| Anterior ethmoidal nerve | |
|---|---|
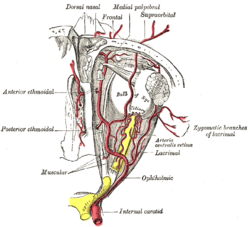 The ophthalmic artery and its branches. (Nerve not pictured, but location is similar to artery.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Nasociliary nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus ethmoidalis anterior |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.030 |
| TA2 | 6208 |
| FMA | 52675 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The anterior ethmoidal nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1)). It arises in the orbit, and enters first the cranial cavity and then the nasal cavity. It provides sensory innervation to part of the meninges, parts of the nasal cavity, and part of the skin of the nose.
The anterior ethmoidal nerve is a terminal branch of the nasociliary nerve, a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). [1] It branches near the medial wall of the orbit.
It passes through the anterior ethmoidal canal alongside the anterior ethmoidal artery [2]: 780 and vein [2]: 566 to emerge in anterior cranial fossa through the anterior ethmoidal foramen [2]: 1464.e13 (at the junction of the cribiform plate of ethmoid bone and orbital part of frontal bone [2]: 566 ).
Within the cranial cavity, it passes anterior-ward (external to the dura mater) along a groove upon the superior surface of the cribriform plate. It descends through an aperture situated lateral to the crista galli to reach the nasal cavity. [2]: 1464.e13
In the nasal cavity, it passes along a groove upon the internal aspect of the nasal bone, and issuing the medial and lateral internal nasal branches. [2]: 1464.e13
It is continued as the external nasal nerve beyond the inferior margin of the nasal bone. [2]: 1464.e13
Within the anterior cranial fossa, it gives sensory fibers to the meninges to provide sensory innervation to part of the meninges. [3]
Its medial internal nasal branch innervates the superior and anterior portions of the nasal septum. [2]: 1464.e13
Its lateral internal nasal branch innervates the anterior portion of the lateral nasal wall. [2]: 1464.e13
It gives off branches to the roof of the nasal cavity, and bifurcates into a lateral internal nasal branch and medial internal nasal branch. It sends sensory fibers to the anterior ethmoid air cells and the middle ethmoidal air cells.[ citation needed]
Its terminal branch - the external nasal nerve - innervates skin of the nose between the nasal bones superiorly and the tip of the nose inferiorly, except the alar portionsurrounding the external nares. [2]: 1464.e13
It is involved in the diving reflex. [4]
- ^ Lucier, Gregory E.; Egizii, Rita (1986). "Central projections of the ethmoidal nerve of the cat as determined by the horseradish peroxidase tracer technique". Journal of Comparative Neurology. 247 (1): 123–132. doi: 10.1002/cne.902470108. ISSN 1096-9861. PMID 3711374. S2CID 23040741.
- ^
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
j Standring, Susan (2020).
Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York.
ISBN
978-0-7020-7707-4.
OCLC
1201341621.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher ( link) - ^ Shimizu, Toshihiko; Suzuki, Norihiro (2010). "3 - Biological sciences related to headache". Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 97. Elsevier. pp. 35–45. doi: 10.1016/S0072-9752(10)97003-6. ISBN 978-0-444-52139-2. ISSN 0072-9752. PMID 20816409.
- ^ Rybka, E. J.; McCulloch, P. F. (23 February 2006). "The anterior ethmoidal nerve is necessary for the initiation of the nasopharyngeal response in the rat". Brain Research. 1075 (1): 122–132. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.12.112. ISSN 0006-8993. PMID 16466647. S2CID 37900942.
| Anterior ethmoidal nerve | |
|---|---|
 The ophthalmic artery and its branches. (Nerve not pictured, but location is similar to artery.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Nasociliary nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus ethmoidalis anterior |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.030 |
| TA2 | 6208 |
| FMA | 52675 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The anterior ethmoidal nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1)). It arises in the orbit, and enters first the cranial cavity and then the nasal cavity. It provides sensory innervation to part of the meninges, parts of the nasal cavity, and part of the skin of the nose.
The anterior ethmoidal nerve is a terminal branch of the nasociliary nerve, a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). [1] It branches near the medial wall of the orbit.
It passes through the anterior ethmoidal canal alongside the anterior ethmoidal artery [2]: 780 and vein [2]: 566 to emerge in anterior cranial fossa through the anterior ethmoidal foramen [2]: 1464.e13 (at the junction of the cribiform plate of ethmoid bone and orbital part of frontal bone [2]: 566 ).
Within the cranial cavity, it passes anterior-ward (external to the dura mater) along a groove upon the superior surface of the cribriform plate. It descends through an aperture situated lateral to the crista galli to reach the nasal cavity. [2]: 1464.e13
In the nasal cavity, it passes along a groove upon the internal aspect of the nasal bone, and issuing the medial and lateral internal nasal branches. [2]: 1464.e13
It is continued as the external nasal nerve beyond the inferior margin of the nasal bone. [2]: 1464.e13
Within the anterior cranial fossa, it gives sensory fibers to the meninges to provide sensory innervation to part of the meninges. [3]
Its medial internal nasal branch innervates the superior and anterior portions of the nasal septum. [2]: 1464.e13
Its lateral internal nasal branch innervates the anterior portion of the lateral nasal wall. [2]: 1464.e13
It gives off branches to the roof of the nasal cavity, and bifurcates into a lateral internal nasal branch and medial internal nasal branch. It sends sensory fibers to the anterior ethmoid air cells and the middle ethmoidal air cells.[ citation needed]
Its terminal branch - the external nasal nerve - innervates skin of the nose between the nasal bones superiorly and the tip of the nose inferiorly, except the alar portionsurrounding the external nares. [2]: 1464.e13
It is involved in the diving reflex. [4]
- ^ Lucier, Gregory E.; Egizii, Rita (1986). "Central projections of the ethmoidal nerve of the cat as determined by the horseradish peroxidase tracer technique". Journal of Comparative Neurology. 247 (1): 123–132. doi: 10.1002/cne.902470108. ISSN 1096-9861. PMID 3711374. S2CID 23040741.
- ^
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
j Standring, Susan (2020).
Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York.
ISBN
978-0-7020-7707-4.
OCLC
1201341621.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher ( link) - ^ Shimizu, Toshihiko; Suzuki, Norihiro (2010). "3 - Biological sciences related to headache". Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 97. Elsevier. pp. 35–45. doi: 10.1016/S0072-9752(10)97003-6. ISBN 978-0-444-52139-2. ISSN 0072-9752. PMID 20816409.
- ^ Rybka, E. J.; McCulloch, P. F. (23 February 2006). "The anterior ethmoidal nerve is necessary for the initiation of the nasopharyngeal response in the rat". Brain Research. 1075 (1): 122–132. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.12.112. ISSN 0006-8993. PMID 16466647. S2CID 37900942.