It has been suggested that this article be
merged with
Anteromedial central arteries,
Posterolateral central arteries and
Posteromedial central arteries to
Central arteries. (
Discuss) Proposed since July 2024. |
| Anterolateral central arteries | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Source | Middle cerebral artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | aa. centrales anterolaterales,
[1] aa. lenticulostriatae [1] |
| TA98 | A12.2.07.048 |
| TA2 | 4510 |
| FMA | 71478 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
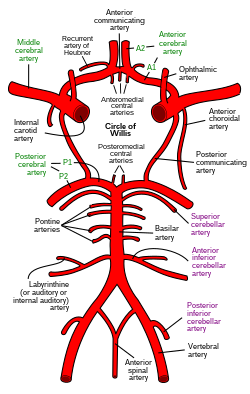
The anterolateral central arteries or lenticulostriate arteries [2] (also anterolateral perforating arteries, anterolateral ganglionic arteries, striate arteries, or lateral striate arteries) are a group of small arteries mostly arising from (the initial M1 part of) the middle cerebral artery that enter the brain through the anterior perforated substance to provide arterial supply to parts of the basal ganglia. [3] They are end arteries.[ citation needed]
The name of these arteries is derived from some of the structures they supply, namely the lentiform nucleus and the striatum.[ citation needed]
Anatomy
Distribution
The ALCAs supply the posterior portion of the striatum, the lateral portion of the globus pallidus, and all parts of the internal capsule. [3]
The medial striate artery (Recurrent artery of Heubner) arises either from the middle cerebral artery or anterior cerebral artery, and supplies the rostral/anterior portion of the caudate nucleus and putamen, and the anterior limb and genu of internal capsule. [3]
Clinical significance
Blockage of the lenticulostriate arteries causes lacunar infarcts. These infarcts are most often due to hyaline arteriosclerosis secondary to hypertension. This can lead to contralateral paresis (muscular weakness) and/or sensory loss of the face and body.
References
- ^ a b Waschke, Jens; Böckers, Tobias M.; Paulsen, Friedrich; Arnold, Wolfgang; Bechmann, Ingo, eds. (2018). Sobotta Anatomy Textbook: English Edition with Latin Nomenclature (1st ed.). München: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7020-6760-0.
- ^ "Anatonomina". terminologia-anatomica.org. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^
a
b
c Standring, Susan (2020).
Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 419.
ISBN
978-0-7020-7707-4.
OCLC
1201341621.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher ( link)
![]() This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 573 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 573 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
Le, Tao and Bhushan, Vikas. First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2017 (p.484). New York: McGraw-Hill Education, 2017.
External links
- MedEd at Loyola Neuro/neurovasc/navigation/mcall.htm
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/part_8/chapter_43.html
It has been suggested that this article be
merged with
Anteromedial central arteries,
Posterolateral central arteries and
Posteromedial central arteries to
Central arteries. (
Discuss) Proposed since July 2024. |
| Anterolateral central arteries | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Source | Middle cerebral artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | aa. centrales anterolaterales,
[1] aa. lenticulostriatae [1] |
| TA98 | A12.2.07.048 |
| TA2 | 4510 |
| FMA | 71478 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anterolateral central arteries or lenticulostriate arteries [2] (also anterolateral perforating arteries, anterolateral ganglionic arteries, striate arteries, or lateral striate arteries) are a group of small arteries mostly arising from (the initial M1 part of) the middle cerebral artery that enter the brain through the anterior perforated substance to provide arterial supply to parts of the basal ganglia. [3] They are end arteries.[ citation needed]
The name of these arteries is derived from some of the structures they supply, namely the lentiform nucleus and the striatum.[ citation needed]
Anatomy
Distribution
The ALCAs supply the posterior portion of the striatum, the lateral portion of the globus pallidus, and all parts of the internal capsule. [3]
The medial striate artery (Recurrent artery of Heubner) arises either from the middle cerebral artery or anterior cerebral artery, and supplies the rostral/anterior portion of the caudate nucleus and putamen, and the anterior limb and genu of internal capsule. [3]
Clinical significance
Blockage of the lenticulostriate arteries causes lacunar infarcts. These infarcts are most often due to hyaline arteriosclerosis secondary to hypertension. This can lead to contralateral paresis (muscular weakness) and/or sensory loss of the face and body.
References
- ^ a b Waschke, Jens; Böckers, Tobias M.; Paulsen, Friedrich; Arnold, Wolfgang; Bechmann, Ingo, eds. (2018). Sobotta Anatomy Textbook: English Edition with Latin Nomenclature (1st ed.). München: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7020-6760-0.
- ^ "Anatonomina". terminologia-anatomica.org. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^
a
b
c Standring, Susan (2020).
Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 419.
ISBN
978-0-7020-7707-4.
OCLC
1201341621.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher ( link)
![]() This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 573 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the
public domain from
page 573 of the 20th edition of
Gray's Anatomy (1918)
Le, Tao and Bhushan, Vikas. First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2017 (p.484). New York: McGraw-Hill Education, 2017.
External links
- MedEd at Loyola Neuro/neurovasc/navigation/mcall.htm
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/part_8/chapter_43.html