| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 ( ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Triangulum Australe |
| Right ascension | 15h 55m 29.59831s [1] |
| Declination | −68° 36′ 10.8101″ [1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +5.08 [2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | G3/5 Ib [3] |
| B−V color index | +1.12 [2] |
| Variable type | suspected SRD [4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +3.9±0.3 [5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) |
RA: −9.36
[1]
mas/
yr Dec.: −6.79 [1] mas/ yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.70 ± 0.26 mas [1] |
| Distance | 1,200 ± 100
ly (370 ± 40 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −2.71 [6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 7.0 [7] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,761 [8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.90 [9] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,658 [10] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.21 [9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 7.7±1.0 [10] km/s |
| Age | 55.2 [7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
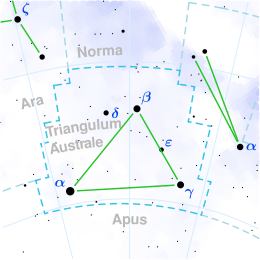
Kappa Trianguli Australis (κ Trianguli Australis) is a star in the constellation Triangulum Australe.
Kappa Trianguli Australis is a yellow G-type supergiant with an apparent magnitude of +5.08. It is around 1,200 light years from Earth.

It is not generally listed as a variable star but Hipparcos photometry showed small amplitude brightness changes. The dominant period was around 600 days and the amplitude less than a hundredth of a magnitude. [13]
References
- ^ a b c d e van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv: 0708.1752, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b Cousins, A. W. J. (1977), "UCBV Magnitudes and Colours of South Circumpolar Stars", South African Astronomical Observatory Circulars, 1: 51, Bibcode: 1977SAAOC...1...51C.
- ^ Houk, N.; Cowley, A. P. (1975), "University of Michigan Catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars", University of Michigan Catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars. Volume I. Declinations -90_ to -53_ƒ0, 1, Bibcode: 1975mcts.book.....H.
- ^ "Kap TrA". The International Variable Star Index. AAVSO – American Association of Variable Star Observers. Retrieved 18 September 2018.
- ^ de Bruijne, J. H. J.; Eilers, A.-C. (October 2012), "Radial velocities for the HIPPARCOS-Gaia Hundred-Thousand-Proper-Motion project", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 546: 14, arXiv: 1208.3048, Bibcode: 2012A&A...546A..61D, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201219219, S2CID 59451347, A61.
- ^ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv: 1108.4971, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A, doi: 10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- ^ a b Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (2011). "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 410 (1): 190–200. arXiv: 1007.4883. Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.410..190T. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x. S2CID 118629873.
- ^ McDonald, I.; et al. (2012), "Fundamental Parameters and Infrared Excesses of Hipparcos Stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 427 (1): 343–57, arXiv: 1208.2037, Bibcode: 2012MNRAS.427..343M, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x, S2CID 118665352.
- ^ a b Soubiran, Caroline; Le Campion, Jean-François; Brouillet, Nathalie; Chemin, Laurent (2016). "The PASTEL catalogue: 2016 version". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 591: A118. arXiv: 1605.07384. Bibcode: 2016A&A...591A.118S. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201628497. S2CID 119258214.
- ^ a b Ammler-von Eiff, Matthias; Reiners, Ansgar (June 2012), "New measurements of rotation and differential rotation in A-F stars: are there two populations of differentially rotating stars?", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 542: A116, arXiv: 1204.2459, Bibcode: 2012A&A...542A.116A, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201118724, S2CID 53666672.
-
^
"kap TrA".
SIMBAD.
Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2017-06-29.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript ( link) - ^ "/ftp/cats/more/HIP/cdroms/cats". Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Strasbourg astronomical Data Center. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
- ^ Koen, Chris; Eyer, Laurent (2002). "New periodic variables from the Hipparcos epoch photometry". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 331 (1): 45–59. arXiv: astro-ph/0112194. Bibcode: 2002MNRAS.331...45K. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-8711.2002.05150.x. S2CID 10505995.
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 ( ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Triangulum Australe |
| Right ascension | 15h 55m 29.59831s [1] |
| Declination | −68° 36′ 10.8101″ [1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +5.08 [2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | G3/5 Ib [3] |
| B−V color index | +1.12 [2] |
| Variable type | suspected SRD [4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +3.9±0.3 [5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) |
RA: −9.36
[1]
mas/
yr Dec.: −6.79 [1] mas/ yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.70 ± 0.26 mas [1] |
| Distance | 1,200 ± 100
ly (370 ± 40 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −2.71 [6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 7.0 [7] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,761 [8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.90 [9] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,658 [10] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.21 [9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 7.7±1.0 [10] km/s |
| Age | 55.2 [7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Kappa Trianguli Australis (κ Trianguli Australis) is a star in the constellation Triangulum Australe.
Kappa Trianguli Australis is a yellow G-type supergiant with an apparent magnitude of +5.08. It is around 1,200 light years from Earth.

It is not generally listed as a variable star but Hipparcos photometry showed small amplitude brightness changes. The dominant period was around 600 days and the amplitude less than a hundredth of a magnitude. [13]
References
- ^ a b c d e van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv: 0708.1752, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b Cousins, A. W. J. (1977), "UCBV Magnitudes and Colours of South Circumpolar Stars", South African Astronomical Observatory Circulars, 1: 51, Bibcode: 1977SAAOC...1...51C.
- ^ Houk, N.; Cowley, A. P. (1975), "University of Michigan Catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars", University of Michigan Catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars. Volume I. Declinations -90_ to -53_ƒ0, 1, Bibcode: 1975mcts.book.....H.
- ^ "Kap TrA". The International Variable Star Index. AAVSO – American Association of Variable Star Observers. Retrieved 18 September 2018.
- ^ de Bruijne, J. H. J.; Eilers, A.-C. (October 2012), "Radial velocities for the HIPPARCOS-Gaia Hundred-Thousand-Proper-Motion project", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 546: 14, arXiv: 1208.3048, Bibcode: 2012A&A...546A..61D, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201219219, S2CID 59451347, A61.
- ^ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv: 1108.4971, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A, doi: 10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- ^ a b Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (2011). "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 410 (1): 190–200. arXiv: 1007.4883. Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.410..190T. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x. S2CID 118629873.
- ^ McDonald, I.; et al. (2012), "Fundamental Parameters and Infrared Excesses of Hipparcos Stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 427 (1): 343–57, arXiv: 1208.2037, Bibcode: 2012MNRAS.427..343M, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x, S2CID 118665352.
- ^ a b Soubiran, Caroline; Le Campion, Jean-François; Brouillet, Nathalie; Chemin, Laurent (2016). "The PASTEL catalogue: 2016 version". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 591: A118. arXiv: 1605.07384. Bibcode: 2016A&A...591A.118S. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201628497. S2CID 119258214.
- ^ a b Ammler-von Eiff, Matthias; Reiners, Ansgar (June 2012), "New measurements of rotation and differential rotation in A-F stars: are there two populations of differentially rotating stars?", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 542: A116, arXiv: 1204.2459, Bibcode: 2012A&A...542A.116A, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201118724, S2CID 53666672.
-
^
"kap TrA".
SIMBAD.
Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2017-06-29.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript ( link) - ^ "/ftp/cats/more/HIP/cdroms/cats". Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Strasbourg astronomical Data Center. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
- ^ Koen, Chris; Eyer, Laurent (2002). "New periodic variables from the Hipparcos epoch photometry". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 331 (1): 45–59. arXiv: astro-ph/0112194. Bibcode: 2002MNRAS.331...45K. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-8711.2002.05150.x. S2CID 10505995.