| Angioma serpiginosum | |
|---|---|
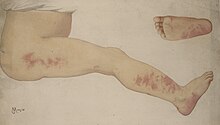 | |
| Angioma serpiginosom. Credit: Wellcome Collection | |
| Specialty |
Dermatology
|
Angioma serpiginosum is characterized by minute, copper-colored to bright red angiomatous puncta that have a tendency to become papular. [1]: 592–3 [2]
Patients usually have no symptoms at all, with no bleeding, discomfort, or inflammation related to the lesions, which mostly affect the lower limbs. [3] Nonetheless, there have been sporadic cases of angioma serpiginosum in the face, hands, feet, and mucous membranes, among other places. [4] [5] According to typical descriptions, angioma serpiginosum has an erythematous backdrop with a purple to coppery-red punctate look that clusters together in serpiginous or gyrate patterns. [3]
It is often observed that the illness progresses gradually, starting as little asymptomatic lesions that expand and coalesce with central clearing around the borders. [3] In addition, the lesions often cease growing throughout puberty after a brief period of initial growth during childhood and stay stable until adulthood. [6] Rarely, large areas are affected, and the symptoms appear later. [7] There have been reports of acral or zosteriform distribution cases. [8] [9]
It is uncertain what specifically causes angioma serpiginosum. While some experts have suggested that angioma serpiginosum could be caused by pathophysiologic changes brought on by freezing temperatures, others have suggested that there might be a hereditary component involved. [3]
Skin biopsy is required for confirmation of an angioma serpiginosum diagnosis; however, diascopy and dermoscopy can be used to further examine the diagnosis. [3]
Experts have suggested laser therapy as the preferred course of treatment. There is no proof that topical therapies are beneficial. [10]
- ^ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1622. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ^ a b c d e Anjaneyan, Gopikrishnan; Syed, Hasnain A.; Kaliyadan, Feroze (2023-11-05). "Angioma Serpiginosum". StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29083693. Retrieved 2024-03-06.
- ^ Poenitz, Nina; Koenen, Wolfgang; Utikal, Jochen; Goerdt, Sergij (2006-07-18). "Angioma serpiginosum following the lines of Blaschko – an effective treatment with the IPL technology". JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 4 (8). Wiley: 650–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1610-0387.2006.06013.x. ISSN 1610-0379. PMID 16895567. S2CID 39242042.
- ^ Das, Anupam; Sancheti, Karan; Podder, Indrashis; Gharami, RameshChandra (2016). "Angioma serpiginosum in a patchy and blaschkoid distribution: A rare condition with an unconventional presentation". Indian Journal of Dermatology. 61 (5). Medknow: 570–572. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.190114. ISSN 0019-5154. PMC 5029250. PMID 27688454.
- ^ Bishara, Michael; Jiaravuthisan, Michael; Weinstein, Miriam (2018-02-09). "A 13-Year-Old Presenting With Recurrent Angioma Serpiginosum". Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 22 (5). SAGE Publications: 511–513. doi: 10.1177/1203475418758987. ISSN 1203-4754. PMID 29421924. S2CID 46867928.
- ^ Chen, Ju-Hsin; Wang, Kuo-Hsien; Hu, Chung-Hong; Chiu, Jainn-Shiun (2008). "Atypical Angioma Serpiginosum". Yonsei Medical Journal. 49 (3). Yonsei University College of Medicine: 509–513. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.3.509. ISSN 0513-5796. PMC 2615349. PMID 18581605.
- ^ Acharya, Kamal P.; Pandey, Prajwal; Shah, Rajan; Bista, Muna; Shrestha, Samir (2021-03-02). "Angioma serpiginosum in zosteriform distribution on abdomen: A rare presentation". Clinical Case Reports. 9 (4). Wiley: 2225–2227. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.3995. ISSN 2050-0904. PMC 8077343. PMID 33936670.
- ^ Pandhi, Deepika; Jakhar, Deepak; Singal, Archana; Sharma, Sonal (2018). "Angioma serpiginosum in a bilateral distribution with acral involvement: An uncommon presentation". Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology. 84 (3). Scientific Scholar: 338. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.ijdvl_539_17. ISSN 0378-6323. PMID 29547138.
- ^ Salphale, Pankaj; Mukherjee, Samipa; Singh, Vandita (2014). "Late onset angioma serpiginosum of the breast with co-existing cherry angioma". Indian Dermatology Online Journal. 5 (3). Medknow: 316–319. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.137789. ISSN 2229-5178. PMC 4144222. PMID 25165654.
- Kuonen, François; Gaide, Olivier (2016). "Clues in DeRmoscopy: dermoscopy of angioma serpiginosum". European Journal of Dermatology. 26 (1). John Libbey Eurotext: 118. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2016.2754. ISSN 1952-4013. PMID 27113009. S2CID 7598391.
- Diociaiuti, Andrea; Cutrone, Mario; Rotunno, Roberta; De Vito, Rita; Neri, Iria; Pisaneschi, Elisa; El Hachem, May (2019-04-27). "Angioma serpiginosum: a case report and review of the literature". Italian Journal of Pediatrics. 45 (1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 53. doi: 10.1186/s13052-019-0644-8. ISSN 1824-7288. PMC 6487031. PMID 31029177.
| Angioma serpiginosum | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Angioma serpiginosom. Credit: Wellcome Collection | |
| Specialty |
Dermatology
|
Angioma serpiginosum is characterized by minute, copper-colored to bright red angiomatous puncta that have a tendency to become papular. [1]: 592–3 [2]
Patients usually have no symptoms at all, with no bleeding, discomfort, or inflammation related to the lesions, which mostly affect the lower limbs. [3] Nonetheless, there have been sporadic cases of angioma serpiginosum in the face, hands, feet, and mucous membranes, among other places. [4] [5] According to typical descriptions, angioma serpiginosum has an erythematous backdrop with a purple to coppery-red punctate look that clusters together in serpiginous or gyrate patterns. [3]
It is often observed that the illness progresses gradually, starting as little asymptomatic lesions that expand and coalesce with central clearing around the borders. [3] In addition, the lesions often cease growing throughout puberty after a brief period of initial growth during childhood and stay stable until adulthood. [6] Rarely, large areas are affected, and the symptoms appear later. [7] There have been reports of acral or zosteriform distribution cases. [8] [9]
It is uncertain what specifically causes angioma serpiginosum. While some experts have suggested that angioma serpiginosum could be caused by pathophysiologic changes brought on by freezing temperatures, others have suggested that there might be a hereditary component involved. [3]
Skin biopsy is required for confirmation of an angioma serpiginosum diagnosis; however, diascopy and dermoscopy can be used to further examine the diagnosis. [3]
Experts have suggested laser therapy as the preferred course of treatment. There is no proof that topical therapies are beneficial. [10]
- ^ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1622. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ^ a b c d e Anjaneyan, Gopikrishnan; Syed, Hasnain A.; Kaliyadan, Feroze (2023-11-05). "Angioma Serpiginosum". StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29083693. Retrieved 2024-03-06.
- ^ Poenitz, Nina; Koenen, Wolfgang; Utikal, Jochen; Goerdt, Sergij (2006-07-18). "Angioma serpiginosum following the lines of Blaschko – an effective treatment with the IPL technology". JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 4 (8). Wiley: 650–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1610-0387.2006.06013.x. ISSN 1610-0379. PMID 16895567. S2CID 39242042.
- ^ Das, Anupam; Sancheti, Karan; Podder, Indrashis; Gharami, RameshChandra (2016). "Angioma serpiginosum in a patchy and blaschkoid distribution: A rare condition with an unconventional presentation". Indian Journal of Dermatology. 61 (5). Medknow: 570–572. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.190114. ISSN 0019-5154. PMC 5029250. PMID 27688454.
- ^ Bishara, Michael; Jiaravuthisan, Michael; Weinstein, Miriam (2018-02-09). "A 13-Year-Old Presenting With Recurrent Angioma Serpiginosum". Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 22 (5). SAGE Publications: 511–513. doi: 10.1177/1203475418758987. ISSN 1203-4754. PMID 29421924. S2CID 46867928.
- ^ Chen, Ju-Hsin; Wang, Kuo-Hsien; Hu, Chung-Hong; Chiu, Jainn-Shiun (2008). "Atypical Angioma Serpiginosum". Yonsei Medical Journal. 49 (3). Yonsei University College of Medicine: 509–513. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.3.509. ISSN 0513-5796. PMC 2615349. PMID 18581605.
- ^ Acharya, Kamal P.; Pandey, Prajwal; Shah, Rajan; Bista, Muna; Shrestha, Samir (2021-03-02). "Angioma serpiginosum in zosteriform distribution on abdomen: A rare presentation". Clinical Case Reports. 9 (4). Wiley: 2225–2227. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.3995. ISSN 2050-0904. PMC 8077343. PMID 33936670.
- ^ Pandhi, Deepika; Jakhar, Deepak; Singal, Archana; Sharma, Sonal (2018). "Angioma serpiginosum in a bilateral distribution with acral involvement: An uncommon presentation". Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology. 84 (3). Scientific Scholar: 338. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.ijdvl_539_17. ISSN 0378-6323. PMID 29547138.
- ^ Salphale, Pankaj; Mukherjee, Samipa; Singh, Vandita (2014). "Late onset angioma serpiginosum of the breast with co-existing cherry angioma". Indian Dermatology Online Journal. 5 (3). Medknow: 316–319. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.137789. ISSN 2229-5178. PMC 4144222. PMID 25165654.
- Kuonen, François; Gaide, Olivier (2016). "Clues in DeRmoscopy: dermoscopy of angioma serpiginosum". European Journal of Dermatology. 26 (1). John Libbey Eurotext: 118. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2016.2754. ISSN 1952-4013. PMID 27113009. S2CID 7598391.
- Diociaiuti, Andrea; Cutrone, Mario; Rotunno, Roberta; De Vito, Rita; Neri, Iria; Pisaneschi, Elisa; El Hachem, May (2019-04-27). "Angioma serpiginosum: a case report and review of the literature". Italian Journal of Pediatrics. 45 (1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 53. doi: 10.1186/s13052-019-0644-8. ISSN 1824-7288. PMC 6487031. PMID 31029177.