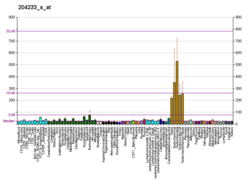
Choline kinase alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CHKA gene. [5] [6] [7]
The major pathway for the biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine occurs via the CDP-choline pathway. The protein encoded by this gene is the initial enzyme in the sequence and may play a regulatory role. The encoded protein also catalyzes the phosphorylation of ethanolamine. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [7]
In melanocytic cells CHKA gene expression may be regulated by MITF. [8]
Mutations of the CHKA gene cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with epilepsy and microcephaly. [9]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000110721 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024843 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Hosaka K, Tanaka S, Nikawa J, Yamashita S (Aug 1992). "Cloning of a human choline kinase cDNA by complementation of the yeast cki mutation". FEBS Lett. 304 (2–3): 229–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80625-Q. PMID 1618328. S2CID 25275208.
- ^ Aoyama C, Liao H, Ishidate K (Mar 2004). "Structure and function of choline kinase isoforms in mammalian cells". Prog Lipid Res. 43 (3): 266–81. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2003.12.001. PMID 15003397.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: CHKA choline kinase alpha".
- ^ Hoek KS, Schlegel NC, Eichhoff OM, et al. (2008). "Novel MITF targets identified using a two-step DNA microarray strategy". Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 21 (6): 665–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2008.00505.x. PMID 19067971. S2CID 24698373.
- ^ Klöckner C, Fernández-Murray JP, Tavasoli M, Sticht H, Stoltenburg-Didinger G, Scholle LM, Bakhtiari S, Kruer MC, Darvish H, Firouzabadi SG, Pagnozzi A, Shukla A, Girisha KM, Narayanan DL, Kaur P, Maroofian R, Zaki MS, Noureldeen MM, Merkenschlager A, Gburek-Augustat J, Cali E, Banu S, Nahar K, Efthymiou S, Houlden H, Jamra RA, Williams J, McMaster CR, Platzer K (June 2022). "Bi-allelic variants in CHKA cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with epilepsy and microcephaly". Brain: A Journal of Neurology. 145 (6): 1916–1923. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac074. PMC 9630884. PMID 35202461.
- Human CHKA genome location and CHKA gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Spanner S, Ansell GB (1979). "Choline kinase and ethanolamine kinase activity in the cytosol of nerve endings from rat forebrain". Biochem. J. 178 (3): 753–60. doi: 10.1042/bj1780753. PMC 1186576. PMID 36885.
- Spanner S, Ansell GB (1978). "Choline and Ethanolamine Kinase Activity in the Cytoplasm of Nerve Endings from Rat Forebrain". Enzymes of Lipid Metabolism. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 101. pp. 237–45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9071-2_23. ISBN 978-1-4615-9073-6. PMID 208357.
- Kaplan O, Cohen JS (1994). "Lymphocyte activation-31P magnetic resonance studies of energy metabolism and phospholipid pathways". ImmunoMethods. 4 (2): 139–47. doi: 10.1006/immu.1994.1015. PMID 8069533.
- Price DJ, Rivnay B, Fu Y, et al. (1997). "Direct association of Csk homologous kinase (CHK) with the diphosphorylated site Tyr568/570 of the activated c-KIT in megakaryocytes". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (9): 5915–20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.9.5915. PMID 9038210.
- Ross BM, Moszczynska A, Blusztajn JK, et al. (1997). "Phospholipid biosynthetic enzymes in human brain". Lipids. 32 (4): 351–8. doi: 10.1007/s11745-997-0044-x. PMID 9113621. S2CID 4003647.
- Nakagami K, Uchida T, Ohwada S, et al. (1999). "Increased choline kinase activity and elevated phosphocholine levels in human colon cancer". Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 90 (4): 419–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1999.tb00764.x. PMC 5926083. PMID 10363580.
- Ramírez de Molina A, Penalva V, Lucas L, Lacal JC (2002). "Regulation of choline kinase activity by Ras proteins involves Ral-GDS and PI3K". Oncogene. 21 (6): 937–46. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205144. PMID 11840339.
- Dubois T, Howell S, Zemlickova E, Aitken A (2002). "Identification of casein kinase Ialpha interacting protein partners". FEBS Lett. 517 (1–3): 167–71. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02614-5. PMID 12062430. S2CID 84792445.
- Ramírez de Molina A, Gutiérrez R, Ramos MA, et al. (2002). "Increased choline kinase activity in human breast carcinomas: clinical evidence for a potential novel antitumor strategy". Oncogene. 21 (27): 4317–22. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205556. PMID 12082619.
- Ramírez de Molina A, Rodríguez-González A, Gutiérrez R, et al. (2002). "Overexpression of choline kinase is a frequent feature in human tumor-derived cell lines and in lung, prostate, and colorectal human cancers". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 296 (3): 580–3. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00920-8. PMID 12176020.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9916899M. doi: 10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi: 10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi: 10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Gallego-Ortega D, Ramirez De Molina A, Gutierrez R, et al. (2006). "Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against choline kinase alpha and their potential use as diagnostic tools in cancer" (PDF). Int. J. Oncol. 29 (2): 335–40. doi: 10.3892/ijo.29.2.335. PMID 16820874.
- Enaw JO, Zhu H, Yang W, et al. (2007). "CHKA and PCYT1A gene polymorphisms, choline intake and spina bifida risk in a California population". BMC Medicine. 4: 36. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-4-36. PMC 1770928. PMID 17184542.
| CHKA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CHKA, CHK, CK, CKI, EK, choline kinase alpha | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 118491; MGI: 107760; HomoloGene: 88575; GeneCards: CHKA; OMA: CHKA - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EC number | 2.7.1.82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Choline kinase alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CHKA gene. [5] [6] [7]
The major pathway for the biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine occurs via the CDP-choline pathway. The protein encoded by this gene is the initial enzyme in the sequence and may play a regulatory role. The encoded protein also catalyzes the phosphorylation of ethanolamine. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [7]
In melanocytic cells CHKA gene expression may be regulated by MITF. [8]
Mutations of the CHKA gene cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with epilepsy and microcephaly. [9]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000110721 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024843 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Hosaka K, Tanaka S, Nikawa J, Yamashita S (Aug 1992). "Cloning of a human choline kinase cDNA by complementation of the yeast cki mutation". FEBS Lett. 304 (2–3): 229–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80625-Q. PMID 1618328. S2CID 25275208.
- ^ Aoyama C, Liao H, Ishidate K (Mar 2004). "Structure and function of choline kinase isoforms in mammalian cells". Prog Lipid Res. 43 (3): 266–81. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2003.12.001. PMID 15003397.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: CHKA choline kinase alpha".
- ^ Hoek KS, Schlegel NC, Eichhoff OM, et al. (2008). "Novel MITF targets identified using a two-step DNA microarray strategy". Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 21 (6): 665–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2008.00505.x. PMID 19067971. S2CID 24698373.
- ^ Klöckner C, Fernández-Murray JP, Tavasoli M, Sticht H, Stoltenburg-Didinger G, Scholle LM, Bakhtiari S, Kruer MC, Darvish H, Firouzabadi SG, Pagnozzi A, Shukla A, Girisha KM, Narayanan DL, Kaur P, Maroofian R, Zaki MS, Noureldeen MM, Merkenschlager A, Gburek-Augustat J, Cali E, Banu S, Nahar K, Efthymiou S, Houlden H, Jamra RA, Williams J, McMaster CR, Platzer K (June 2022). "Bi-allelic variants in CHKA cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with epilepsy and microcephaly". Brain: A Journal of Neurology. 145 (6): 1916–1923. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac074. PMC 9630884. PMID 35202461.
- Human CHKA genome location and CHKA gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Spanner S, Ansell GB (1979). "Choline kinase and ethanolamine kinase activity in the cytosol of nerve endings from rat forebrain". Biochem. J. 178 (3): 753–60. doi: 10.1042/bj1780753. PMC 1186576. PMID 36885.
- Spanner S, Ansell GB (1978). "Choline and Ethanolamine Kinase Activity in the Cytoplasm of Nerve Endings from Rat Forebrain". Enzymes of Lipid Metabolism. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 101. pp. 237–45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9071-2_23. ISBN 978-1-4615-9073-6. PMID 208357.
- Kaplan O, Cohen JS (1994). "Lymphocyte activation-31P magnetic resonance studies of energy metabolism and phospholipid pathways". ImmunoMethods. 4 (2): 139–47. doi: 10.1006/immu.1994.1015. PMID 8069533.
- Price DJ, Rivnay B, Fu Y, et al. (1997). "Direct association of Csk homologous kinase (CHK) with the diphosphorylated site Tyr568/570 of the activated c-KIT in megakaryocytes". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (9): 5915–20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.9.5915. PMID 9038210.
- Ross BM, Moszczynska A, Blusztajn JK, et al. (1997). "Phospholipid biosynthetic enzymes in human brain". Lipids. 32 (4): 351–8. doi: 10.1007/s11745-997-0044-x. PMID 9113621. S2CID 4003647.
- Nakagami K, Uchida T, Ohwada S, et al. (1999). "Increased choline kinase activity and elevated phosphocholine levels in human colon cancer". Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 90 (4): 419–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1999.tb00764.x. PMC 5926083. PMID 10363580.
- Ramírez de Molina A, Penalva V, Lucas L, Lacal JC (2002). "Regulation of choline kinase activity by Ras proteins involves Ral-GDS and PI3K". Oncogene. 21 (6): 937–46. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205144. PMID 11840339.
- Dubois T, Howell S, Zemlickova E, Aitken A (2002). "Identification of casein kinase Ialpha interacting protein partners". FEBS Lett. 517 (1–3): 167–71. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02614-5. PMID 12062430. S2CID 84792445.
- Ramírez de Molina A, Gutiérrez R, Ramos MA, et al. (2002). "Increased choline kinase activity in human breast carcinomas: clinical evidence for a potential novel antitumor strategy". Oncogene. 21 (27): 4317–22. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205556. PMID 12082619.
- Ramírez de Molina A, Rodríguez-González A, Gutiérrez R, et al. (2002). "Overexpression of choline kinase is a frequent feature in human tumor-derived cell lines and in lung, prostate, and colorectal human cancers". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 296 (3): 580–3. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00920-8. PMID 12176020.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9916899M. doi: 10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi: 10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi: 10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Gallego-Ortega D, Ramirez De Molina A, Gutierrez R, et al. (2006). "Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against choline kinase alpha and their potential use as diagnostic tools in cancer" (PDF). Int. J. Oncol. 29 (2): 335–40. doi: 10.3892/ijo.29.2.335. PMID 16820874.
- Enaw JO, Zhu H, Yang W, et al. (2007). "CHKA and PCYT1A gene polymorphisms, choline intake and spina bifida risk in a California population". BMC Medicine. 4: 36. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-4-36. PMC 1770928. PMID 17184542.