| LBSh | |
|---|---|
| |
| Role | Light attack aircraft |
| National origin | |
| Designer | Sergei Aleksandrovich Kochyerigin |
| Status | prototype only |
| Number built | 2 |
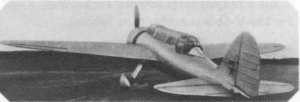
LBSh ( Russian: ЛБШ, initially known simply as Ш, short for shturmovik) was a light ground attack aircraft (shturmovik) designed in 1939 by Sergei Aleksandrovich Kochyerigin. [1]
A low-wing monoplane of mixed construction with fixed undercarriage, the design proved underpowered although decently armed. [1] Offensive armament included two ShVAK 20 mm autocannons in the wing roots, two ShKAS machine guns in the wings and up to 600 kg of bombload. [1] Defensive armament consisted of one turret-mounted ShKAS machine gun firing rearwards. [1]
Only two prototypes were ever built: Sh-1 powered by Tumansky M-88 air-cooled radial engine and Sh-2 powered by earlier Tumansky M-87A. [1] Initially the Sh-1 was accepted by the Soviet aviation into serial production, but the decision was soon overturned and the Factory No. 292 was ordered to focus on Yatsenko I-28 and Yakovlev Yak-1 fighters instead. [1]
General characteristics Performance
- Dale Volkov (ed.). Ш (ЛБШ) [Sh (LBSh)]. Ugolok neba (in Russian). Retrieved 2013-07-20.
| LBSh | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | Light attack aircraft |
| National origin | |
| Designer | Sergei Aleksandrovich Kochyerigin |
| Status | prototype only |
| Number built | 2 |
LBSh ( Russian: ЛБШ, initially known simply as Ш, short for shturmovik) was a light ground attack aircraft (shturmovik) designed in 1939 by Sergei Aleksandrovich Kochyerigin. [1]
A low-wing monoplane of mixed construction with fixed undercarriage, the design proved underpowered although decently armed. [1] Offensive armament included two ShVAK 20 mm autocannons in the wing roots, two ShKAS machine guns in the wings and up to 600 kg of bombload. [1] Defensive armament consisted of one turret-mounted ShKAS machine gun firing rearwards. [1]
Only two prototypes were ever built: Sh-1 powered by Tumansky M-88 air-cooled radial engine and Sh-2 powered by earlier Tumansky M-87A. [1] Initially the Sh-1 was accepted by the Soviet aviation into serial production, but the decision was soon overturned and the Factory No. 292 was ordered to focus on Yatsenko I-28 and Yakovlev Yak-1 fighters instead. [1]
General characteristics Performance
- Dale Volkov (ed.). Ш (ЛБШ) [Sh (LBSh)]. Ugolok neba (in Russian). Retrieved 2013-07-20.