Dislocation_pileup.png (290 × 281 pixels, file size: 7 KB, MIME type: image/png)
| This is a file from the
Wikimedia Commons. Information from its
description page there is shown below. Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
Summary

|
File:Dislocation pileup.svg is a vector version of this file. It should be used in place of this PNG file when not inferior.
File:Dislocation pileup.png →
File:Dislocation pileup.svg
For more information, see
Help:SVG.
|
| DescriptionDislocation pileup.png |
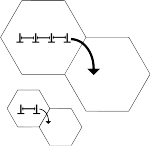
English: This is a schematic roughly illustrating the concept of dislocation pile up and how it affects the strength of the material. A material with larger grain size is able to have more dislocation to pile up leading to a bigger driving force for dislocations to move from one grain to another. Thus you will have to apply less force to move a dislocation from a larger than from a smaller grain, leading materials with smaller grains to exhibit higher yield stress. |
| Source | own work (Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons by Zerodamage using CommonsHelper.) |
| Author | Siamrut at English Wikipedia |
| Other versions | Derivative works of this file: Dislocation pileup.svg |
Licensing

|
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled GNU Free Documentation License.http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue |
| This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. | ||
| Attribution: Siamrut at the English Wikipedia | ||
| ||
| This licensing tag was added to this file as part of the GFDL licensing update.http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/CC BY-SA 3.0Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0truetrue |
Original upload log
- 2007-11-25 22:36 Siamrut 290×281× (7119 bytes) This is a schematic roughly illustrating the concept of dislocation pile up and how it effects the strength of the material. A material with larger grain size is able to have more dislocation to pile up leading to a bigger driving force for dislocations
Captions
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:58, 9 August 2012 |
 | 290 × 281 (7 KB) | File Upload Bot (Magnus Manske) | Transfered from en.wikipedia by User:zerodamage using CommonsHelper |
File usage
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Horizontal resolution | 28.35 dpc |
|---|---|
| Vertical resolution | 28.35 dpc |
| Software used |
Dislocation_pileup.png (290 × 281 pixels, file size: 7 KB, MIME type: image/png)
| This is a file from the
Wikimedia Commons. Information from its
description page there is shown below. Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
Summary

|
File:Dislocation pileup.svg is a vector version of this file. It should be used in place of this PNG file when not inferior.
File:Dislocation pileup.png →
File:Dislocation pileup.svg
For more information, see
Help:SVG.
|
| DescriptionDislocation pileup.png |
English: This is a schematic roughly illustrating the concept of dislocation pile up and how it affects the strength of the material. A material with larger grain size is able to have more dislocation to pile up leading to a bigger driving force for dislocations to move from one grain to another. Thus you will have to apply less force to move a dislocation from a larger than from a smaller grain, leading materials with smaller grains to exhibit higher yield stress. |
| Source | own work (Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons by Zerodamage using CommonsHelper.) |
| Author | Siamrut at English Wikipedia |
| Other versions | Derivative works of this file: Dislocation pileup.svg |
Licensing

|
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled GNU Free Documentation License.http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue |
| This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. | ||
| Attribution: Siamrut at the English Wikipedia | ||
| ||
| This licensing tag was added to this file as part of the GFDL licensing update.http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/CC BY-SA 3.0Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0truetrue |
Original upload log
- 2007-11-25 22:36 Siamrut 290×281× (7119 bytes) This is a schematic roughly illustrating the concept of dislocation pile up and how it effects the strength of the material. A material with larger grain size is able to have more dislocation to pile up leading to a bigger driving force for dislocations
Captions
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:58, 9 August 2012 |
 | 290 × 281 (7 KB) | File Upload Bot (Magnus Manske) | Transfered from en.wikipedia by User:zerodamage using CommonsHelper |
File usage
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Horizontal resolution | 28.35 dpc |
|---|---|
| Vertical resolution | 28.35 dpc |
| Software used |