| Aditus to mastoid antrum | |
|---|---|
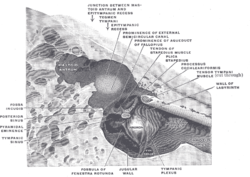 The medial wall and part of the posterior and anterior walls of the right
tympanic cavity, side view. | |
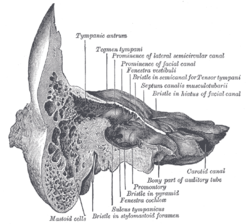
Coronal section of right
temporal bone | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | aditus ad antrum mastoideum |
| TA98 | A15.3.02.021 |
| TA2 | 6910 |
| FMA | 56797 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The aditus to mastoid antrum (otomastoid foramen) is a large, irregular opening [1] upon the posterior wall of the tympanic cavity by which the mastoid antrum (situated posteriorly) communicates with the epitympanic recess of the tympanic cavity (situated anteriorly). [2] The walls of the antrum are lined by mucosa which is continuous with that lining the mastoid cells and tympanic cavity. [3]
The medial wall of the aditus features a ridge created by the underlying facial canal, and a bulge created by the underlying ampulla of the lateral semicircular canal. The short limb of incus is lodged in a shallow fossa upon the posterior wall of the tympanic cavity just inferior to the aditus. The pyramidal eminence is situated inferior to the aditus. [2]
See also
References
- ^ Gray, Henry (1918). Gray's Anatomy (20th ed.). p. 1042.
- ^ a b Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). Elsevier Australia. p. 416. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
-
^ Standring, Susan (2020).
Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 746.
ISBN
978-0-7020-7707-4.
OCLC
1201341621.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher ( link)
External links
- Description at umich.edu
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/figures/chapter_44/44-5.HTM Archived 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machine
| Aditus to mastoid antrum | |
|---|---|
 The medial wall and part of the posterior and anterior walls of the right
tympanic cavity, side view. | |

Coronal section of right
temporal bone | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | aditus ad antrum mastoideum |
| TA98 | A15.3.02.021 |
| TA2 | 6910 |
| FMA | 56797 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The aditus to mastoid antrum (otomastoid foramen) is a large, irregular opening [1] upon the posterior wall of the tympanic cavity by which the mastoid antrum (situated posteriorly) communicates with the epitympanic recess of the tympanic cavity (situated anteriorly). [2] The walls of the antrum are lined by mucosa which is continuous with that lining the mastoid cells and tympanic cavity. [3]
The medial wall of the aditus features a ridge created by the underlying facial canal, and a bulge created by the underlying ampulla of the lateral semicircular canal. The short limb of incus is lodged in a shallow fossa upon the posterior wall of the tympanic cavity just inferior to the aditus. The pyramidal eminence is situated inferior to the aditus. [2]
See also
References
- ^ Gray, Henry (1918). Gray's Anatomy (20th ed.). p. 1042.
- ^ a b Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). Elsevier Australia. p. 416. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
-
^ Standring, Susan (2020).
Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 746.
ISBN
978-0-7020-7707-4.
OCLC
1201341621.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher ( link)
External links
- Description at umich.edu
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/figures/chapter_44/44-5.HTM Archived 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machine