| Convention of 13 January 2000 on the International Protection of Adults | |
|---|---|
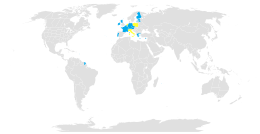 Party
Signatory that did not ratify | |
| Signed | 13 January 2000 |
| Location | The Hague, The Netherlands |
| Effective | 1 January 2009 |
| Condition | Ratification by 3 states [1] |
| Signatories | 19 [2] |
| Parties | 15 [2] |
| Depositary | Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Netherlands) [1] |
| Languages | English and French [1] |
The Hague Protection of Adults Convention, formally the Convention on the International Protection of Adults, is a convention concluded by the Hague Conference on Private International Law in 2000. [1] The convention entered into force in 2009 and currently applies in ten states. [2] The convention is aimed at the protection of vulnerable adults, persons who are "by reason of an impairment or insufficiency of their personal faculties, are not in a position to protect their interests". The convention
- determines which courts have jurisdiction to take protection measures
- determines which law is to be applied in the circumstances; and who may be a vulnerable person
- establishes a system of central authorities which should cooperate, locate vulnerable adults and give information on the status of vulnerable persons to other authorities.
Parties
As of March 2023, the convention applies in fifteen states.
| State | Signature | Ratification/accession | Entry into force | Territorial application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 July 2013 | 9 October 2013 | 1 February 2014 | ||
| 6 February 2017 | 30 September 2020 | 1 January 2021 [3] | ||
| 1 April 2009 | 18 September 2018 | 1 November 2018 | ||
| 1 April 2009 | 18 April 2012 | 1 August 2012 | ||
| 13 December 2010 | 1 March 2011 | |||
| 18 September 2008 | 19 November 2010 | 1 March 2011 | ||
| 13 July 2001 | 18 September 2008 | 1 January 2009 | ||
| 22 December 2003 | 3 April 2007 | 1 January 2009 | ||
| 18 September 2008 | 28 July 2022 | 1 November 2022 | ||
| 18 September 2008 | ||||
| 31 October 2008 | ||||
| 15 December 2016 | 24 November 2017 | 1 March 2018 | ||
| 18 September 2008 | ||||
| 11 November 2022 | 8 March 2023 | 1 July 2023 | ||
| 4 March 2016 | 4 March 2016 | 1 December 2016 | ||
| 13 January 2000 | ||||
| 18 September 2008 | ||||
| 18 September 2008 | 14 March 2018 | 1 July 2018 | ||
| 1 April 2003 | 5 November 2003 | 1 January 2009 | UK ratified on behalf of Scotland | |
| 3 April 2007 | 27 March 2009 | 1 July 2009 |
References
- ^ a b c d "35: Convention of 13 January 2000 on the International Protection of Adults". HCCH. Retrieved 8 February 2017.
- ^ a b c "Convention on the international protection of adults, Treaty data". Treaty Database of the Netherlands. Retrieved 8 February 2017.
- ^ "België erkent Nederlandse levenstestamenten per 1 januari | Koninklijke Notariële Beroepsorganisatie". www.knb.nl. Retrieved 5 January 2021.
- Hague Conference on Private International Law conventions
- Treaties concluded in 2000
- Treaties entered into force in 2009
- Family law treaties
- Vulnerable adults
- Treaties of Austria
- Treaties of Belgium
- Treaties of Cyprus
- Treaties of the Czech Republic
- Treaties of Estonia
- Treaties of Finland
- Treaties of France
- Treaties of Germany
- Treaties of Greece
- Treaties of Latvia
- Treaties of Malta
- Treaties of Monaco
- Treaties of Portugal
- Treaties of Switzerland
- Treaties of Scotland
| Convention of 13 January 2000 on the International Protection of Adults | |
|---|---|
 Party
Signatory that did not ratify | |
| Signed | 13 January 2000 |
| Location | The Hague, The Netherlands |
| Effective | 1 January 2009 |
| Condition | Ratification by 3 states [1] |
| Signatories | 19 [2] |
| Parties | 15 [2] |
| Depositary | Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Netherlands) [1] |
| Languages | English and French [1] |
The Hague Protection of Adults Convention, formally the Convention on the International Protection of Adults, is a convention concluded by the Hague Conference on Private International Law in 2000. [1] The convention entered into force in 2009 and currently applies in ten states. [2] The convention is aimed at the protection of vulnerable adults, persons who are "by reason of an impairment or insufficiency of their personal faculties, are not in a position to protect their interests". The convention
- determines which courts have jurisdiction to take protection measures
- determines which law is to be applied in the circumstances; and who may be a vulnerable person
- establishes a system of central authorities which should cooperate, locate vulnerable adults and give information on the status of vulnerable persons to other authorities.
Parties
As of March 2023, the convention applies in fifteen states.
| State | Signature | Ratification/accession | Entry into force | Territorial application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 July 2013 | 9 October 2013 | 1 February 2014 | ||
| 6 February 2017 | 30 September 2020 | 1 January 2021 [3] | ||
| 1 April 2009 | 18 September 2018 | 1 November 2018 | ||
| 1 April 2009 | 18 April 2012 | 1 August 2012 | ||
| 13 December 2010 | 1 March 2011 | |||
| 18 September 2008 | 19 November 2010 | 1 March 2011 | ||
| 13 July 2001 | 18 September 2008 | 1 January 2009 | ||
| 22 December 2003 | 3 April 2007 | 1 January 2009 | ||
| 18 September 2008 | 28 July 2022 | 1 November 2022 | ||
| 18 September 2008 | ||||
| 31 October 2008 | ||||
| 15 December 2016 | 24 November 2017 | 1 March 2018 | ||
| 18 September 2008 | ||||
| 11 November 2022 | 8 March 2023 | 1 July 2023 | ||
| 4 March 2016 | 4 March 2016 | 1 December 2016 | ||
| 13 January 2000 | ||||
| 18 September 2008 | ||||
| 18 September 2008 | 14 March 2018 | 1 July 2018 | ||
| 1 April 2003 | 5 November 2003 | 1 January 2009 | UK ratified on behalf of Scotland | |
| 3 April 2007 | 27 March 2009 | 1 July 2009 |
References
- ^ a b c d "35: Convention of 13 January 2000 on the International Protection of Adults". HCCH. Retrieved 8 February 2017.
- ^ a b c "Convention on the international protection of adults, Treaty data". Treaty Database of the Netherlands. Retrieved 8 February 2017.
- ^ "België erkent Nederlandse levenstestamenten per 1 januari | Koninklijke Notariële Beroepsorganisatie". www.knb.nl. Retrieved 5 January 2021.
- Hague Conference on Private International Law conventions
- Treaties concluded in 2000
- Treaties entered into force in 2009
- Family law treaties
- Vulnerable adults
- Treaties of Austria
- Treaties of Belgium
- Treaties of Cyprus
- Treaties of the Czech Republic
- Treaties of Estonia
- Treaties of Finland
- Treaties of France
- Treaties of Germany
- Treaties of Greece
- Treaties of Latvia
- Treaties of Malta
- Treaties of Monaco
- Treaties of Portugal
- Treaties of Switzerland
- Treaties of Scotland