| Macronovirus | |
|---|---|
| |
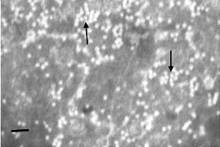
| Transmission electron micrographs of negatively-stained extra small virus species Macrobrachium satellite virus 1; bar = 50 nm | |
|
Virus classification
| |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Family: | Sarthroviridae |
| Genus: | Macronovirus |
| Species | |
| |
Macronovirus is the only genus of the family Sarthroviridae and only contains the species Macrobrachium satellite virus 1 [1]
It is found in The French West Indies, Thailand, Taiwan, China, and India. [2]
Etymology
The genus name, Macronovirus, is a combination of Macro, from type species host Macrobrachium rosenbergii and no, from helper virus nodavirus. [2]
The family name, Sarthroviridae, is a combination of S, from Small and arthro, from host arthropoda. [3]
Hosts
Macronovirus's cell tropism is muscle and connective cells of diseased animals, and its natural hosts are arthropods [3]
Structure
The virion Macrobrachium satellite virus 1 has a genome consisting of linear single-stranded RNA of positive polarity, 0.8kb in size, with two genes. This encodes two capsid proteins, CP-17 and CP-16. The virion is non-enveloped, spherical, with a capsid of about 15 nm with icosahedral symmetry. The virion is constructed from two capsid proteins CP-17 and CP-16. It has a Monopartite, linear, ssRNA(+) genome. [2]
Gene expression
The virion RNA is infectious and serves as both the genome and viral messenger RNA. [2]
Replication
Its replication is cytoplasmic, and has 8 steps. [2]
- Attachement to host receptors mediates entry into the host cell.
- Uncoating, and release of the viral genomic RNA into the cytoplasm.
- Viral RNA is translated in a polyprotein to produce replication proteins.
- Replication by helper virus occurs in viral factories made of membrane vesicles derived from the ER. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+).
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- Expression of the capsid proteins.
- Assembly of new virus particles.
- Virus release.
Disease
Whitish muscle disease, which develops in post-larvae of freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii and is caused by Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and its associate Macrobrachium satellite virus 1. Main symptom is a whitish appearance of the muscles, particularly noticeable in the abdomen. Mortalities can reach 100%. [2]
References
- ^ "Virus Taxonomy: 2022 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^
a
b
c
d
e
f
"Macronovirus ~ ViralZone report". ViralZone. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the
CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the
CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^
a
b
"Sarthroviridae ~ ViralZone report". ViralZone. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the
CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the
CC BY 4.0 license.
| Macronovirus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Transmission electron micrographs of negatively-stained extra small virus species Macrobrachium satellite virus 1; bar = 50 nm | |
|
Virus classification
| |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Family: | Sarthroviridae |
| Genus: | Macronovirus |
| Species | |
| |
Macronovirus is the only genus of the family Sarthroviridae and only contains the species Macrobrachium satellite virus 1 [1]
It is found in The French West Indies, Thailand, Taiwan, China, and India. [2]
Etymology
The genus name, Macronovirus, is a combination of Macro, from type species host Macrobrachium rosenbergii and no, from helper virus nodavirus. [2]
The family name, Sarthroviridae, is a combination of S, from Small and arthro, from host arthropoda. [3]
Hosts
Macronovirus's cell tropism is muscle and connective cells of diseased animals, and its natural hosts are arthropods [3]
Structure
The virion Macrobrachium satellite virus 1 has a genome consisting of linear single-stranded RNA of positive polarity, 0.8kb in size, with two genes. This encodes two capsid proteins, CP-17 and CP-16. The virion is non-enveloped, spherical, with a capsid of about 15 nm with icosahedral symmetry. The virion is constructed from two capsid proteins CP-17 and CP-16. It has a Monopartite, linear, ssRNA(+) genome. [2]
Gene expression
The virion RNA is infectious and serves as both the genome and viral messenger RNA. [2]
Replication
Its replication is cytoplasmic, and has 8 steps. [2]
- Attachement to host receptors mediates entry into the host cell.
- Uncoating, and release of the viral genomic RNA into the cytoplasm.
- Viral RNA is translated in a polyprotein to produce replication proteins.
- Replication by helper virus occurs in viral factories made of membrane vesicles derived from the ER. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+).
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- Expression of the capsid proteins.
- Assembly of new virus particles.
- Virus release.
Disease
Whitish muscle disease, which develops in post-larvae of freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii and is caused by Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and its associate Macrobrachium satellite virus 1. Main symptom is a whitish appearance of the muscles, particularly noticeable in the abdomen. Mortalities can reach 100%. [2]
References
- ^ "Virus Taxonomy: 2022 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^
a
b
c
d
e
f
"Macronovirus ~ ViralZone report". ViralZone. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the
CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the
CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^
a
b
"Sarthroviridae ~ ViralZone report". ViralZone. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the
CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the
CC BY 4.0 license.