| Phragmoplastophyta | |
|---|---|

| |
| Examples of phragmoplastophytes: top left, Cycas circinalis; top right, Chara globularis; bottom left, various mosses; bottom right, Polypodium virginianum | |
|
Scientific classification
| |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| (unranked): | Archaeplastida |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Streptophyta |
| Clade: |
Phragmoplastophyta Lecointre & Guyader 2006 |
| Subclades | |
sister: Klebsormidiophyceae | |
The Phragmoplastophyta (Lecointre & Guyader 2006) are a proposed sister clade of the Klebsormidiaceae in the Streptophyte/ Charophyte clade. [1] [2] [3] [4] The Phragmoplastophyta consist of the Charophycaea and another unnamed clade which contains the Coleochaetophyceae, Zygnematophyceae, Mesotaeniaceae, and Embryophytes (land plants). It is an important step in the emergence of land plants within the green algae. It is equivalent to the ZCC clade/grade, cladistically granting the Embryophyta. [5]
The mitosis of Phragmoplastophyta takes place via a phragmoplast.
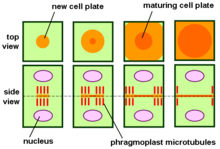
Another synapomorphy of this clade is the synthesis of cellulose microfibrils by a complex of octameric cellulose synthetases. This complex crosses the plasma membrane and polymerizes molecules from the cytoplasm into cellulose microfibrils, which, together with each other, form fibrils, necessary in the formation of the wall. The Phragmoplastophyte wall is also formed of phenolic compounds.
It is within Phragmoplastophyta we find the three clades of charophyte/streptophyte algae with true multicellular organization with differentiated cell types; Charophyceae, Coleochaetophyceae and land plants. The other charophyte algae are either unicellular, colonial, sarcinoid (three-dimensional packets of cells) or unbranched filamentous. [7]
Below is a consensus reconstruction of green algal relationships, mainly based on molecular data. [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [2] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21][ excessive citations]
| Viridiplantae/ |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| green algae |
References
-
^ Lecointre, Guillaume; Guyader, Hervé Le (2006).
The Tree of Life: A Phylogenetic Classification. Harvard University Press. p.
158.
ISBN
9780674021839.
Phragmoplastophyta.
- ^ a b Adl, Sina M.; Simpson, Alastair G. B.; Lane, Christopher E.; Lukeš, Julius; Bass, David; Bowser, Samuel S.; Brown, Matthew W.; Burki, Fabien; Dunthorn, Micah (2012-09-01). "The Revised Classification of Eukaryotes". Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 59 (5): 429–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2012.00644.x. ISSN 1550-7408. PMC 3483872. PMID 23020233.
- ^ Silar, Philippe (2016), "Protistes Eucaryotes: Origine, Evolution et Biologie des Microbes Eucaryotes", HAL Archives-ouvertes: 1–462
- ^ "Streptophyta - NCBI Taxonomy - Overview - Encyclopedia of Life". Encyclopedia of Life. Retrieved 2017-09-10.
- ^ Gould, Sven B.; Archibald, John M.; Stanton, Amanda; Vries, Jan de (2016-06-01). "Streptophyte Terrestrialization in Light of Plastid Evolution". Trends in Plant Science. 21 (6): 467–476. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2016.01.021. ISSN 1360-1385. PMID 26895731.
- ^ P.H. Raven, R.F. Evert, S.E. Eichhorn (2005): Biology of Plants, 7th Edition, W.H. Freeman and Company Publishers, New York, ISBN 0-7167-1007-2
- ^ Becker, B.; Marin, B. (2009). "Streptophyte algae and the origin of embryophytes". Annals of Botany. 103 (7): 999–1004. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp044. PMC 2707909. PMID 19273476.
- ^ Leliaert, Frederik; Smith, David R.; Moreau, Hervé; Herron, Matthew D.; Verbruggen, Heroen; Delwiche, Charles F.; De Clerck, Olivier (2012). "Phylogeny and Molecular Evolution of the Green Algae" (PDF). Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences. 31: 1–46. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2011.615705. S2CID 17603352.
- ^ Marin, Birger (2012). "Nested in the Chlorellales or Independent Class? Phylogeny and Classification of the Pedinophyceae (Viridiplantae) Revealed by Molecular Phylogenetic Analyses of Complete Nuclear and Plastid-encoded rRNA Operons". Protist. 163 (5): 778–805. doi: 10.1016/j.protis.2011.11.004. PMID 22192529.
- ^ Laurin-Lemay, Simon; Brinkmann, Henner; Philippe, Hervé (2012). "Origin of land plants revisited in the light of sequence contamination and missing data". Current Biology. 22 (15): R593–R594. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.06.013. PMID 22877776.
- ^ Leliaert, Frederik; Tronholm, Ana; Lemieux, Claude; Turmel, Monique; DePriest, Michael S.; Bhattacharya, Debashish; Karol, Kenneth G.; Fredericq, Suzanne; Zechman, Frederick W. (2016-05-09). "Chloroplast phylogenomic analyses reveal the deepest-branching lineage of the Chlorophyta, Palmophyllophyceae class. nov". Scientific Reports. 6: 25367. Bibcode: 2016NatSR...625367L. doi: 10.1038/srep25367. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 4860620. PMID 27157793.
- ^ Cook, Martha E.; Graham, Linda E. (2017). "Chlorokybophyceae, Klebsormidiophyceae, Coleochaetophyceae". In Archibald, John M.; Simpson, Alastair G. B.; Slamovits, Claudio H. (eds.). Handbook of the Protists. Springer International Publishing. pp. 185–204. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-28149-0_36. ISBN 9783319281476.
- ^ Lewis, Louise A.; Richard M. McCourt (2004). "Green algae and the origin of land plants". American Journal of Botany. 91 (10): 1535–1556. doi: 10.3732/ajb.91.10.1535. PMID 21652308.
- ^ Ruhfel, Brad R.; Gitzendanner, Matthew A.; Soltis, Pamela S.; Soltis, Douglas E.; Burleigh, J. Gordon (2014-02-17). "From algae to angiosperms–inferring the phylogeny of green plants (Viridiplantae) from 360 plastid genomes". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 14: 23. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-14-23. ISSN 1471-2148. PMC 3933183. PMID 24533922.
- ^ Umen, James G. (2014-11-01). "Green Algae and the Origins of Multicellularity in the Plant Kingdom". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 6 (11): a016170. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016170. ISSN 1943-0264. PMC 4413236. PMID 25324214.
- ^ de Vries, Jan; Archibald, John M.; Gould, Sven B. (2017-02-01). "The Carboxy Terminus of YCF1 Contains a Motif Conserved throughout >500 Myr of Streptophyte Evolution". Genome Biology and Evolution. 9 (2): 473–479. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx013. PMC 5381667. PMID 28164224.
- ^ Sánchez-Baracaldo, Patricia; Raven, John A.; Pisani, Davide; Knoll, Andrew H. (2017-09-12). "Early photosynthetic eukaryotes inhabited low-salinity habitats". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 114 (37): E7737–E7745. Bibcode: 2017PNAS..114E7737S. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620089114. PMC 5603991. PMID 28808007.
- ^ Gitzendanner, Matthew A.; Soltis, Pamela S.; Wong, Gane K.-S.; Ruhfel, Brad R.; Soltis, Douglas E. (2018). "Plastid phylogenomic analysis of green plants: A billion years of evolutionary history". American Journal of Botany. 105 (3): 291–301. doi: 10.1002/ajb2.1048. ISSN 0002-9122. PMID 29603143.
- ^ Linzhou Li; Sibo Wang; Hongli Wang; Sunil Kumar Sahu; Birger Marin; Haoyuan Li; Yan Xu; Hongping Liang; Zhen Li; Shifeng Chen; Tanja Reder; Zehra Çebi; Sebastian Wittek; Morten Petersen; Barbara Melkonian; Hongli Du; Huanming Yang; Jian Wang; Gane Ka-Shu Wong; Xun Xu; Xin Liu; Yves Van de Peer; Michael Melkonian; Huan Liu (22 June 2020). "The genome of Prasinoderma coloniale unveils the existence of a third phylum within green plants". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 4 (9): 1220–1231. doi: 10.1038/s41559-020-1221-7. PMC 7455551. PMID 32572216.
- ^ Mikhailyuk, Tatiana; Lukešová, Alena; Glaser, Karin; Holzinger, Andreas; Obwegeser, Sabrina; Nyporko, Svetlana; Friedl, Thomas; Karsten, Ulf (2018-07-01). "New Taxa of Streptophyte Algae (Streptophyta) from Terrestrial Habitats Revealed Using an Integrative Approach". Protist. 169 (3): 406–431. doi: 10.1016/j.protis.2018.03.002. ISSN 1434-4610. PMC 6071840. PMID 29860113.
- ^ Glass, Sarah (2021-01-01). "Chloroplast Genome Evolution in the Klebsormidiophyceae and Streptofilum". Theses.
| Phragmoplastophyta | |
|---|---|

| |
| Examples of phragmoplastophytes: top left, Cycas circinalis; top right, Chara globularis; bottom left, various mosses; bottom right, Polypodium virginianum | |
|
Scientific classification
| |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| (unranked): | Archaeplastida |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Streptophyta |
| Clade: |
Phragmoplastophyta Lecointre & Guyader 2006 |
| Subclades | |
sister: Klebsormidiophyceae | |
The Phragmoplastophyta (Lecointre & Guyader 2006) are a proposed sister clade of the Klebsormidiaceae in the Streptophyte/ Charophyte clade. [1] [2] [3] [4] The Phragmoplastophyta consist of the Charophycaea and another unnamed clade which contains the Coleochaetophyceae, Zygnematophyceae, Mesotaeniaceae, and Embryophytes (land plants). It is an important step in the emergence of land plants within the green algae. It is equivalent to the ZCC clade/grade, cladistically granting the Embryophyta. [5]
The mitosis of Phragmoplastophyta takes place via a phragmoplast.

Another synapomorphy of this clade is the synthesis of cellulose microfibrils by a complex of octameric cellulose synthetases. This complex crosses the plasma membrane and polymerizes molecules from the cytoplasm into cellulose microfibrils, which, together with each other, form fibrils, necessary in the formation of the wall. The Phragmoplastophyte wall is also formed of phenolic compounds.
It is within Phragmoplastophyta we find the three clades of charophyte/streptophyte algae with true multicellular organization with differentiated cell types; Charophyceae, Coleochaetophyceae and land plants. The other charophyte algae are either unicellular, colonial, sarcinoid (three-dimensional packets of cells) or unbranched filamentous. [7]
Below is a consensus reconstruction of green algal relationships, mainly based on molecular data. [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [2] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21][ excessive citations]
| Viridiplantae/ |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| green algae |
References
-
^ Lecointre, Guillaume; Guyader, Hervé Le (2006).
The Tree of Life: A Phylogenetic Classification. Harvard University Press. p.
158.
ISBN
9780674021839.
Phragmoplastophyta.
- ^ a b Adl, Sina M.; Simpson, Alastair G. B.; Lane, Christopher E.; Lukeš, Julius; Bass, David; Bowser, Samuel S.; Brown, Matthew W.; Burki, Fabien; Dunthorn, Micah (2012-09-01). "The Revised Classification of Eukaryotes". Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 59 (5): 429–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2012.00644.x. ISSN 1550-7408. PMC 3483872. PMID 23020233.
- ^ Silar, Philippe (2016), "Protistes Eucaryotes: Origine, Evolution et Biologie des Microbes Eucaryotes", HAL Archives-ouvertes: 1–462
- ^ "Streptophyta - NCBI Taxonomy - Overview - Encyclopedia of Life". Encyclopedia of Life. Retrieved 2017-09-10.
- ^ Gould, Sven B.; Archibald, John M.; Stanton, Amanda; Vries, Jan de (2016-06-01). "Streptophyte Terrestrialization in Light of Plastid Evolution". Trends in Plant Science. 21 (6): 467–476. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2016.01.021. ISSN 1360-1385. PMID 26895731.
- ^ P.H. Raven, R.F. Evert, S.E. Eichhorn (2005): Biology of Plants, 7th Edition, W.H. Freeman and Company Publishers, New York, ISBN 0-7167-1007-2
- ^ Becker, B.; Marin, B. (2009). "Streptophyte algae and the origin of embryophytes". Annals of Botany. 103 (7): 999–1004. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp044. PMC 2707909. PMID 19273476.
- ^ Leliaert, Frederik; Smith, David R.; Moreau, Hervé; Herron, Matthew D.; Verbruggen, Heroen; Delwiche, Charles F.; De Clerck, Olivier (2012). "Phylogeny and Molecular Evolution of the Green Algae" (PDF). Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences. 31: 1–46. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2011.615705. S2CID 17603352.
- ^ Marin, Birger (2012). "Nested in the Chlorellales or Independent Class? Phylogeny and Classification of the Pedinophyceae (Viridiplantae) Revealed by Molecular Phylogenetic Analyses of Complete Nuclear and Plastid-encoded rRNA Operons". Protist. 163 (5): 778–805. doi: 10.1016/j.protis.2011.11.004. PMID 22192529.
- ^ Laurin-Lemay, Simon; Brinkmann, Henner; Philippe, Hervé (2012). "Origin of land plants revisited in the light of sequence contamination and missing data". Current Biology. 22 (15): R593–R594. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.06.013. PMID 22877776.
- ^ Leliaert, Frederik; Tronholm, Ana; Lemieux, Claude; Turmel, Monique; DePriest, Michael S.; Bhattacharya, Debashish; Karol, Kenneth G.; Fredericq, Suzanne; Zechman, Frederick W. (2016-05-09). "Chloroplast phylogenomic analyses reveal the deepest-branching lineage of the Chlorophyta, Palmophyllophyceae class. nov". Scientific Reports. 6: 25367. Bibcode: 2016NatSR...625367L. doi: 10.1038/srep25367. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 4860620. PMID 27157793.
- ^ Cook, Martha E.; Graham, Linda E. (2017). "Chlorokybophyceae, Klebsormidiophyceae, Coleochaetophyceae". In Archibald, John M.; Simpson, Alastair G. B.; Slamovits, Claudio H. (eds.). Handbook of the Protists. Springer International Publishing. pp. 185–204. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-28149-0_36. ISBN 9783319281476.
- ^ Lewis, Louise A.; Richard M. McCourt (2004). "Green algae and the origin of land plants". American Journal of Botany. 91 (10): 1535–1556. doi: 10.3732/ajb.91.10.1535. PMID 21652308.
- ^ Ruhfel, Brad R.; Gitzendanner, Matthew A.; Soltis, Pamela S.; Soltis, Douglas E.; Burleigh, J. Gordon (2014-02-17). "From algae to angiosperms–inferring the phylogeny of green plants (Viridiplantae) from 360 plastid genomes". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 14: 23. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-14-23. ISSN 1471-2148. PMC 3933183. PMID 24533922.
- ^ Umen, James G. (2014-11-01). "Green Algae and the Origins of Multicellularity in the Plant Kingdom". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 6 (11): a016170. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016170. ISSN 1943-0264. PMC 4413236. PMID 25324214.
- ^ de Vries, Jan; Archibald, John M.; Gould, Sven B. (2017-02-01). "The Carboxy Terminus of YCF1 Contains a Motif Conserved throughout >500 Myr of Streptophyte Evolution". Genome Biology and Evolution. 9 (2): 473–479. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx013. PMC 5381667. PMID 28164224.
- ^ Sánchez-Baracaldo, Patricia; Raven, John A.; Pisani, Davide; Knoll, Andrew H. (2017-09-12). "Early photosynthetic eukaryotes inhabited low-salinity habitats". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 114 (37): E7737–E7745. Bibcode: 2017PNAS..114E7737S. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620089114. PMC 5603991. PMID 28808007.
- ^ Gitzendanner, Matthew A.; Soltis, Pamela S.; Wong, Gane K.-S.; Ruhfel, Brad R.; Soltis, Douglas E. (2018). "Plastid phylogenomic analysis of green plants: A billion years of evolutionary history". American Journal of Botany. 105 (3): 291–301. doi: 10.1002/ajb2.1048. ISSN 0002-9122. PMID 29603143.
- ^ Linzhou Li; Sibo Wang; Hongli Wang; Sunil Kumar Sahu; Birger Marin; Haoyuan Li; Yan Xu; Hongping Liang; Zhen Li; Shifeng Chen; Tanja Reder; Zehra Çebi; Sebastian Wittek; Morten Petersen; Barbara Melkonian; Hongli Du; Huanming Yang; Jian Wang; Gane Ka-Shu Wong; Xun Xu; Xin Liu; Yves Van de Peer; Michael Melkonian; Huan Liu (22 June 2020). "The genome of Prasinoderma coloniale unveils the existence of a third phylum within green plants". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 4 (9): 1220–1231. doi: 10.1038/s41559-020-1221-7. PMC 7455551. PMID 32572216.
- ^ Mikhailyuk, Tatiana; Lukešová, Alena; Glaser, Karin; Holzinger, Andreas; Obwegeser, Sabrina; Nyporko, Svetlana; Friedl, Thomas; Karsten, Ulf (2018-07-01). "New Taxa of Streptophyte Algae (Streptophyta) from Terrestrial Habitats Revealed Using an Integrative Approach". Protist. 169 (3): 406–431. doi: 10.1016/j.protis.2018.03.002. ISSN 1434-4610. PMC 6071840. PMID 29860113.
- ^ Glass, Sarah (2021-01-01). "Chloroplast Genome Evolution in the Klebsormidiophyceae and Streptofilum". Theses.