| Enterobacteria greA leader | |
|---|---|
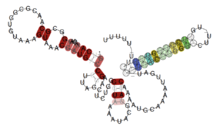 Conserved
secondary structure of greA leader, colours represent the fraction of canonical base pairs | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | greA_leader |
| Rfam | RF01769 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg; leader |
| Domain(s) | Enterobacteriales |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
The Enterobacteria greA leader is a putative attenuator element identified by bioinformatics within bacteria of the γ-proteobacterial Enterobacteriales order. [1] It is located upstream of the rnk gene, encoding a transcription elongation factor, and presents a Rho-independent terminator at the 3' end. This RNA is presumed to operate as a non-coding leader, which regulatory mechanism remains to be elucidated. [1] The short abortive form of the greA transcript may also play a role as an independent sRNA: Potrykus et al. have shown that its overexpression leads to the repression of several genes. [2] The motif might be related to other rnk leaders such as the Pseudomonas rnk leader and the Enterobacteria rnk leader. [1]
- ^ Potrykus K, Murphy H, Chen X, Epstein JA, Cashel M (March 2010). "Imprecise transcription termination within Escherichia coli greA leader gives rise to an array of short transcripts, GraL". Nucleic Acids Research. 38 (5): 1636–1651. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1150. PMC 2836576. PMID 20008510.
| Enterobacteria greA leader | |
|---|---|
 Conserved
secondary structure of greA leader, colours represent the fraction of canonical base pairs | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | greA_leader |
| Rfam | RF01769 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg; leader |
| Domain(s) | Enterobacteriales |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
The Enterobacteria greA leader is a putative attenuator element identified by bioinformatics within bacteria of the γ-proteobacterial Enterobacteriales order. [1] It is located upstream of the rnk gene, encoding a transcription elongation factor, and presents a Rho-independent terminator at the 3' end. This RNA is presumed to operate as a non-coding leader, which regulatory mechanism remains to be elucidated. [1] The short abortive form of the greA transcript may also play a role as an independent sRNA: Potrykus et al. have shown that its overexpression leads to the repression of several genes. [2] The motif might be related to other rnk leaders such as the Pseudomonas rnk leader and the Enterobacteria rnk leader. [1]
- ^ Potrykus K, Murphy H, Chen X, Epstein JA, Cashel M (March 2010). "Imprecise transcription termination within Escherichia coli greA leader gives rise to an array of short transcripts, GraL". Nucleic Acids Research. 38 (5): 1636–1651. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1150. PMC 2836576. PMID 20008510.