| DCPS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DCPS, DCS1, HINT-5, HINT5, HSL1, ARS, HSPC015, decapping enzyme, scavenger | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 610534; MGI: 1916555; HomoloGene: 32202; GeneCards: DCPS; OMA: DCPS - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme (DcpS) N-terminal | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
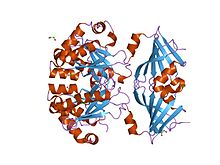 crystal structure of mrna decapping enzyme (dcps) from mus musculus at 1.83 a resolution | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | DcpS | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF05652 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR008594 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1st4 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme C-term binding | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | DcpS_C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF11969 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0265 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1st4 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Scavenger mRNA-decapping enzyme DcpS is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCPS gene. [5] [6] [7]
The scavenger mRNA decapping enzymes include Dcp2 and DcpS. DcpS is a scavenger pyrophosphatase that hydrolyses the residual cap structure following 3' to 5' mRNA degradation. DcpS uses cap dinucleotides or capped oligonucleotides as substrates to release m(7)GMP (N7-methyl GMP), while Dcp2 uses capped mRNA as a substrate in order to hydrolyse the cap to release m(7)GDP (N7-methyl GDP). [8] The association of DcpS with 3' to 5' exonuclease exosome components suggests that these two activities are linked and there is a coupled exonucleolytic decay-dependent decapping pathway. The family contains a histidine triad (HIT) sequence in its C-terminal domain, with three histidines separated by hydrophobic residues. [9] The central histidine within the DcpS HIT motif is critical for decapping activity and defines the HIT motif as a new mRNA decapping domain, making DcpS the first member of the HIT family of proteins with a defined biological function.
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000110063 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000032040 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Liu H, Rodgers ND, Jiao X, Kiledjian M (Aug 2002). "The scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme DcpS is a member of the HIT family of pyrophosphatases". EMBO J. 21 (17): 4699–4708. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf448. PMC 126188. PMID 12198172.
- ^ van Dijk E, Le Hir H, Seraphin B (Oct 2003). "DcpS can act in the 5'-3' mRNA decay pathway in addition to the 3'-5' pathway". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100 (21): 12081–12086. Bibcode: 2003PNAS..10012081V. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1635192100. PMC 218716. PMID 14523240.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: DCPS decapping enzyme, scavenger".
- ^ Liu H, Kiledjian M (February 2006). "Decapping the message: a beginning or an end". Biochem. Soc. Trans. 34 (Pt 1): 35–8. doi: 10.1042/BST20060035. PMID 16246173.
- ^ Han GW, Schwarzenbacher R, McMullan D, Abdubek P, Ambing E, Axelrod H, Biorac T, Canaves JM, Chiu HJ, Dai X, Deacon AM, DiDonato M, Elsliger MA, Godzik A, Grittini C, Grzechnik SK, Hale J, Hampton E, Haugen J, Hornsby M, Jaroszewski L, Klock HE, Koesema E, Kreusch A, Kuhn P, Lesley SA, McPhillips TM, Miller MD, Moy K, Nigoghossian E, Paulsen J, Quijano K, Reyes R, Spraggon G, Stevens RC, van den Bedem H, Velasquez J, Vincent J, White A, Wolf G, Xu Q, Hodgson KO, Wooley J, Wilson IA (September 2005). "Crystal structure of an Apo mRNA decapping enzyme (DcpS) from Mouse at 1.83 A resolution". Proteins. 60 (4): 797–802. doi: 10.1002/prot.20467. PMID 16001405. S2CID 20494085.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–156. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, et al. (2001). "Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells". Genome Res. 10 (10): 1546–1560. doi: 10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- Wang Z, Kiledjian M (2002). "Functional link between the mammalian exosome and mRNA decapping". Cell. 107 (6): 751–762. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00592-X. PMID 11747811. S2CID 8098116.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9916899M. doi: 10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Kwasnicka DA, Krakowiak A, Thacker C, et al. (2003). "Coordinate expression of NADPH-dependent flavin reductase, Fre-1, and Hint-related 7meGMP-directed hydrolase, DCS-1". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (40): 39051–39058. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306355200. PMC 2556063. PMID 12871939.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–45. doi: 10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gu M, Fabrega C, Liu SW, et al. (2004). "Insights into the structure, mechanism, and regulation of scavenger mRNA decapping activity". Mol. Cell. 14 (1): 67–80. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(04)00180-7. PMID 15068804.
- Liu SW, Jiao X, Liu H, et al. (2004). "Functional analysis of mRNA scavenger decapping enzymes". RNA. 10 (9): 1412–1422. doi: 10.1261/rna.7660804. PMC 1370627. PMID 15273322.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–2127. doi: 10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Malys N, Carroll K, Miyan J, Tollervey D, McCarthy JE (2004). "The 'scavenger' m7GpppX pyrophosphatase activity of Dcs1 modulates nutrient-induced responses in yeast". Nucleic Acids Res. 32 (12): 3590–3600. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh687. PMC 484174. PMID 15240832.
- Chen N, Walsh MA, Liu Y, et al. (2005). "Crystal structures of human DcpS in ligand-free and m7GDP-bound forms suggest a dynamic mechanism for scavenger mRNA decapping". J. Mol. Biol. 347 (4): 707–718. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.01.062. PMID 15769464.
- Kwaśnicka-Crawford DA, Vincent SR (2005). "Role of a novel dual flavin reductase (NR1) and an associated histidine triad protein (DCS-1) in menadione-induced cytotoxicity". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336 (2): 565–571. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.129. PMID 16140270.
- Malys N, McCarthy JEG (2006). "Dcs2, a novel stress-induced modulator of m7GpppX pyrophosphatase activity that locates to P bodies". J. Mol. Biol. 363 (2): 370–382. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.08.015. PMID 16963086.
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human m7GpppX diphosphatase (DCPS)
| DCPS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DCPS, DCS1, HINT-5, HINT5, HSL1, ARS, HSPC015, decapping enzyme, scavenger | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 610534; MGI: 1916555; HomoloGene: 32202; GeneCards: DCPS; OMA: DCPS - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme (DcpS) N-terminal | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 crystal structure of mrna decapping enzyme (dcps) from mus musculus at 1.83 a resolution | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | DcpS | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF05652 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR008594 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1st4 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme C-term binding | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | DcpS_C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF11969 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0265 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1st4 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Scavenger mRNA-decapping enzyme DcpS is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCPS gene. [5] [6] [7]
The scavenger mRNA decapping enzymes include Dcp2 and DcpS. DcpS is a scavenger pyrophosphatase that hydrolyses the residual cap structure following 3' to 5' mRNA degradation. DcpS uses cap dinucleotides or capped oligonucleotides as substrates to release m(7)GMP (N7-methyl GMP), while Dcp2 uses capped mRNA as a substrate in order to hydrolyse the cap to release m(7)GDP (N7-methyl GDP). [8] The association of DcpS with 3' to 5' exonuclease exosome components suggests that these two activities are linked and there is a coupled exonucleolytic decay-dependent decapping pathway. The family contains a histidine triad (HIT) sequence in its C-terminal domain, with three histidines separated by hydrophobic residues. [9] The central histidine within the DcpS HIT motif is critical for decapping activity and defines the HIT motif as a new mRNA decapping domain, making DcpS the first member of the HIT family of proteins with a defined biological function.
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000110063 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000032040 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Liu H, Rodgers ND, Jiao X, Kiledjian M (Aug 2002). "The scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme DcpS is a member of the HIT family of pyrophosphatases". EMBO J. 21 (17): 4699–4708. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf448. PMC 126188. PMID 12198172.
- ^ van Dijk E, Le Hir H, Seraphin B (Oct 2003). "DcpS can act in the 5'-3' mRNA decay pathway in addition to the 3'-5' pathway". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100 (21): 12081–12086. Bibcode: 2003PNAS..10012081V. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1635192100. PMC 218716. PMID 14523240.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: DCPS decapping enzyme, scavenger".
- ^ Liu H, Kiledjian M (February 2006). "Decapping the message: a beginning or an end". Biochem. Soc. Trans. 34 (Pt 1): 35–8. doi: 10.1042/BST20060035. PMID 16246173.
- ^ Han GW, Schwarzenbacher R, McMullan D, Abdubek P, Ambing E, Axelrod H, Biorac T, Canaves JM, Chiu HJ, Dai X, Deacon AM, DiDonato M, Elsliger MA, Godzik A, Grittini C, Grzechnik SK, Hale J, Hampton E, Haugen J, Hornsby M, Jaroszewski L, Klock HE, Koesema E, Kreusch A, Kuhn P, Lesley SA, McPhillips TM, Miller MD, Moy K, Nigoghossian E, Paulsen J, Quijano K, Reyes R, Spraggon G, Stevens RC, van den Bedem H, Velasquez J, Vincent J, White A, Wolf G, Xu Q, Hodgson KO, Wooley J, Wilson IA (September 2005). "Crystal structure of an Apo mRNA decapping enzyme (DcpS) from Mouse at 1.83 A resolution". Proteins. 60 (4): 797–802. doi: 10.1002/prot.20467. PMID 16001405. S2CID 20494085.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–156. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, et al. (2001). "Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells". Genome Res. 10 (10): 1546–1560. doi: 10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- Wang Z, Kiledjian M (2002). "Functional link between the mammalian exosome and mRNA decapping". Cell. 107 (6): 751–762. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00592-X. PMID 11747811. S2CID 8098116.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9916899M. doi: 10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Kwasnicka DA, Krakowiak A, Thacker C, et al. (2003). "Coordinate expression of NADPH-dependent flavin reductase, Fre-1, and Hint-related 7meGMP-directed hydrolase, DCS-1". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (40): 39051–39058. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306355200. PMC 2556063. PMID 12871939.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–45. doi: 10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gu M, Fabrega C, Liu SW, et al. (2004). "Insights into the structure, mechanism, and regulation of scavenger mRNA decapping activity". Mol. Cell. 14 (1): 67–80. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(04)00180-7. PMID 15068804.
- Liu SW, Jiao X, Liu H, et al. (2004). "Functional analysis of mRNA scavenger decapping enzymes". RNA. 10 (9): 1412–1422. doi: 10.1261/rna.7660804. PMC 1370627. PMID 15273322.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–2127. doi: 10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Malys N, Carroll K, Miyan J, Tollervey D, McCarthy JE (2004). "The 'scavenger' m7GpppX pyrophosphatase activity of Dcs1 modulates nutrient-induced responses in yeast". Nucleic Acids Res. 32 (12): 3590–3600. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh687. PMC 484174. PMID 15240832.
- Chen N, Walsh MA, Liu Y, et al. (2005). "Crystal structures of human DcpS in ligand-free and m7GDP-bound forms suggest a dynamic mechanism for scavenger mRNA decapping". J. Mol. Biol. 347 (4): 707–718. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.01.062. PMID 15769464.
- Kwaśnicka-Crawford DA, Vincent SR (2005). "Role of a novel dual flavin reductase (NR1) and an associated histidine triad protein (DCS-1) in menadione-induced cytotoxicity". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336 (2): 565–571. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.129. PMID 16140270.
- Malys N, McCarthy JEG (2006). "Dcs2, a novel stress-induced modulator of m7GpppX pyrophosphatase activity that locates to P bodies". J. Mol. Biol. 363 (2): 370–382. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.08.015. PMID 16963086.
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human m7GpppX diphosphatase (DCPS)







