Tropical Cyclone Kimi intensifying over the
Coral Sea on 17 January | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | 15 January 2021 |
| Dissipated | 19 January 2021 |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone | |
| 10-minute sustained ( BOM) | |
| Highest winds | 85 km/h (50 mph) |
| Highest gusts | 120 km/h (75 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 990 hPa ( mbar); 29.23 inHg |
| Tropical storm | |
| 1-minute sustained ( SSHWS/ JTWC) | |
| Highest winds | 100 km/h (65 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 990 hPa ( mbar); 29.23 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | None reported |
| Damage | None |
| Areas affected | Queensland |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 2020–21 Australian region cyclone season | |
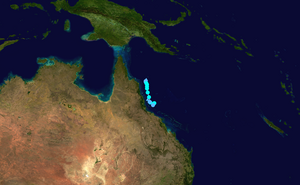
Tropical Cyclone Kimi was a small tropical cyclone which briefly threatened the Eastern Coast of North Queensland in January 2021. The tenth tropical low and third tropical cyclone of the 2020–21 Australian region cyclone season, Kimi originated from a weak tropical low which formed northeast of Queensland on 16 January. The low strengthened into Tropical Cyclone Kimi early the next day, as it slowly moved towards the coastline of northeastern Australia. Despite most forecasts depicting a track south into the coast, a vigorous increase in wind shear made the storm shift west away from the coastline just hours ahead of a potential landfall and caused Kimi to significantly weaken, becoming a tropical low by 18 January and dissipating entirely the next day.
Preparations of the storm begun shortly after formation, with watches and warnings being issued for the land in the path of Kimi. Impacts were anticipated to be significant, with the effects of the previous storm to hit the state at the time, Cyclone Imogen, to be exacerbated from the heavy rainfall if it had made landfall. The cyclone's unexpected weakening due to a sudden and unexpected increase of wind shear early on 18 January led to tropical cyclone warnings being cancelled as Kimi became a tropical low. It soon dissipated on 19 January.
Meteorological history
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
On 12 January, the Bureau of Meteorology noted that a monsoonal trough could develop within a week, that would make conditions in the Australian Region basin favorable for tropical cyclogenesis. [1] On 16 January, a weak tropical low formed to the northeast of Queensland. [2] Later that day, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert on the system. [3] At 02:10 UTC on 17 January, the Bureau of Meteorology upgraded the tropical low into Tropical Cyclone Kimi, while located northeast of Cooktown. [4] A tiny tropical cyclone, Kimi moved slowly southward while remaining offshore of the Australian coastline. [5]
Late on 17 January, radar imagery from Cairns showed low-level convective rainbands, which wrapped into the storm's center of circulation. [6] Around this time, Kimi grew large bursts of convection, with a well-defined circulation visible on satellite imagery. [7] However organization began to slow on 18 January, with convection becoming displaced to the west of the center. [8] Radar from Townsville and satellite imagery showed that wind shear had caused convection to now become displaced to the southeast of the center, as the deep convection itself began to weaken. [9] Late on 18 January, Tropical Cyclone Kimi weakened into a tropical low while moving slowly off the North Queensland coast. [10] At 21:00 UTC that same day, the JTWC issued their final warning on Kimi. [11]
Preparations and impact

On 17 January, a Tropical Cyclone Warning was put in effect from Cape Melville to Cardwell in Queensland, which extended inland to Palmer and Chillagoe. [12] By the next day, a Tropical Cyclone Watch had been issued from Ayr to Bowen, while most of the initial warning zone had been cancelled. [13] A Flood Watch was issued for areas expected to receive heavy rainfall from the storm. [14] The Queensland Fire and Emergency Services advised residents to prepare emergency supplies in the limited time available before the storm. [15] The emergency services also provided sandbags and tarps to protect structures. [16] The Cairns Central was closed on 18 January. [17] The Flecker Botanical Gardens briefly ceased operation starting on 17 January, and the Daintree River Ferry operated for only a part of 18 January. [18] Offshore Cairns, roughly 200 people on Fitzroy Island were evacuated. Ports in Cairns, Port Douglas, Innisfail, and Cooktown were only open for emergency movements, as well as Half Moon Bay Marina. Meteorologist Shane Kennedy said that Kimi will bring significant impacts regardless if it intensifies or not. They also noted that there was a flood risk due to the impacts of Cyclone Imogen. Eleanor Rosam of the SES said crews, such as swiftwater rescue personnel, have been sent on stand-by for the potential impacts of Kimi. She urged those in the path of the incoming storm to prepare. [19] As Kimi became less of a threat to Cairns, many places and services that had previously announced cancellations and closure were reopened. [20]
As Kimi moved further south, the Townsville Airport ceased operations between 18 and 19 January. The cyclone prompted an emergency alert for Palm Island, which expected a close pass. [21] Once preparations were complete, many residents of Queensland hunkered down for the storm. [22] However, forecast tracks soon depicted Kimi moving away from the coast of Australia. [23] The Bureau of Meteorology officials called the storm "erratic" and "unusually unpredictable" due to its small size. [24]
As early as 18 January, large waves occurred between the towns of Yarrabah and Lucinda in the Australian state of Queensland. [25] At that time, stormy weather was also affecting portions of the state. [26] Areas still received flash flooding despite the absence of a direct hit from Kimi, most notably around Innisfail, which recorded some of the highest rainfall totals including a 158 mm (6.22 in) reading at a gauge in the town. [27]
See also
References
- ^ "Weekly Tropical Climate Note". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 12, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
-
^
"Tropical Cyclone Outlook for the Coral Sea". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. 16 January 2021. Archived from the original on 25 January 2019. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown ( link) - ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert Graphic". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 16, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
-
^
"Flash Tropical Cyclone Advice Number 1 (Kimi)". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. 17 January 2021. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown ( link) -
^
"Tropical Cyclone Advice Number 6 (Kimi)". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. 18 January 2021. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown ( link) - ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE 11P (KIMI) WARNING NR 004". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 17, 2021. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE TECHNICAL BULLETIN: AUSTRALIA – EASTERN REGION". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE TECHNICAL BULLETIN: AUSTRALIA – EASTERN REGION". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE 11P (KIMI) WARNING NR 007". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 18, 2021. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
-
^
"Tropical Cyclone Advice Number 15 (Kimi)". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. 18 January 2021. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown ( link) - ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE 11P (KIMI) WARNING NR 008". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 18, 2021. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 19, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Advice Number 2". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE ADVICE NUMBER 10". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "Cyclone Kimi approaches far north Queensland, while WA coast feels the effects of another cyclone". The New Daily. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ AFP (January 17, 2021). "Tropical Cyclone Kimi forms off north-eastern Australia, likely to hit coast on Jan 18". The Straits Times. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "Cyclone Kimi: Category two storm set to batter Far North Queensland". 9news.com.au. 9 News Australia. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical cyclone Kimi could move further south, new track map shows". The Cairns Post. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ Callum Godde (January 17, 2021). "Cyclone Kimi set to cross far north Qld". perthnow.com.au. PerthNow. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ Walsh, Lia (January 17, 2021). "BOM warns Tropical Cyclone Kimi due to make landfall in Far North Queensland tonight". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical cyclone Kimi set to track towards Cassowary Coast". cairnspost.com.au. The Cairns Post. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "Townsville airport closes, but Tropical Cyclone Kimi weakens, is unlikely to cross coast". abc.net.au. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ Callum Godde (January 17, 2021). "Tropical cyclone forms in far north Queensland". 7news.com.au. 7 News Australia. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone 11P (Kimi) Warning #7 Graphic". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 18, 2021. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Kimi: 'Destructive' weather hitting towns". www.theaustralian.com.au. 2021-01-18. Retrieved 2021-01-19.
- ^ "Cyclone Kimi set to dodge Cairns, hit Hinchinbrook Island". tropicnow.com.au. TropicNow. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ Mark Saunokonoko (January 18, 2021). "Cyclone Kimi intensifies to category two". 9news.com.au. 9 News Australia. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "'Mother Nature hasn't turned the tap off yet': Tropical Cyclone Kimi downgraded but could reform". www.abc.net.au. 2021-01-18. Retrieved 2021-01-19.
External links
 Tropical Cyclone Kimi intensifying over the
Coral Sea on 17 January | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | 15 January 2021 |
| Dissipated | 19 January 2021 |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone | |
| 10-minute sustained ( BOM) | |
| Highest winds | 85 km/h (50 mph) |
| Highest gusts | 120 km/h (75 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 990 hPa ( mbar); 29.23 inHg |
| Tropical storm | |
| 1-minute sustained ( SSHWS/ JTWC) | |
| Highest winds | 100 km/h (65 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 990 hPa ( mbar); 29.23 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | None reported |
| Damage | None |
| Areas affected | Queensland |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 2020–21 Australian region cyclone season | |
Tropical Cyclone Kimi was a small tropical cyclone which briefly threatened the Eastern Coast of North Queensland in January 2021. The tenth tropical low and third tropical cyclone of the 2020–21 Australian region cyclone season, Kimi originated from a weak tropical low which formed northeast of Queensland on 16 January. The low strengthened into Tropical Cyclone Kimi early the next day, as it slowly moved towards the coastline of northeastern Australia. Despite most forecasts depicting a track south into the coast, a vigorous increase in wind shear made the storm shift west away from the coastline just hours ahead of a potential landfall and caused Kimi to significantly weaken, becoming a tropical low by 18 January and dissipating entirely the next day.
Preparations of the storm begun shortly after formation, with watches and warnings being issued for the land in the path of Kimi. Impacts were anticipated to be significant, with the effects of the previous storm to hit the state at the time, Cyclone Imogen, to be exacerbated from the heavy rainfall if it had made landfall. The cyclone's unexpected weakening due to a sudden and unexpected increase of wind shear early on 18 January led to tropical cyclone warnings being cancelled as Kimi became a tropical low. It soon dissipated on 19 January.
Meteorological history

Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
On 12 January, the Bureau of Meteorology noted that a monsoonal trough could develop within a week, that would make conditions in the Australian Region basin favorable for tropical cyclogenesis. [1] On 16 January, a weak tropical low formed to the northeast of Queensland. [2] Later that day, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert on the system. [3] At 02:10 UTC on 17 January, the Bureau of Meteorology upgraded the tropical low into Tropical Cyclone Kimi, while located northeast of Cooktown. [4] A tiny tropical cyclone, Kimi moved slowly southward while remaining offshore of the Australian coastline. [5]
Late on 17 January, radar imagery from Cairns showed low-level convective rainbands, which wrapped into the storm's center of circulation. [6] Around this time, Kimi grew large bursts of convection, with a well-defined circulation visible on satellite imagery. [7] However organization began to slow on 18 January, with convection becoming displaced to the west of the center. [8] Radar from Townsville and satellite imagery showed that wind shear had caused convection to now become displaced to the southeast of the center, as the deep convection itself began to weaken. [9] Late on 18 January, Tropical Cyclone Kimi weakened into a tropical low while moving slowly off the North Queensland coast. [10] At 21:00 UTC that same day, the JTWC issued their final warning on Kimi. [11]
Preparations and impact

On 17 January, a Tropical Cyclone Warning was put in effect from Cape Melville to Cardwell in Queensland, which extended inland to Palmer and Chillagoe. [12] By the next day, a Tropical Cyclone Watch had been issued from Ayr to Bowen, while most of the initial warning zone had been cancelled. [13] A Flood Watch was issued for areas expected to receive heavy rainfall from the storm. [14] The Queensland Fire and Emergency Services advised residents to prepare emergency supplies in the limited time available before the storm. [15] The emergency services also provided sandbags and tarps to protect structures. [16] The Cairns Central was closed on 18 January. [17] The Flecker Botanical Gardens briefly ceased operation starting on 17 January, and the Daintree River Ferry operated for only a part of 18 January. [18] Offshore Cairns, roughly 200 people on Fitzroy Island were evacuated. Ports in Cairns, Port Douglas, Innisfail, and Cooktown were only open for emergency movements, as well as Half Moon Bay Marina. Meteorologist Shane Kennedy said that Kimi will bring significant impacts regardless if it intensifies or not. They also noted that there was a flood risk due to the impacts of Cyclone Imogen. Eleanor Rosam of the SES said crews, such as swiftwater rescue personnel, have been sent on stand-by for the potential impacts of Kimi. She urged those in the path of the incoming storm to prepare. [19] As Kimi became less of a threat to Cairns, many places and services that had previously announced cancellations and closure were reopened. [20]
As Kimi moved further south, the Townsville Airport ceased operations between 18 and 19 January. The cyclone prompted an emergency alert for Palm Island, which expected a close pass. [21] Once preparations were complete, many residents of Queensland hunkered down for the storm. [22] However, forecast tracks soon depicted Kimi moving away from the coast of Australia. [23] The Bureau of Meteorology officials called the storm "erratic" and "unusually unpredictable" due to its small size. [24]
As early as 18 January, large waves occurred between the towns of Yarrabah and Lucinda in the Australian state of Queensland. [25] At that time, stormy weather was also affecting portions of the state. [26] Areas still received flash flooding despite the absence of a direct hit from Kimi, most notably around Innisfail, which recorded some of the highest rainfall totals including a 158 mm (6.22 in) reading at a gauge in the town. [27]
See also
References
- ^ "Weekly Tropical Climate Note". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 12, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
-
^
"Tropical Cyclone Outlook for the Coral Sea". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. 16 January 2021. Archived from the original on 25 January 2019. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown ( link) - ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert Graphic". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 16, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
-
^
"Flash Tropical Cyclone Advice Number 1 (Kimi)". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. 17 January 2021. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown ( link) -
^
"Tropical Cyclone Advice Number 6 (Kimi)". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. 18 January 2021. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown ( link) - ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE 11P (KIMI) WARNING NR 004". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 17, 2021. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE TECHNICAL BULLETIN: AUSTRALIA – EASTERN REGION". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE TECHNICAL BULLETIN: AUSTRALIA – EASTERN REGION". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE 11P (KIMI) WARNING NR 007". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 18, 2021. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
-
^
"Tropical Cyclone Advice Number 15 (Kimi)". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. 18 January 2021. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
{{ cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown ( link) - ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE 11P (KIMI) WARNING NR 008". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 18, 2021. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 19, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Advice Number 2". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE ADVICE NUMBER 10". bom.gov.au. Bureau of Meteorology. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "Cyclone Kimi approaches far north Queensland, while WA coast feels the effects of another cyclone". The New Daily. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ AFP (January 17, 2021). "Tropical Cyclone Kimi forms off north-eastern Australia, likely to hit coast on Jan 18". The Straits Times. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "Cyclone Kimi: Category two storm set to batter Far North Queensland". 9news.com.au. 9 News Australia. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical cyclone Kimi could move further south, new track map shows". The Cairns Post. January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ Callum Godde (January 17, 2021). "Cyclone Kimi set to cross far north Qld". perthnow.com.au. PerthNow. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ Walsh, Lia (January 17, 2021). "BOM warns Tropical Cyclone Kimi due to make landfall in Far North Queensland tonight". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical cyclone Kimi set to track towards Cassowary Coast". cairnspost.com.au. The Cairns Post. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "Townsville airport closes, but Tropical Cyclone Kimi weakens, is unlikely to cross coast". abc.net.au. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ Callum Godde (January 17, 2021). "Tropical cyclone forms in far north Queensland". 7news.com.au. 7 News Australia. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone 11P (Kimi) Warning #7 Graphic". metoc.navy.mil. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 18, 2021. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Kimi: 'Destructive' weather hitting towns". www.theaustralian.com.au. 2021-01-18. Retrieved 2021-01-19.
- ^ "Cyclone Kimi set to dodge Cairns, hit Hinchinbrook Island". tropicnow.com.au. TropicNow. January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ Mark Saunokonoko (January 18, 2021). "Cyclone Kimi intensifies to category two". 9news.com.au. 9 News Australia. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "'Mother Nature hasn't turned the tap off yet': Tropical Cyclone Kimi downgraded but could reform". www.abc.net.au. 2021-01-18. Retrieved 2021-01-19.