| Rhombicosacron | |
|---|---|
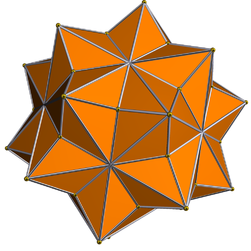
| |
| Type | Star polyhedron |
| Face |

|
| Elements | F = 60, E = 120 V = 50 (χ = −10) |
| Symmetry group | Ih, [5,3], *532 |
| Index references | DU56 |
| dual polyhedron | Rhombicosahedron |
In geometry, the rhombicosacron (or midly dipteral ditriacontahedron) is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the uniform rhombicosahedron, U56. It has 50 vertices, 120 edges, and 60 crossed-quadrilateral faces.
Proportions
Each face has two angles of and two angles of . The diagonals of each antiparallelogram intersect at an angle of . The dihedral angle equals . The ratio between the lengths of the long edges and the short ones equals , which is the square of the golden ratio.
References
- Wenninger, Magnus (1983), Dual Models, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-54325-5, MR 0730208
External links
| Rhombicosacron | |
|---|---|

| |
| Type | Star polyhedron |
| Face |

|
| Elements | F = 60, E = 120 V = 50 (χ = −10) |
| Symmetry group | Ih, [5,3], *532 |
| Index references | DU56 |
| dual polyhedron | Rhombicosahedron |
In geometry, the rhombicosacron (or midly dipteral ditriacontahedron) is a nonconvex isohedral polyhedron. It is the dual of the uniform rhombicosahedron, U56. It has 50 vertices, 120 edges, and 60 crossed-quadrilateral faces.
Proportions
Each face has two angles of and two angles of . The diagonals of each antiparallelogram intersect at an angle of . The dihedral angle equals . The ratio between the lengths of the long edges and the short ones equals , which is the square of the golden ratio.
References
- Wenninger, Magnus (1983), Dual Models, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-54325-5, MR 0730208
External links




