| Hanseniaspora | |
|---|---|
| |
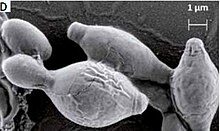
| Hanseniaspora uvarum | |
|
Scientific classification
| |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Saccharomycetes |
| Order: | Saccharomycetales |
| Family: | Saccharomycodaceae |
| Genus: |
Hanseniaspora Zikes ex Klöcker (1912) |
| Type species | |
|
Hanseniaspora valbyensis Klöcker (1912)
| |
| Species [1] | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms [2] | |
|
List
| |
Hanseniaspora is a genus of yeasts. [3] The name Kloeckera is applied to its anamorph form. They are typically apiculate (lemon-shaped) in shape and often found in grape musts pre-fermentation.
The genus name Hanseniaspora honours Emil Christian Hansen (1842–1909), who was a Danish mycologist and fermentation physiologist. [4] It was initially circumscribed by H. Zikes in 1911, but not validly published. [5] Albert Klöcker published the name validly the following year. [6]
The genus is notable for its loss of many highly conserved genes responsible for cell cycle regulation and genome integrity, resulting in increased evolution rates and genome size reduction. It can be divided into two lineages: a faster-evolving lineage (FEL) diversifying about 87 mya, and a slower one diversifying about 52 mya. The FEL has more of such gene losses, resulting in more dramatic changes in the genome and inactivation of multiple metabolic pathways. However, it has managed to diversity and thrive, showing that life can function without such regulation. [7]
Species
- Hanseniaspora clermontiae Čadež et al. (2003)
- Hanseniaspora gamundiae Libkind, Čadež & Hittinger (2019) [8]
- Hanseniaspora guilliermondii Pijper (1928)
- Hanseniaspora lachancei Čadež et al. (2003)
- Hanseniaspora lindneri (Klöcker) Čadež & Libkind (2019) [9]
- Hanseniaspora meyeri Čadež et al. (2003)
- Hanseniaspora mollemarum M. Groenew., G. Péter, S.A. James, Dlauchy & M.T. Sm. (2018) [10]
- Hanseniaspora nectarophila Čadež, Pagnocca, Raspor & C.A. Rosa (2014) [11]
- Hanseniaspora occidentalis M.T.Smith (1974)
- Hanseniaspora opuntiae Čadež et al. (2003)
- Hanseniaspora osmophila (Niehaus) Phaff et al. (1956)
- Hanseniaspora pseudoguilliermondii Čadež et al. (2006)
- Hanseniaspora smithiae Libkind, Čadež & Hittinger (2021) [12]
- Hanseniaspora uvarum (Niehaus) Shehata et al. (1984)
- Hanseniaspora valbyensis Klöcker (1912)
- Hanseniaspora vineae van der Walt & Tscheuschner (1957)
See also
References
- ^ Kurtzman, Cletus P.; Fell, Jack W.; Boekhout, Teun, eds. (2011). The Yeasts: A Taxonomic Study. Vol. 1 (5th ed.). Elsevier. p. 595.
- ^ "Synonymy. Current Name: Hanseniaspora Zikes ex Klöcker, Centbl. Bakt. ParasitKde, Abt. II 35: 385 (1912)". Species Fungorum. Retrieved 22 November 2022.
- ^ "Hanseniaspora Zikes, 1911". www.gbif.org. Retrieved 26 March 2022.
- ^ Burkhardt, Lotte (2022). Eine Enzyklopädie zu eponymischen Pflanzennamen [Encyclopedia of eponymic plant names] (pdf) (in German). Berlin: Botanic Garden and Botanical Museum, Freie Universität Berlin. doi: 10.3372/epolist2022. ISBN 978-3-946292-41-8. S2CID 246307410. Retrieved January 27, 2022.
- ^ "Record Details: Hanseniaspora Zikes, Centbl. Bakt. ParasitKde, Abt. II 30: 148 (1911)". Index Fungorum. Retrieved 22 November 2022.
- ^ Klöcker, A. (1912). "Beschreibungen von 17 "Saccharomyces apiculatus"-Formen". Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie und Parasitenkunde, Abteilung 2. (in German). 35: 375–388.
- ^ Steenwyk, Jacob L.; Opulente, Dana A.; Kominek, Jacek; Shen, Xing-Xing; Zhou, Xiaofan; Labella, Abigail L.; Bradley, Noah P.; Eichman, Brandt F.; Čadež, Neža; Libkind, Diego; DeVirgilio, Jeremy; Hulfachor, Amanda Beth; Kurtzman, Cletus P.; Hittinger, Chris Todd; Rokas, Antonis (21 May 2019). "Extensive loss of cell-cycle and DNA repair genes in an ancient lineage of bipolar budding yeasts". PLOS Biology. 17 (5): e3000255. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000255. PMC 6528967. PMID 31112549. S2CID 162169621.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora gamundiae Libkind, Čadež & Hittinger". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora lindneri (Klöcker) Čadež & Libkind". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora mollemarum M. Groenew., G. Péter, S.A. James, Dlauchy & M.T. Sm". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora nectarophila Čadež, Pagnocca, Raspor & C.A. Rosa". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora smithiae Libkind, Čadež & Hittinger". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
| Hanseniaspora | |
|---|---|

| |
| Hanseniaspora uvarum | |
|
Scientific classification
| |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Saccharomycetes |
| Order: | Saccharomycetales |
| Family: | Saccharomycodaceae |
| Genus: |
Hanseniaspora Zikes ex Klöcker (1912) |
| Type species | |
|
Hanseniaspora valbyensis Klöcker (1912)
| |
| Species [1] | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms [2] | |
|
List
| |
Hanseniaspora is a genus of yeasts. [3] The name Kloeckera is applied to its anamorph form. They are typically apiculate (lemon-shaped) in shape and often found in grape musts pre-fermentation.
The genus name Hanseniaspora honours Emil Christian Hansen (1842–1909), who was a Danish mycologist and fermentation physiologist. [4] It was initially circumscribed by H. Zikes in 1911, but not validly published. [5] Albert Klöcker published the name validly the following year. [6]
The genus is notable for its loss of many highly conserved genes responsible for cell cycle regulation and genome integrity, resulting in increased evolution rates and genome size reduction. It can be divided into two lineages: a faster-evolving lineage (FEL) diversifying about 87 mya, and a slower one diversifying about 52 mya. The FEL has more of such gene losses, resulting in more dramatic changes in the genome and inactivation of multiple metabolic pathways. However, it has managed to diversity and thrive, showing that life can function without such regulation. [7]
Species
- Hanseniaspora clermontiae Čadež et al. (2003)
- Hanseniaspora gamundiae Libkind, Čadež & Hittinger (2019) [8]
- Hanseniaspora guilliermondii Pijper (1928)
- Hanseniaspora lachancei Čadež et al. (2003)
- Hanseniaspora lindneri (Klöcker) Čadež & Libkind (2019) [9]
- Hanseniaspora meyeri Čadež et al. (2003)
- Hanseniaspora mollemarum M. Groenew., G. Péter, S.A. James, Dlauchy & M.T. Sm. (2018) [10]
- Hanseniaspora nectarophila Čadež, Pagnocca, Raspor & C.A. Rosa (2014) [11]
- Hanseniaspora occidentalis M.T.Smith (1974)
- Hanseniaspora opuntiae Čadež et al. (2003)
- Hanseniaspora osmophila (Niehaus) Phaff et al. (1956)
- Hanseniaspora pseudoguilliermondii Čadež et al. (2006)
- Hanseniaspora smithiae Libkind, Čadež & Hittinger (2021) [12]
- Hanseniaspora uvarum (Niehaus) Shehata et al. (1984)
- Hanseniaspora valbyensis Klöcker (1912)
- Hanseniaspora vineae van der Walt & Tscheuschner (1957)
See also
References
- ^ Kurtzman, Cletus P.; Fell, Jack W.; Boekhout, Teun, eds. (2011). The Yeasts: A Taxonomic Study. Vol. 1 (5th ed.). Elsevier. p. 595.
- ^ "Synonymy. Current Name: Hanseniaspora Zikes ex Klöcker, Centbl. Bakt. ParasitKde, Abt. II 35: 385 (1912)". Species Fungorum. Retrieved 22 November 2022.
- ^ "Hanseniaspora Zikes, 1911". www.gbif.org. Retrieved 26 March 2022.
- ^ Burkhardt, Lotte (2022). Eine Enzyklopädie zu eponymischen Pflanzennamen [Encyclopedia of eponymic plant names] (pdf) (in German). Berlin: Botanic Garden and Botanical Museum, Freie Universität Berlin. doi: 10.3372/epolist2022. ISBN 978-3-946292-41-8. S2CID 246307410. Retrieved January 27, 2022.
- ^ "Record Details: Hanseniaspora Zikes, Centbl. Bakt. ParasitKde, Abt. II 30: 148 (1911)". Index Fungorum. Retrieved 22 November 2022.
- ^ Klöcker, A. (1912). "Beschreibungen von 17 "Saccharomyces apiculatus"-Formen". Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie und Parasitenkunde, Abteilung 2. (in German). 35: 375–388.
- ^ Steenwyk, Jacob L.; Opulente, Dana A.; Kominek, Jacek; Shen, Xing-Xing; Zhou, Xiaofan; Labella, Abigail L.; Bradley, Noah P.; Eichman, Brandt F.; Čadež, Neža; Libkind, Diego; DeVirgilio, Jeremy; Hulfachor, Amanda Beth; Kurtzman, Cletus P.; Hittinger, Chris Todd; Rokas, Antonis (21 May 2019). "Extensive loss of cell-cycle and DNA repair genes in an ancient lineage of bipolar budding yeasts". PLOS Biology. 17 (5): e3000255. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000255. PMC 6528967. PMID 31112549. S2CID 162169621.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora gamundiae Libkind, Čadež & Hittinger". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora lindneri (Klöcker) Čadež & Libkind". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora mollemarum M. Groenew., G. Péter, S.A. James, Dlauchy & M.T. Sm". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora nectarophila Čadež, Pagnocca, Raspor & C.A. Rosa". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- ^ Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M.; et al., eds. (Jan 2023). "Hanseniaspora smithiae Libkind, Čadež & Hittinger". Catalogue of Life. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. doi: 10.48580/dfrdl-4hj. Retrieved 19 March 2024., citing Kirk, Paul (2023). "Species Fungorum Plus". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.