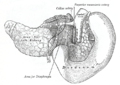
| Inferior mesenteric vein | |
|---|---|
 The
portal vein and its tributaries. The
superior mesenteric vein and
splenic vein, into which the inferior mesenteric vein empties. Leinal vein is an old term for splenic vein.
Anatomical position. | |
 Superior and inferior duodenal fossæ. | |
| Details | |
| System | Hepatic portal system |
| Drains from | Gastrointestinal tract |
| Source | Left colic vein, Sigmoid veins, Superior rectal vein, |
| Drains to | splenic vein |
| Artery | inferior mesenteric artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena mesenterica inferior |
| TA98 | A12.3.12.032 |
| TA2 | 5127 |
| FMA | 15391 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric vein (IMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the large intestine. It usually terminates when reaching the splenic vein, which goes on to form the portal vein with the superior mesenteric vein (SMV).
Structure
The inferior mesenteric vein merges with the splenic vein, posterior to the middle of the body of the pancreas. [1] The splenic vein then merges with the superior mesenteric vein to form the portal vein. [1]
Tributaries
Tributaries of the inferior mesenteric vein drain the large intestine, sigmoid colon and rectum. These include:
- left colic vein
- sigmoid veins
- superior rectal vein
- rectosigmoid veins
Variation
Anatomical variations include the inferior mesenteric vein draining into the confluence of the superior mesenteric vein and splenic vein and the inferior mesenteric vein draining in the superior mesenteric vein.
Clinical significance
The inferior mesenteric vein may be damaged during surgery on the body and tail of the pancreas. [2] If a serious laceration occurs, the inferior mesenteric vein may be ligated, as other veins can drain the large intestine. [2]
Additional images
-
The pancreas and duodenum from behind.
References
- ^ a b Pirog, T. P. (December 2019). "POST-HARVEST TREATMENT OF VEGETABLES WITH EXOMETABOLITES OF Nocardia vaccinii IMV B-7405, Аcinetobacter calcoaceticus IMV В-7241 AND Rhodococcus erythropolis IMV Ас-5017 TO EXTEND THEIR SHELF LIFE". Biotechnologia Acta. 12 (6): 46–55. doi: 10.15407/biotech12.06.046. ISSN 2410-7751.
- ^ a b Dhanireddy, Kiran K.; Fishbein, Thomas M. (2009-01-01), Evans, Stephen R. T. (ed.), "Chapter 36 - Distal Pancreatectomy", Surgical Pitfalls, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 375–378, doi: 10.1016/b978-141602951-9.50046-3, ISBN 978-1-4160-2951-9, retrieved 2021-02-06
External links
- "Mesenteric vein inferior". Medcyclopaedia. GE. Archived from the original on 2011-05-26.
- Anatomy photo:39:06-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Intestines and Pancreas: Tributaries of Inferior Mesenteric Vein"
- Anatomy image:8568 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:8694 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
| Inferior mesenteric vein | |
|---|---|
 The
portal vein and its tributaries. The
superior mesenteric vein and
splenic vein, into which the inferior mesenteric vein empties. Leinal vein is an old term for splenic vein.
Anatomical position. | |
 Superior and inferior duodenal fossæ. | |
| Details | |
| System | Hepatic portal system |
| Drains from | Gastrointestinal tract |
| Source | Left colic vein, Sigmoid veins, Superior rectal vein, |
| Drains to | splenic vein |
| Artery | inferior mesenteric artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena mesenterica inferior |
| TA98 | A12.3.12.032 |
| TA2 | 5127 |
| FMA | 15391 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric vein (IMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the large intestine. It usually terminates when reaching the splenic vein, which goes on to form the portal vein with the superior mesenteric vein (SMV).
Structure
The inferior mesenteric vein merges with the splenic vein, posterior to the middle of the body of the pancreas. [1] The splenic vein then merges with the superior mesenteric vein to form the portal vein. [1]
Tributaries
Tributaries of the inferior mesenteric vein drain the large intestine, sigmoid colon and rectum. These include:
- left colic vein
- sigmoid veins
- superior rectal vein
- rectosigmoid veins
Variation
Anatomical variations include the inferior mesenteric vein draining into the confluence of the superior mesenteric vein and splenic vein and the inferior mesenteric vein draining in the superior mesenteric vein.
Clinical significance
The inferior mesenteric vein may be damaged during surgery on the body and tail of the pancreas. [2] If a serious laceration occurs, the inferior mesenteric vein may be ligated, as other veins can drain the large intestine. [2]
Additional images
-
The pancreas and duodenum from behind.
References
- ^ a b Pirog, T. P. (December 2019). "POST-HARVEST TREATMENT OF VEGETABLES WITH EXOMETABOLITES OF Nocardia vaccinii IMV B-7405, Аcinetobacter calcoaceticus IMV В-7241 AND Rhodococcus erythropolis IMV Ас-5017 TO EXTEND THEIR SHELF LIFE". Biotechnologia Acta. 12 (6): 46–55. doi: 10.15407/biotech12.06.046. ISSN 2410-7751.
- ^ a b Dhanireddy, Kiran K.; Fishbein, Thomas M. (2009-01-01), Evans, Stephen R. T. (ed.), "Chapter 36 - Distal Pancreatectomy", Surgical Pitfalls, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 375–378, doi: 10.1016/b978-141602951-9.50046-3, ISBN 978-1-4160-2951-9, retrieved 2021-02-06
External links
- "Mesenteric vein inferior". Medcyclopaedia. GE. Archived from the original on 2011-05-26.
- Anatomy photo:39:06-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Intestines and Pancreas: Tributaries of Inferior Mesenteric Vein"
- Anatomy image:8568 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:8694 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center