| FranceâItaly border | |
|---|---|

Mont Blanc, here seen from France, is the highest mountain in
Western Europe, located on the FranceâItaly border. | |
| Characteristics | |
| Entities | |
| Length | 515 km (320 mi) |
The FranceâItaly border is 515 km (320 mi) long. It runs from the Alps in the north, a region in which it passes over Mont Blanc, down to the Mediterranean coast in the south. Three national parks are located along the border: Vanoise National Park and Mercantour National Park on the French side and Gran Paradiso National Park on the Italian side.
Features
The FranceâItaly border is mainly mountainous. It is 515 kilometres (320 mi) long, [1] in southeast France and northwest Italy. It begins at the west tripoint of FranceâItalyâSwitzerland ( 45°55â˛23âłN 07°02â˛40âłE / 45.92306°N 7.04444°E) near the top of Mont Dolent (3,820 m), in the French commune of Chamonix (department of Haute-Savoie), the Italian city of Courmayeur ( Aosta Valley) and the Swiss commune of Orsières (canton of Valais).
The boundary then follows a general direction towards south, to the Mediterranean, it reaches the sea at Menton in France and Ventimiglia in Italy. The border separates three regions ( Aosta Valley, Piedmont and Liguria) and four provinces of Italy ( Aosta, Turin, Cuneo and Imperia) from two regions ( Auvergne-RhĂ´ne-Alpes and Provence-Alpes-CĂ´te d'Azur) and five departments of France ( Haute-Savoie, Savoie, Hautes-Alpes, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and Alpes-Maritimes).
-
Cime de la MalĂŠdie
-
A marker on the French side of the border in Alpes-Maritimes
-
Following the Treaty of Paris, the end of the Saint-Nicolas plateau now delimits the border 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) below the Mont Cenis Pass.
-
The Pont Saint-Ludovic / Ponte San Ludovico border crossing point between Menton, France and Ventimiglia, Italy
Road crossings
The points of paved road crossings between the two countries are quoted in this exhaustive list, from North to South:
- Mont Blanc Tunnel
- Little St Bernard Pass
- The Saint Nicolas plateau below the Mont Cenis pass
- FrĂŠjus Road Tunnel
- Pian del Colle (near Col de l'Ăchelle)
- Col de Montgenèvre (near Claviere)
- Col Agnel
- Maddalena Pass
- Col de la Lombarde
- Tende Tunnel
- Fanghetto, one of two villages in the municipality of Olivetta San Michele
- Olivetta San Michele
- Menton ( France) and Ventimiglia ( Italy)
In 1999, there was a large fire in the Mont Blanc Tunnel after a truck crashed into other vehicles. Emergency personnel from both sides of the border tried their best to intervene but 39 people died. The tunnel was closed for nearly three years following the fire. [2]
History
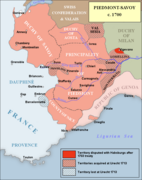
-
Border between France and the Italian states in 1700.
-
English map representing the North West Regions of Italy ( Kingdom of Sardinia, Duchy of Milan, Republic of Genoa) and the border with France in the 18th century.
-
Border in 1814 after the Treaty of Paris
-
Border changes 1859â1947
The border between the two countries dates back to that separating the Kingdom of Sardinia and France during the 19th century. In 1860, the Treaty of Turin links the Savoy and County of Nice to France; the border between the French Empire and the Kingdom of Sardinia was surveyed the following year.
At the conclusion of the Battle of France in World War II, Italy claimed and administered French territory under the terms of the armistice of 24 June 1940 (the Franco-Italian armistice signed at the Incisa villa near Rome) which were extended from 11 November 1942. The Germans occupied the Italian zone from 1943, and the territory was finally liberated by France in 1944. The border was then changed by the Treaty of Paris in 1947, when France acquired Tende, La Brigue, Mont Chaberton and the Lake of Mont Cenis.
In the 21st century, an ongoing issue to be resolved concerns the demarcation of the border at the top of Mont Blanc. [3]
References
| FranceâItaly border | |
|---|---|

Mont Blanc, here seen from France, is the highest mountain in
Western Europe, located on the FranceâItaly border. | |
| Characteristics | |
| Entities | |
| Length | 515 km (320 mi) |
The FranceâItaly border is 515 km (320 mi) long. It runs from the Alps in the north, a region in which it passes over Mont Blanc, down to the Mediterranean coast in the south. Three national parks are located along the border: Vanoise National Park and Mercantour National Park on the French side and Gran Paradiso National Park on the Italian side.
Features
The FranceâItaly border is mainly mountainous. It is 515 kilometres (320 mi) long, [1] in southeast France and northwest Italy. It begins at the west tripoint of FranceâItalyâSwitzerland ( 45°55â˛23âłN 07°02â˛40âłE / 45.92306°N 7.04444°E) near the top of Mont Dolent (3,820 m), in the French commune of Chamonix (department of Haute-Savoie), the Italian city of Courmayeur ( Aosta Valley) and the Swiss commune of Orsières (canton of Valais).
The boundary then follows a general direction towards south, to the Mediterranean, it reaches the sea at Menton in France and Ventimiglia in Italy. The border separates three regions ( Aosta Valley, Piedmont and Liguria) and four provinces of Italy ( Aosta, Turin, Cuneo and Imperia) from two regions ( Auvergne-RhĂ´ne-Alpes and Provence-Alpes-CĂ´te d'Azur) and five departments of France ( Haute-Savoie, Savoie, Hautes-Alpes, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and Alpes-Maritimes).
-
Cime de la MalĂŠdie
-
A marker on the French side of the border in Alpes-Maritimes
-
Following the Treaty of Paris, the end of the Saint-Nicolas plateau now delimits the border 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) below the Mont Cenis Pass.
-
The Pont Saint-Ludovic / Ponte San Ludovico border crossing point between Menton, France and Ventimiglia, Italy
Road crossings
The points of paved road crossings between the two countries are quoted in this exhaustive list, from North to South:
- Mont Blanc Tunnel
- Little St Bernard Pass
- The Saint Nicolas plateau below the Mont Cenis pass
- FrĂŠjus Road Tunnel
- Pian del Colle (near Col de l'Ăchelle)
- Col de Montgenèvre (near Claviere)
- Col Agnel
- Maddalena Pass
- Col de la Lombarde
- Tende Tunnel
- Fanghetto, one of two villages in the municipality of Olivetta San Michele
- Olivetta San Michele
- Menton ( France) and Ventimiglia ( Italy)
In 1999, there was a large fire in the Mont Blanc Tunnel after a truck crashed into other vehicles. Emergency personnel from both sides of the border tried their best to intervene but 39 people died. The tunnel was closed for nearly three years following the fire. [2]
History
-
Border between France and the Italian states in 1700.
-
English map representing the North West Regions of Italy ( Kingdom of Sardinia, Duchy of Milan, Republic of Genoa) and the border with France in the 18th century.
-
Border in 1814 after the Treaty of Paris
-
Border changes 1859â1947
The border between the two countries dates back to that separating the Kingdom of Sardinia and France during the 19th century. In 1860, the Treaty of Turin links the Savoy and County of Nice to France; the border between the French Empire and the Kingdom of Sardinia was surveyed the following year.
At the conclusion of the Battle of France in World War II, Italy claimed and administered French territory under the terms of the armistice of 24 June 1940 (the Franco-Italian armistice signed at the Incisa villa near Rome) which were extended from 11 November 1942. The Germans occupied the Italian zone from 1943, and the territory was finally liberated by France in 1944. The border was then changed by the Treaty of Paris in 1947, when France acquired Tende, La Brigue, Mont Chaberton and the Lake of Mont Cenis.
In the 21st century, an ongoing issue to be resolved concerns the demarcation of the border at the top of Mont Blanc. [3]