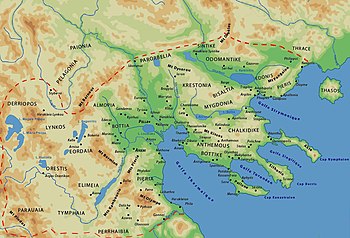
Bisaltia ( Greek: Βισαλτία) or Bisaltica was an ancient country which was bordered by Sintice on the north, Crestonia on the west, Mygdonia on the south and was separated by Odomantis on the north-east and Edonis on the south-east by river Strymon.The eponymous inhabitants, known as the Bisaltae, were a Thracian people. Later, the region was annexed by the kingdom of Macedon and became one of its districts. The most important town in Bisaltia was the Greek city of Argilos. [1] There was also a river named Bisaltes in the region, which has not been certainly identified.
Bisaltia, along with Crestonia, was ruled by a Thracian prince at the time of the invasion of Xerxes I of Persia, but by the onset of the Peloponnesian War it was annexed by Macedon.
In Roman times, Bisaltia crossed a branch of the via Egnatia, in which the Roman sources (Itineraria) mention four horses change stations : Trinlo (=Tragilos), Graero, Arason (=Arolos) and Euporia. [2] In various sites of Bisaltia have been found so far several interesting inscriptions of imperial times. [3]
Important towns of Bisaltia were Argilos, Berge and Brea.
Bisaltia is contained within the Serres regional unit and part of the Thessaloniki regional unit in Greece.
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen,2005, ISBN 0-19-814099-1,page 810,"There were three polis in Bisaltia of which one was considered a colony of Andros"
- ^ "049 ΔΗΜ. Κ. ΣΑΜΣΑΡΗΣ". web.archive.org. 2017-04-24. Retrieved 2024-08-02.
- ^ D. C. Samsaris, La vallée du Bas-Strymon á l’ époque impériale (Contribution épigraphique á la topographie, l’ onomastique, l’ histoire et aux cultes de la province romaine de Macédoine), Dodona 18 (1989), fasc. 1, p. 215-225, n. 1-23 = The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 1, # PH150638) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 2, # PH150639) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 3, # PH150640) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 4, # PH150641) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 5, # PH150642) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 6, # PH150643) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 7, # PH150644) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 8, # PH150645) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 9, # PH150646) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 10, # PH150647) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 11, # PH150648) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 12, # PH150649) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 13, # PH150650) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 14, # PH150651) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 15, # PH150652) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 16, # PH150653) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 17, # PH150654) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 18, # PH150655) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 19, # PH150656) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 20, # PH150657) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 21 # PH150658) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 22 # PH150659) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 23 # PH150660)
-
 Media related to
Bisaltia at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to
Bisaltia at Wikimedia Commons

Bisaltia ( Greek: Βισαλτία) or Bisaltica was an ancient country which was bordered by Sintice on the north, Crestonia on the west, Mygdonia on the south and was separated by Odomantis on the north-east and Edonis on the south-east by river Strymon.The eponymous inhabitants, known as the Bisaltae, were a Thracian people. Later, the region was annexed by the kingdom of Macedon and became one of its districts. The most important town in Bisaltia was the Greek city of Argilos. [1] There was also a river named Bisaltes in the region, which has not been certainly identified.
Bisaltia, along with Crestonia, was ruled by a Thracian prince at the time of the invasion of Xerxes I of Persia, but by the onset of the Peloponnesian War it was annexed by Macedon.
In Roman times, Bisaltia crossed a branch of the via Egnatia, in which the Roman sources (Itineraria) mention four horses change stations : Trinlo (=Tragilos), Graero, Arason (=Arolos) and Euporia. [2] In various sites of Bisaltia have been found so far several interesting inscriptions of imperial times. [3]
Important towns of Bisaltia were Argilos, Berge and Brea.
Bisaltia is contained within the Serres regional unit and part of the Thessaloniki regional unit in Greece.
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen,2005, ISBN 0-19-814099-1,page 810,"There were three polis in Bisaltia of which one was considered a colony of Andros"
- ^ "049 ΔΗΜ. Κ. ΣΑΜΣΑΡΗΣ". web.archive.org. 2017-04-24. Retrieved 2024-08-02.
- ^ D. C. Samsaris, La vallée du Bas-Strymon á l’ époque impériale (Contribution épigraphique á la topographie, l’ onomastique, l’ histoire et aux cultes de la province romaine de Macédoine), Dodona 18 (1989), fasc. 1, p. 215-225, n. 1-23 = The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 1, # PH150638) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 2, # PH150639) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 3, # PH150640) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 4, # PH150641) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 5, # PH150642) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 6, # PH150643) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 7, # PH150644) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 8, # PH150645) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 9, # PH150646) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 10, # PH150647) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 11, # PH150648) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 12, # PH150649) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 13, # PH150650) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 14, # PH150651) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 15, # PH150652) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 16, # PH150653) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 17, # PH150654) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 18, # PH150655) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 19, # PH150656) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 20, # PH150657) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 21 # PH150658) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 22 # PH150659) The Packard Humanities Institute (Samsaris, Bas-Strymon 23 # PH150660)
-
 Media related to
Bisaltia at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to
Bisaltia at Wikimedia Commons