This article is an
orphan, as no other articles
link to it. Please
introduce links to this page from
related articles; try the
Find link tool for suggestions. (June 2024) |
| Btz | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
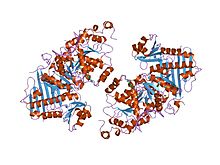 structure of the human exon junction complex with a trapped dead-box helicase bound to rna | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Btz | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09405 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR018545 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the Btz domain (CASC3/Barentsz eIF4AIII binding domain) is a protein domain found on CASC3 (cancer susceptibility candidate gene 3 protein) which is also known as Barentsz (Btz). CASC3 is a component of the EJC ( exon junction complex) which is a complex that is involved in post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA in metazoa. The complex is formed by the association of four proteins ( eIF4AIII, Barentsz, Mago, and Y14), mRNA, and ATP. This domain wraps around eIF4AIII and stacks against the 5' nucleotide. [1] [2]
References
- ^ Bono F, Ebert J, Lorentzen E, Conti E (August 2006). "The crystal structure of the exon junction complex reveals how it maintains a stable grip on mRNA". Cell. 126 (4): 713–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.006. PMID 16923391. S2CID 16137076.
- ^ Palacios IM, Gatfield D, St Johnston D, Izaurralde E (February 2004). "An eIF4AIII-containing complex required for mRNA localization and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay". Nature. 427 (6976): 753–7. doi: 10.1038/nature02351. PMID 14973490. S2CID 4400243.
This article is an
orphan, as no other articles
link to it. Please
introduce links to this page from
related articles; try the
Find link tool for suggestions. (June 2024) |
| Btz | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 structure of the human exon junction complex with a trapped dead-box helicase bound to rna | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Btz | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09405 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR018545 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the Btz domain (CASC3/Barentsz eIF4AIII binding domain) is a protein domain found on CASC3 (cancer susceptibility candidate gene 3 protein) which is also known as Barentsz (Btz). CASC3 is a component of the EJC ( exon junction complex) which is a complex that is involved in post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA in metazoa. The complex is formed by the association of four proteins ( eIF4AIII, Barentsz, Mago, and Y14), mRNA, and ATP. This domain wraps around eIF4AIII and stacks against the 5' nucleotide. [1] [2]
References
- ^ Bono F, Ebert J, Lorentzen E, Conti E (August 2006). "The crystal structure of the exon junction complex reveals how it maintains a stable grip on mRNA". Cell. 126 (4): 713–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.006. PMID 16923391. S2CID 16137076.
- ^ Palacios IM, Gatfield D, St Johnston D, Izaurralde E (February 2004). "An eIF4AIII-containing complex required for mRNA localization and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay". Nature. 427 (6976): 753–7. doi: 10.1038/nature02351. PMID 14973490. S2CID 4400243.