IntroductionWelcome to the Pan-Africanism portal!
Bienvenue sur le portail panafricanisme!   Pan-Africanism is a worldwide movement that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all indigenous peoples and diasporas of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atlantic slave trade, the movement extends beyond continental Africans with a substantial support base among the African diaspora in the Americas and Europe. Pan-Africanism can be said to have its origins in the struggles of the African people against enslavement and colonization and this struggle may be traced back to the first resistance on slave ships—rebellions and suicides—through the constant plantation and colonial uprisings and the "Back to Africa" movements of the 19th century. Based on the belief that unity is vital to economic, social, and political progress, it aims to "unify and uplift" people of African ancestry. ( Full article...) Selected article  The Pan-African colours are: green, gold (not yellow, despite its appearance), and red (inspired by the flag of Ethiopia). Red, black, and green are the colours of Black Nationalism, which should not be taken for a symbol of Pan-Africanism. It is often confused as such, given the political tendency’s support of Black self-determination. Selected biography
François-Dominique Toussaint Louverture (French: [fʁɑ̃swa dɔminik tusɛ̃ luvɛʁtyʁ] 9 May 1743 – 7 April 1803), also known as Toussaint L'Ouverture or Toussaint Bréda, was the best-known leader of the Haitian Revolution. He was a leader of the growing resistance. His military and political acumen saved the gains of the first Black insurrection in November 1791. He first fought for the Spanish against the French; then for France against Spain and Great Britain; and finally, for Saint-Domingue against Napoleonic France. He then helped transform the insurgency into a revolutionary movement, which by 1800 had turned Saint-Domingue, the most prosperous slave colony of the time, into the first free colonial society to have explicitly rejected race as the basis of social ranking. Though Louverture did not sever ties with France, his actions in 1800 constituted a de facto autonomous colony. The colony's constitution proclaimed him governor for life even against Napoleon Bonaparte's wishes. He died betrayed before the final and most violent stage of the armed conflict. However, his achievements set the grounds for the Black army's absolute victory and for Jean-Jacques Dessalines to declare the sovereign state of Haiti in January 1804. Louverture's prominent role in the Haitian success over colonialism and slavery had earned him the admiration of friends and detractors alike. Selected history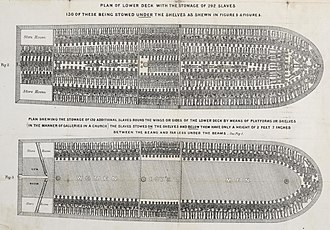  The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were enslaved and transported in the transatlantic slave trade were people from central and western Africa, who had been sold by other West Africans to Western European slave traders (with a small number being captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids), who brought them to the Americas. The South Atlantic and Caribbean economies especially were dependent on the supply of secure labour for the production of commodity crops, making goods and clothing to sell in Europe. This was crucial to those western European countries which, in the late 17th and 18th centuries, were vying with each other to create overseas empires. The Portuguese were the first to engage in the Atlantic slave trade in the 16th century. In 1526, they completed the first transatlantic slave voyage to Brazil, and other European countries soon followed. Shipowners regarded the slaves as cargo to be transported to the Americas as quickly and cheaply as possible, there to be sold to work on coffee, tobacco, cocoa, sugar and cotton plantations, gold and silver mines, rice fields, construction industry, cutting timber for ships, in skilled labour, and as domestic servants. The first Africans imported to the English colonies were classified as " indentured servants", like workers coming from England, and also as "apprentices for life". By the middle of the 17th century, slavery had hardened as a racial caste, with the slaves and their offspring being legally the property of their owners, and children born to slave mothers were also slaves. As property, the people were considered merchandise or units of labour, and were sold at markets with other goods and services. Selected cultureThe term Caribbean culture summarises the artistic, musical, literary, culinary, political and social elements that are representative of the Caribbean people all over the world. The Caribbean's culture has historically been influenced by that of African and Amerindian traditions. It has also been strongly influenced by that of its linguistic, economic, and cultural neighbor, the United States. As a collection of settler nations, the contemporary Caribbean has been shaped by waves of migration that have combined to form a unique blend of customs, cuisine, and traditions that have marked the socio-cultural development of the area. Selected imagesOrganisations
All-African People's Revolutionary Party ·
African Society for Cultural Relations with Independent Africa ·
African Unification Front ·
African Union ·
African Queens and Women Cultural Leaders Network ·
Conseil de l'Entente ·
Convention People's Party ·
East African Community ·
Economic Freedom Fighters ·
Global Afrikan Congress ·
International African Service Bureau ·
International League for Darker People ·
Organisation of African Unity ·
Pan African Association ·
Pan-African Congress ·
Pan Africanist Congress of Azania ·
Rassemblement Démocratique Africain ·
Pan Africa Chemistry Network ·
Pan African Federation of Accountants ·
Pan-African Freedom Movement for East and Central Africa ·
Sahara and Sahel Observatory ·
UNIA-ACL ·
ZANU–PF
See also
& Festivals Photo by Helinä Rautavaara (1977) Publications
Films and TVAudios and videosDid you knowArchbishop
Desmond Tutu and
Thabo Mbeki, former
President of South Africa. ... Selected quotesIn addressing imperialism at a Salisbury (Southern Rhodesia) meeting held on 9 April 1962, the former President of Zimbabwe
Robert Mugabe delivered the following speech:
Pan-Africanism topicsCategoriesThings you can do
Related portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using
portals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
IntroductionWelcome to the Pan-Africanism portal!
Bienvenue sur le portail panafricanisme!   Pan-Africanism is a worldwide movement that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all indigenous peoples and diasporas of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atlantic slave trade, the movement extends beyond continental Africans with a substantial support base among the African diaspora in the Americas and Europe. Pan-Africanism can be said to have its origins in the struggles of the African people against enslavement and colonization and this struggle may be traced back to the first resistance on slave ships—rebellions and suicides—through the constant plantation and colonial uprisings and the "Back to Africa" movements of the 19th century. Based on the belief that unity is vital to economic, social, and political progress, it aims to "unify and uplift" people of African ancestry. ( Full article...) Selected article  The Pan-African colours are: green, gold (not yellow, despite its appearance), and red (inspired by the flag of Ethiopia). Red, black, and green are the colours of Black Nationalism, which should not be taken for a symbol of Pan-Africanism. It is often confused as such, given the political tendency’s support of Black self-determination. Selected biography
François-Dominique Toussaint Louverture (French: [fʁɑ̃swa dɔminik tusɛ̃ luvɛʁtyʁ] 9 May 1743 – 7 April 1803), also known as Toussaint L'Ouverture or Toussaint Bréda, was the best-known leader of the Haitian Revolution. He was a leader of the growing resistance. His military and political acumen saved the gains of the first Black insurrection in November 1791. He first fought for the Spanish against the French; then for France against Spain and Great Britain; and finally, for Saint-Domingue against Napoleonic France. He then helped transform the insurgency into a revolutionary movement, which by 1800 had turned Saint-Domingue, the most prosperous slave colony of the time, into the first free colonial society to have explicitly rejected race as the basis of social ranking. Though Louverture did not sever ties with France, his actions in 1800 constituted a de facto autonomous colony. The colony's constitution proclaimed him governor for life even against Napoleon Bonaparte's wishes. He died betrayed before the final and most violent stage of the armed conflict. However, his achievements set the grounds for the Black army's absolute victory and for Jean-Jacques Dessalines to declare the sovereign state of Haiti in January 1804. Louverture's prominent role in the Haitian success over colonialism and slavery had earned him the admiration of friends and detractors alike. Selected history  The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were enslaved and transported in the transatlantic slave trade were people from central and western Africa, who had been sold by other West Africans to Western European slave traders (with a small number being captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids), who brought them to the Americas. The South Atlantic and Caribbean economies especially were dependent on the supply of secure labour for the production of commodity crops, making goods and clothing to sell in Europe. This was crucial to those western European countries which, in the late 17th and 18th centuries, were vying with each other to create overseas empires. The Portuguese were the first to engage in the Atlantic slave trade in the 16th century. In 1526, they completed the first transatlantic slave voyage to Brazil, and other European countries soon followed. Shipowners regarded the slaves as cargo to be transported to the Americas as quickly and cheaply as possible, there to be sold to work on coffee, tobacco, cocoa, sugar and cotton plantations, gold and silver mines, rice fields, construction industry, cutting timber for ships, in skilled labour, and as domestic servants. The first Africans imported to the English colonies were classified as " indentured servants", like workers coming from England, and also as "apprentices for life". By the middle of the 17th century, slavery had hardened as a racial caste, with the slaves and their offspring being legally the property of their owners, and children born to slave mothers were also slaves. As property, the people were considered merchandise or units of labour, and were sold at markets with other goods and services. Selected cultureThe term Caribbean culture summarises the artistic, musical, literary, culinary, political and social elements that are representative of the Caribbean people all over the world. The Caribbean's culture has historically been influenced by that of African and Amerindian traditions. It has also been strongly influenced by that of its linguistic, economic, and cultural neighbor, the United States. As a collection of settler nations, the contemporary Caribbean has been shaped by waves of migration that have combined to form a unique blend of customs, cuisine, and traditions that have marked the socio-cultural development of the area. Selected imagesOrganisations
All-African People's Revolutionary Party ·
African Society for Cultural Relations with Independent Africa ·
African Unification Front ·
African Union ·
African Queens and Women Cultural Leaders Network ·
Conseil de l'Entente ·
Convention People's Party ·
East African Community ·
Economic Freedom Fighters ·
Global Afrikan Congress ·
International African Service Bureau ·
International League for Darker People ·
Organisation of African Unity ·
Pan African Association ·
Pan-African Congress ·
Pan Africanist Congress of Azania ·
Rassemblement Démocratique Africain ·
Pan Africa Chemistry Network ·
Pan African Federation of Accountants ·
Pan-African Freedom Movement for East and Central Africa ·
Sahara and Sahel Observatory ·
UNIA-ACL ·
ZANU–PF
See also
& Festivals Photo by Helinä Rautavaara (1977) Publications
Films and TVAudios and videosDid you knowArchbishop
Desmond Tutu and
Thabo Mbeki, former
President of South Africa. ... Selected quotesIn addressing imperialism at a Salisbury (Southern Rhodesia) meeting held on 9 April 1962, the former President of Zimbabwe
Robert Mugabe delivered the following speech:
Pan-Africanism topicsCategoriesThings you can do
Related portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using
portals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
































