The Michigan Portal  Michigan ( /ˈmɪʃɪɡən/ ⓘ MISH-ig-ən) is a state in the Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwestern United States. It borders Wisconsin to the northwest in the Upper Peninsula, and Indiana and Ohio to the south in the Lower Peninsula; it is also connected by Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, and Erie to Minnesota and Illinois, and the Canadian province of Ontario. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of 96,716 sq mi (250,490 km2), Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the largest by area east of the Mississippi River. Its capital is Lansing, and its largest city is Detroit. Metro Detroit is among the nation's most populous and largest metropolitan economies. The name derives from a gallicized variant of the original Ojibwe word ᒥᓯᑲᒥ (mishigami), meaning "large water" or "large lake". Michigan consists of two peninsulas. The Lower Peninsula resembles the shape of a mitten, and comprises a majority of the state's land area. The Upper Peninsula (often called "the U.P.") is separated from the Lower Peninsula by the Straits of Mackinac, a five-mile (8 km) channel that joins Lake Huron to Lake Michigan. The Mackinac Bridge connects the peninsulas. Michigan has the longest freshwater coastline of any political subdivision in the United States, being bordered by four of the five Great Lakes and Lake St. Clair. It also has 64,980 inland lakes and ponds. Michigan has the second-most water area of any state, behind only Alaska. The area was first occupied by a succession of Native American tribes over thousands of years. In the 17th century, French explorers claimed it as part of the New France colony, when it was largely inhabited by indigenous peoples. French and Canadian traders and settlers, Métis, and others migrated to the area, settling largely along the waterways. After France's defeat in the French and Indian War in 1762, the region came under British rule. Britain ceded the territory to the newly independent United States after its defeat in the American Revolutionary War. The area was part of the larger Northwest Territory until 1800, when western Michigan became part of the Indiana Territory. Michigan Territory was formed in 1805, but some of the northern border with Canada was not agreed upon until after the War of 1812. Michigan was admitted into the Union in 1837 as the 26th state, a free one. It soon became an important center of industry and trade in the Great Lakes region, attracting immigrants in the late 19th and early 20th centuries from many European countries. Immigrants from Finland, Macedonia, and the Netherlands were especially numerous. Migration from Appalachia and of Black Southerners as part of the Great Migration increased in the 1930s, with many settling in Metro Detroit. ( Full article...) Entries here consist of
Good and
Featured articles, which meet a core set of high editorial standards.
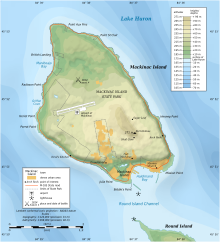
Mackinac Island ( /ˈmækənɔː/ MAK-ə-naw, locally /ˈmækənə/ MAK-ə-nə; French: Île Mackinac; Ojibwe: Mishimikinaak ᒥᔑᒥᑭᓈᒃ; Ottawa: Michilimackinac) is an island and resort area, covering 4.35 square miles (11.3 km2) in land area, in the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the island in Odawa is Michilimackinac and "Mitchimakinak" in Ojibwemowin, meaning "Great Turtle". It is located in Lake Huron, at the eastern end of the Straits of Mackinac, between the state's Upper and Lower Peninsulas. The island was long home to an Odawa settlement and previous indigenous cultures before European colonization began in the 17th century. It was a strategic center of the fur trade around the Great Lakes. Based on a former trading post, Fort Mackinac was constructed on the island by the British during the American Revolutionary War. It was the site of two battles during the War of 1812 before the northern border was settled and the US gained this island in its territory. In the late 19th century, Mackinac Island became a popular tourist attraction and summer colony. Many of the structures on the island have undergone extensive historical preservation and restoration. Because of its historic significance, the entire island is listed as a National Historic Landmark. It is well known for numerous cultural events; a wide variety of architectural styles, including the Victorian Grand Hotel; and its ban on almost all motor vehicles, with exceptions only for city emergency vehicles (ambulance, police cars and fire trucks), city service vehicles and snowmobiles in winter. More than 80 percent of the island is preserved as Mackinac Island State Park. ( Full article...)Selected picture - The Huron-Manistee National Forests are actually two National Forests combined in 1945 for administration purposes and which comprise 978,725 acres (3,960 km2) of public lands, including 5,786 acres (23 km2) of wetlands, extending across the northern Lower Peninsula of Michigan. Did you know -
Related portalsSelected article -
Howard Henry Peckham, (July 13, 1910 – July 6, 1995) was a professor and historian and an authority on
colonial and
early American history who published a number of works on those subjects. His academic career encompassed a wide variety of involvements in educational institutions and various
historical societies. Peckham played a fundamental role in establishing professional
academic standards for the management of historical
manuscripts and historical society work in the 20th century that have endured to this day. He was a founding member of the
Society of American Archivists and the Director of the
William L. Clements Library at the
University of Michigan. Peckham and his associate, Lloyd A. Brown, were the first historians to publish the
American Revolutionary War journals of
Henry Dearborn, in 1939, making them available to the general public for the first time. He is also noted for establishing more accurate numbers of
American Revolutionary War deaths, which were much greater than previously assumed. (
Full article...)
Selected biography -Timothy Duane Hardaway Jr. (born March 16, 1992) is an American professional basketball player for the Dallas Mavericks of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He played college basketball for the Michigan Wolverines and declared for the NBA draft after his junior season for the national runner-up 2012–13 team. Hardaway was selected with the 24th overall pick in the 2013 NBA draft by the New York Knicks. He has had two stints with the Knicks and has also played for the Atlanta Hawks. He is the son of Hall of Famer Tim Hardaway. As a freshman during the 2010–11 NCAA Division I men's basketball season, he earned four Big Ten Conference Freshman of the Week awards, including three in the final four weeks during which he averaged over 20 points a game to help the 2010–11 team to climb up to fourth in the 2010–11 Big Ten Conference men's basketball season standings. He was an honorable mention All-Big Ten selection and a unanimous Big Ten All-Freshman team selection following the season. He established the Michigan freshman record for single-season three-point shots made. He was a 2011 Collegeinsider.com Freshmen All-America selection and participated as a member of Team USA in the 2011 FIBA Under-19 World Championship. As a sophomore for the 2011–12 team, he earned the 2011–12 All-Big Ten 3rd team recognition. He earned 2012–13 All-Big Ten (1st team: coaches and 2nd team: media) recognition. ( Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Michigan-related articles on Wikipedia.
TopicsCategoriesSymbols
Lists
Related pagesWikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Things you can doDiscover Wikipedia using
portals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Michigan Portal  Michigan ( /ˈmɪʃɪɡən/ ⓘ MISH-ig-ən) is a state in the Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwestern United States. It borders Wisconsin to the northwest in the Upper Peninsula, and Indiana and Ohio to the south in the Lower Peninsula; it is also connected by Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, and Erie to Minnesota and Illinois, and the Canadian province of Ontario. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of 96,716 sq mi (250,490 km2), Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the largest by area east of the Mississippi River. Its capital is Lansing, and its largest city is Detroit. Metro Detroit is among the nation's most populous and largest metropolitan economies. The name derives from a gallicized variant of the original Ojibwe word ᒥᓯᑲᒥ (mishigami), meaning "large water" or "large lake". Michigan consists of two peninsulas. The Lower Peninsula resembles the shape of a mitten, and comprises a majority of the state's land area. The Upper Peninsula (often called "the U.P.") is separated from the Lower Peninsula by the Straits of Mackinac, a five-mile (8 km) channel that joins Lake Huron to Lake Michigan. The Mackinac Bridge connects the peninsulas. Michigan has the longest freshwater coastline of any political subdivision in the United States, being bordered by four of the five Great Lakes and Lake St. Clair. It also has 64,980 inland lakes and ponds. Michigan has the second-most water area of any state, behind only Alaska. The area was first occupied by a succession of Native American tribes over thousands of years. In the 17th century, French explorers claimed it as part of the New France colony, when it was largely inhabited by indigenous peoples. French and Canadian traders and settlers, Métis, and others migrated to the area, settling largely along the waterways. After France's defeat in the French and Indian War in 1762, the region came under British rule. Britain ceded the territory to the newly independent United States after its defeat in the American Revolutionary War. The area was part of the larger Northwest Territory until 1800, when western Michigan became part of the Indiana Territory. Michigan Territory was formed in 1805, but some of the northern border with Canada was not agreed upon until after the War of 1812. Michigan was admitted into the Union in 1837 as the 26th state, a free one. It soon became an important center of industry and trade in the Great Lakes region, attracting immigrants in the late 19th and early 20th centuries from many European countries. Immigrants from Finland, Macedonia, and the Netherlands were especially numerous. Migration from Appalachia and of Black Southerners as part of the Great Migration increased in the 1930s, with many settling in Metro Detroit. ( Full article...) Entries here consist of
Good and
Featured articles, which meet a core set of high editorial standards.
Mackinac Island ( /ˈmækənɔː/ MAK-ə-naw, locally /ˈmækənə/ MAK-ə-nə; French: Île Mackinac; Ojibwe: Mishimikinaak ᒥᔑᒥᑭᓈᒃ; Ottawa: Michilimackinac) is an island and resort area, covering 4.35 square miles (11.3 km2) in land area, in the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the island in Odawa is Michilimackinac and "Mitchimakinak" in Ojibwemowin, meaning "Great Turtle". It is located in Lake Huron, at the eastern end of the Straits of Mackinac, between the state's Upper and Lower Peninsulas. The island was long home to an Odawa settlement and previous indigenous cultures before European colonization began in the 17th century. It was a strategic center of the fur trade around the Great Lakes. Based on a former trading post, Fort Mackinac was constructed on the island by the British during the American Revolutionary War. It was the site of two battles during the War of 1812 before the northern border was settled and the US gained this island in its territory. In the late 19th century, Mackinac Island became a popular tourist attraction and summer colony. Many of the structures on the island have undergone extensive historical preservation and restoration. Because of its historic significance, the entire island is listed as a National Historic Landmark. It is well known for numerous cultural events; a wide variety of architectural styles, including the Victorian Grand Hotel; and its ban on almost all motor vehicles, with exceptions only for city emergency vehicles (ambulance, police cars and fire trucks), city service vehicles and snowmobiles in winter. More than 80 percent of the island is preserved as Mackinac Island State Park. ( Full article...)Selected picture - The Huron-Manistee National Forests are actually two National Forests combined in 1945 for administration purposes and which comprise 978,725 acres (3,960 km2) of public lands, including 5,786 acres (23 km2) of wetlands, extending across the northern Lower Peninsula of Michigan. Did you know -
Related portalsSelected article -
Howard Henry Peckham, (July 13, 1910 – July 6, 1995) was a professor and historian and an authority on
colonial and
early American history who published a number of works on those subjects. His academic career encompassed a wide variety of involvements in educational institutions and various
historical societies. Peckham played a fundamental role in establishing professional
academic standards for the management of historical
manuscripts and historical society work in the 20th century that have endured to this day. He was a founding member of the
Society of American Archivists and the Director of the
William L. Clements Library at the
University of Michigan. Peckham and his associate, Lloyd A. Brown, were the first historians to publish the
American Revolutionary War journals of
Henry Dearborn, in 1939, making them available to the general public for the first time. He is also noted for establishing more accurate numbers of
American Revolutionary War deaths, which were much greater than previously assumed. (
Full article...)
Selected biography -Timothy Duane Hardaway Jr. (born March 16, 1992) is an American professional basketball player for the Dallas Mavericks of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He played college basketball for the Michigan Wolverines and declared for the NBA draft after his junior season for the national runner-up 2012–13 team. Hardaway was selected with the 24th overall pick in the 2013 NBA draft by the New York Knicks. He has had two stints with the Knicks and has also played for the Atlanta Hawks. He is the son of Hall of Famer Tim Hardaway. As a freshman during the 2010–11 NCAA Division I men's basketball season, he earned four Big Ten Conference Freshman of the Week awards, including three in the final four weeks during which he averaged over 20 points a game to help the 2010–11 team to climb up to fourth in the 2010–11 Big Ten Conference men's basketball season standings. He was an honorable mention All-Big Ten selection and a unanimous Big Ten All-Freshman team selection following the season. He established the Michigan freshman record for single-season three-point shots made. He was a 2011 Collegeinsider.com Freshmen All-America selection and participated as a member of Team USA in the 2011 FIBA Under-19 World Championship. As a sophomore for the 2011–12 team, he earned the 2011–12 All-Big Ten 3rd team recognition. He earned 2012–13 All-Big Ten (1st team: coaches and 2nd team: media) recognition. ( Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Michigan-related articles on Wikipedia.
TopicsCategoriesSymbols
Lists
Related pagesWikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Things you can doDiscover Wikipedia using
portals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||