Z, Barrick JE, Yao Z, et al. (2007). "Identification of 22 candidate structured RNAs in bacteria using the CMfinder comparative genomics pipeline". Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (14): 4809–4819. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm487. PMC 1950547. PMID 17621584.
- ^ a b Edwards AL, Reyes FE, Héroux A, Batey RT (September 2010). "Structural basis for recognition of S-adenosylhomocysteine by riboswitches". RNA. 16 (11): 2144–2155. doi: 10.1261/rna.2341610. PMC 2957054. PMID 20864509.
External links
| S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine riboswitch | |
|---|---|
 Predicted
secondary structure and
sequence conservation of SAH_riboswitch | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SAH_riboswitch |
| Rfam | RF01057 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg; riboswitch |
| Domain(s) | Bacteria |
| SO | SO:0005836 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
SAH riboswitches are a kind of riboswitch that bind S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). [1] When the coenzyme S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) is used in a methylation reaction, SAH is produced. SAH riboswitches typically up-regulate genes involved in recycling SAH to create more SAM (or the metabolically related methionine). This is particularly relevant to cells, because high levels of SAH can be toxic. [2] Originally identified by bioinformatics, [3] SAH riboswitches are apparent in many species of bacteria, predominantly certain Pseudomonadota and Actinomycetota. The atomic-resolution 3-dimensional structure of an SAH riboswitch has been solved using X-ray crystallography. [4]

References
- ^ a b Wang JX, Lee ER, Morales DR, Lim J, Breaker RR (2008). "Riboswitches that Sense S-adenosylhomocysteine and Activate Genes Involved in Coenzyme Recycling". Mol. Cell. 29 (6): 691–702. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.012. PMC 2712820. PMID 18374645.
- ^ Ueland PM (1982). "Pharmacological and biochemical aspects of S-adenosylhomocysteine and S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase". Pharmacol. Rev. 34 (3): 223–253. PMID 6760211.
- ^ Weinberg Z, Barrick JE, Yao Z, et al. (2007). "Identification of 22 candidate structured RNAs in bacteria using the CMfinder comparative genomics pipeline". Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (14): 4809–4819. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm487. PMC 1950547. PMID 17621584.
- ^ a b Edwards AL, Reyes FE, Héroux A, Batey RT (September 2010). "Structural basis for recognition of S-adenosylhomocysteine by riboswitches". RNA. 16 (11): 2144–2155. doi: 10.1261/rna.2341610. PMC 2957054. PMID 20864509.