Mean airway pressure typically refers to the mean pressure applied during positive-pressure mechanical ventilation. Mean airway pressure correlates with alveolar ventilation, arterial oxygenation, [1] hemodynamic performance, and barotrauma. [2] It can also match the alveolar pressure if there is no difference between inspiratory and expiratory resistance. [3]
Equations
There are several equations aimed at determining the real mean airway pressure.
Volume control ventilation
In ventilation with a square flow waveform this equation can be used:
where:
- = mean airway pressure
- = peak inspiratory pressure
- = peak end expiratory pressure
- = inspiratory time
- = cycle time
Pressure control ventilation
During pressure control ventilation this variant of the equation can be used:
where:
- = mean airway pressure
- = peak inspiratory pressure
- = peak end expiratory pressure
- = inspiratory time
- = cycle time [3]
Airway pressure release ventilation
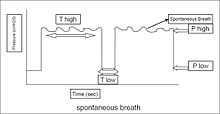
In airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) a variation of the previous equation must be used for the variables:
- where:
- = mean airway pressure
- = peak inspiratory pressure (PIP)
- = peak end expiratory pressure
- = time spent at
- = time spent at [4]
Other equations
Clinical significance
Mean airway pressure has been shown to have a similar correlation as plateau pressure to mortality. [6]
MAP is closely associated with mean alveolar pressure and shows the stresses exerted on the lung parenchyma on mechanical ventilation. [7]
In high frequency oscillatory ventilation, it has been suggested to set the mean airway pressure six above the lower inflection point on the lungs P-V curve. [8]
See also
References
- ^ Stewart AR, Finer NN, Peters KL (1981). "Effects of alterations of inspiratory and expiratory pressures and inspiratory/expiratory ratios on mean airway pressure, blood gases, and intracranial pressure". Pediatrics. 67 (4): 474–81. doi: 10.1542/peds.67.4.474. PMID 6789294. S2CID 2214900.
- ^ Marini JJ, Ravenscraft SA (1992). "Mean airway pressure: physiologic determinants and clinical importance--Part 2: Clinical implications". Crit Care Med. 20 (11): 1604–16. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199211000-00020. PMID 1424706. S2CID 42496727.
- ^ a b Hess, Dean (October 21, 2014). "Respiratory Mechanics in Mechanically Ventilated Patients" (PDF). Respiratory Care. 59 (11): 1773–1794. doi: 10.4187/respcare.03410. PMID 25336536. S2CID 5706765.
- ^ Daoud, Ehab G. (2007). "Airway pressure release ventilation". Annals of Thoracic Medicine. 2 (4): 176–179. doi: 10.4103/1817-1737.36556. ISSN 1817-1737. PMC 2732103. PMID 19727373.
- ^ David W. Chang (1999). Respiratory care calculations. Cengage Learning. pp. 251–. ISBN 978-0-7668-0517-0. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ^ Sahetya, Sarina; Wu, David; Brooks, Morgan (May 2020). "Mean Airway Pressure As a Predictor of 90-Day Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Patients". Critical Care Medicine. 48 (5): 688–695. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004268. PMC 8273919. PMID 32079893.
- ^ Su, Longxiang; Pan, Pan; Liu, Dawei; Long, Yun (2021-10-01). "Mean airway pressure has the potential to become the core pressure indicator of mechanical ventilation: Raising to the front from behind the clinical scenes". Journal of Intensive Medicine. 1 (2): 96–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jointm.2021.04.002. ISSN 2667-100X. PMC 9923962. PMID 36788801. S2CID 236575021.
- ^ Goddon, Sven; Fujino, Yuji; Hromi, Jonathan M.; Kacmarek, Robert M. (May 2001). "Optimal Mean Airway Pressure during High-frequency Oscillation: Predicted by the Pressure–Volume Curve". Anesthesiology. 94 (5): 862–869. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200105000-00026. ISSN 0003-3022. PMID 11388539. S2CID 9604584.
Mean airway pressure typically refers to the mean pressure applied during positive-pressure mechanical ventilation. Mean airway pressure correlates with alveolar ventilation, arterial oxygenation, [1] hemodynamic performance, and barotrauma. [2] It can also match the alveolar pressure if there is no difference between inspiratory and expiratory resistance. [3]
Equations
There are several equations aimed at determining the real mean airway pressure.
Volume control ventilation
In ventilation with a square flow waveform this equation can be used:
where:
- = mean airway pressure
- = peak inspiratory pressure
- = peak end expiratory pressure
- = inspiratory time
- = cycle time
Pressure control ventilation
During pressure control ventilation this variant of the equation can be used:
where:
- = mean airway pressure
- = peak inspiratory pressure
- = peak end expiratory pressure
- = inspiratory time
- = cycle time [3]
Airway pressure release ventilation

In airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) a variation of the previous equation must be used for the variables:
- where:
- = mean airway pressure
- = peak inspiratory pressure (PIP)
- = peak end expiratory pressure
- = time spent at
- = time spent at [4]
Other equations
Clinical significance
Mean airway pressure has been shown to have a similar correlation as plateau pressure to mortality. [6]
MAP is closely associated with mean alveolar pressure and shows the stresses exerted on the lung parenchyma on mechanical ventilation. [7]
In high frequency oscillatory ventilation, it has been suggested to set the mean airway pressure six above the lower inflection point on the lungs P-V curve. [8]
See also
References
- ^ Stewart AR, Finer NN, Peters KL (1981). "Effects of alterations of inspiratory and expiratory pressures and inspiratory/expiratory ratios on mean airway pressure, blood gases, and intracranial pressure". Pediatrics. 67 (4): 474–81. doi: 10.1542/peds.67.4.474. PMID 6789294. S2CID 2214900.
- ^ Marini JJ, Ravenscraft SA (1992). "Mean airway pressure: physiologic determinants and clinical importance--Part 2: Clinical implications". Crit Care Med. 20 (11): 1604–16. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199211000-00020. PMID 1424706. S2CID 42496727.
- ^ a b Hess, Dean (October 21, 2014). "Respiratory Mechanics in Mechanically Ventilated Patients" (PDF). Respiratory Care. 59 (11): 1773–1794. doi: 10.4187/respcare.03410. PMID 25336536. S2CID 5706765.
- ^ Daoud, Ehab G. (2007). "Airway pressure release ventilation". Annals of Thoracic Medicine. 2 (4): 176–179. doi: 10.4103/1817-1737.36556. ISSN 1817-1737. PMC 2732103. PMID 19727373.
- ^ David W. Chang (1999). Respiratory care calculations. Cengage Learning. pp. 251–. ISBN 978-0-7668-0517-0. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ^ Sahetya, Sarina; Wu, David; Brooks, Morgan (May 2020). "Mean Airway Pressure As a Predictor of 90-Day Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Patients". Critical Care Medicine. 48 (5): 688–695. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004268. PMC 8273919. PMID 32079893.
- ^ Su, Longxiang; Pan, Pan; Liu, Dawei; Long, Yun (2021-10-01). "Mean airway pressure has the potential to become the core pressure indicator of mechanical ventilation: Raising to the front from behind the clinical scenes". Journal of Intensive Medicine. 1 (2): 96–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jointm.2021.04.002. ISSN 2667-100X. PMC 9923962. PMID 36788801. S2CID 236575021.
- ^ Goddon, Sven; Fujino, Yuji; Hromi, Jonathan M.; Kacmarek, Robert M. (May 2001). "Optimal Mean Airway Pressure during High-frequency Oscillation: Predicted by the Pressure–Volume Curve". Anesthesiology. 94 (5): 862–869. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200105000-00026. ISSN 0003-3022. PMID 11388539. S2CID 9604584.














}{60}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c386d4e8bc294a8206393853507d118b5ef8f1c9)
