| Hebesphenomegacorona | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type |
Johnson J88 – J89 – J90 |
| Faces | 3x2+3x4
triangles 1+2 squares |
| Edges | 33 |
| Vertices | 14 |
| Vertex configuration | 4(32.42) 2+2x2(35) 4(34.4) |
| Symmetry group | C2v |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
 | |

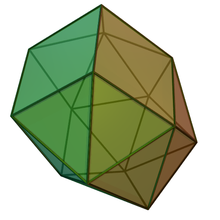
In geometry, the hebesphenomegacorona is a Johnson solid with 18 equilateral triangles and 3 squares as its faces.
Properties
The hebesphenomegacorona is named by Johnson (1966) in which he used the prefix hebespheno- referring to a blunt wedge-like complex formed by three adjacent lunes—a square with equilateral triangles attached on its opposite sides. The suffix -megacorona refers to a crownlike complex of 12 triangles. [1] By joining both complexes together, the result polyhedron has 18 equilateral triangles and 3 squares, making 21 faces. [2]. All of its faces are regular polygons, categorizing the hebesphenomegacorona as a Johnson solid—a convex polyhedron in which all of its faces are regular polygons—enumerated as 89th Johnson solid . [3] It is elementary, meaning it cannot be separated by a plane into two small regular-faced polyhedra. [4]
The surface area of a hebesphenomegacorona with edge length can be determined by adding the area of its faces, 18 equilateral triangles and 3 squares and its volume is . [2]
Cartesian coordinates
Let be the second smallest positive root of the polynomial Then, Cartesian coordinates of a hebesphenomegacorona with edge length 2 are given by the union of the orbits of the points under the action of the group generated by reflections about the xz-plane and the yz-plane. [5]
References
- ^ Johnson, N. W. (1966). "Convex polyhedra with regular faces". Canadian Journal of Mathematics. 18: 169–200. doi: 10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8. MR 0185507. S2CID 122006114. Zbl 0132.14603.
- ^ a b Berman, M. (1971). "Regular-faced convex polyhedra". Journal of the Franklin Institute. 291 (5): 329–352. doi: 10.1016/0016-0032(71)90071-8. MR 0290245.
- ^ Francis, D. (August 2013). "Johnson solids & their acronyms". Word Ways. 46 (3): 177.
- ^ Cromwell, P. R. (1997). Polyhedra. Cambridge University Press. p. 86–87, 89. ISBN 978-0-521-66405-9.
- ^ Timofeenko, A. V. (2009). "The non-Platonic and non-Archimedean noncomposite polyhedra". Journal of Mathematical Science. 162 (5): 717. doi: 10.1007/s10958-009-9655-0. S2CID 120114341.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., " Hebesphenomegacorona" (" Johnson solid") at MathWorld.
| Hebesphenomegacorona | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type |
Johnson J88 – J89 – J90 |
| Faces | 3x2+3x4
triangles 1+2 squares |
| Edges | 33 |
| Vertices | 14 |
| Vertex configuration | 4(32.42) 2+2x2(35) 4(34.4) |
| Symmetry group | C2v |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
 | |

In geometry, the hebesphenomegacorona is a Johnson solid with 18 equilateral triangles and 3 squares as its faces.
Properties
The hebesphenomegacorona is named by Johnson (1966) in which he used the prefix hebespheno- referring to a blunt wedge-like complex formed by three adjacent lunes—a square with equilateral triangles attached on its opposite sides. The suffix -megacorona refers to a crownlike complex of 12 triangles. [1] By joining both complexes together, the result polyhedron has 18 equilateral triangles and 3 squares, making 21 faces. [2]. All of its faces are regular polygons, categorizing the hebesphenomegacorona as a Johnson solid—a convex polyhedron in which all of its faces are regular polygons—enumerated as 89th Johnson solid . [3] It is elementary, meaning it cannot be separated by a plane into two small regular-faced polyhedra. [4]
The surface area of a hebesphenomegacorona with edge length can be determined by adding the area of its faces, 18 equilateral triangles and 3 squares and its volume is . [2]
Cartesian coordinates
Let be the second smallest positive root of the polynomial Then, Cartesian coordinates of a hebesphenomegacorona with edge length 2 are given by the union of the orbits of the points under the action of the group generated by reflections about the xz-plane and the yz-plane. [5]
References
- ^ Johnson, N. W. (1966). "Convex polyhedra with regular faces". Canadian Journal of Mathematics. 18: 169–200. doi: 10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8. MR 0185507. S2CID 122006114. Zbl 0132.14603.
- ^ a b Berman, M. (1971). "Regular-faced convex polyhedra". Journal of the Franklin Institute. 291 (5): 329–352. doi: 10.1016/0016-0032(71)90071-8. MR 0290245.
- ^ Francis, D. (August 2013). "Johnson solids & their acronyms". Word Ways. 46 (3): 177.
- ^ Cromwell, P. R. (1997). Polyhedra. Cambridge University Press. p. 86–87, 89. ISBN 978-0-521-66405-9.
- ^ Timofeenko, A. V. (2009). "The non-Platonic and non-Archimedean noncomposite polyhedra". Journal of Mathematical Science. 162 (5): 717. doi: 10.1007/s10958-009-9655-0. S2CID 120114341.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., " Hebesphenomegacorona" (" Johnson solid") at MathWorld.






